Abstract
Background
Victimisation in childhood may be associated with adult psychosis. The current study examined this association in the crucial developmental period of early adolescence and investigated whether (1) unwanted sexual experiences, and (2) being bullied, were associated with non-clinical delusional ideation and hallucinatory experiences in a general population sample of 14 year olds.
Methods
Data were derived from standard health screenings of the Youth Health Care Divisions of the Municipal Health Services in Maastricht, the Netherlands. A self-report questionnaire was filled out by a total of 1290 adolescents to assess non-clinical psychotic experiences, as well as experiences of being bullied and sexual trauma.
Results
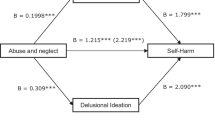
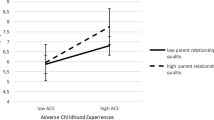
Non-clinical psychotic experiences were strongly and independently associated with both bullying (OR=2.9, 95% CI 1.8–4.8) and sexual trauma (OR=4.8, 95% CI 2.3–10.1).
Conclusions
The results suggest that reported associations between childhood victimisation and adult psychosis can be understood in a developmental framework of onset of at-risk mental states in early adolescence. In addition, the data suggest that the traumatic experience of being bullied may also feed the cognitive and biological mechanisms underlying formation of psychotic ideation.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Spataro J, Mullen PE, Burgess PM, Wells DL, Moss SA (2004) Impact of child sexual abuse on mental health: prospective study in males and females. Br J Psychiatry 184:416–421
Bebbington PE, Bhugra D, Brugha T, Singleton N, Farrell M, Jenkins R, Lewis G, Meltzer H (2004) Psychosis, victimisation and childhood disadvantage: evidence from the second British National Survey of Psychiatric Morbidity. Br J Psychiatry 185:220–226
Briere J, Woo R, McRae B, Foltz J, Sitzman R (1997) Lifetime victimization history, demographics, and clinical status in female psychiatric emergency room patients. J Nervous Mental Disease 185(2):95–101
Janssen I, Krabbendam L, Bak M, Hanssen M, Vollebergh W, De Graaf R, Van Os J (2004) Childhood abuse as a risk factor for psychotic experiences. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 109(1):38–45
Read J (1997) Child abuse and psychosis: a literature review and implications for professional practice. Professional Psychol: Res Practice 28(5):448–456
Read J (1998) Child abuse and severity of disturbance among adult psychiatric inpatients. Child Abuse Neglect 22(5):359–368
Read J, Agar K, Argyle N, Aderhold V (2003) Sexual and physical abuse during childhood and adulthood as predictors of hallucinations, delusions and thought disorder. Psychol Psychother 76(Pt 1):1–22
Ross CA, Anderson G, Clark P (1994) Childhood abuse and the positive symptoms of schizophrenia. Hosp Community Psychiatry 45(5):489–491
Johns LC, Van Os J (2001) The continuity of psychotic experiences in the general population. Clin Psychol Rev 21(8):1125–1141
Startup M (1999) Schizotypy, dissociative experiences and childhood abuse: relationships among self-report measures. Br J Clin Psychol 38(4):333–344
Craig WM (1998) The relationship among bullying, victimization, depression, anxiety, and aggression in elementary school children. Pers Individ Dif 24(1):123–130
Kumpulainen K, Raesaenen E, Puura K (2001) Psychiatric disorders and the use of mental health services among children involved in bullying. Aggress Behav 27(2):102–110
Kumpulainen K, Rasanen E, Henttonen I, Almqvist F, Kresanov K, Linna SL, Moilanen I, Piha J, Puura K, Tamminen T (1998) Bullying and psychiatric symptoms among elementary school-age children. Child Abuse Neglect 22(7):705–717
Birchwood M, Gilbert P, Gilbert J, Trower P, Meaden A, Hay J, Murray E, Miles JN (2004) Interpersonal and role-related schema influence the relationship with the dominant ‘voice’ in schizophrenia: a comparison of three models. Psychol Med 34(8):1571–1580
Garety PA, Kuipers E, Fowler D, Freeman D, Bebbington PE (2001) A cognitive model of the positive symptoms of psychosis. Psychol Med 31(2):189–195
Morrison AP, Frame L, Larkin W (2003) Relationships between trauma and psychosis: a review and integration. Br J Clin Psychol 42(4):331–353
Read J, Perry BD, Moskowitz A, Connolly J (2001) The contribution of early traumatic events to schizophrenia in some patients: a traumagenic neurodevelopmental model. Psychiatry 64(4):319–345
Hanssen M, Bak M, Bijl R, Vollebergh W, Van Os J (2005) The incidence and outcome of subclinical psychotic experiences in the general population. Br J Clin Psychol 44(Pt 2):181–191
Poulton R, Caspi A, Moffitt TE, Cannon M, Murray R, Harrington H (2000) Children’s self-reported psychotic symptoms and adult schizophreniform disorder: a 15-year longitudinal study. Arch Gen Psychiatry 57(11):1053–1058
Galdos PM, van Os JJ, Murray RM (1993) Puberty and the onset of psychosis. Schizophr Res 10(1):7–14
Escher S, Romme M, Buiks A, Delespaul P, Van Os J (2002) Independent course of childhood auditory hallucinations: a sequential 3-year follow-up study. Br J Psychiatry 43(supplement):s10–18
Escher S, Romme M, Buiks A, Delespaul P, Van Os J (2002) Formation of delusional ideation in adolescents hearing voices: a prospective study. Am J Med Genet 114(8):913–920
Fleming J, Mullen PE, Sibthorpe B, Bammer G (1999) The long-term impact of childhood sexual abuse in Australian women. Child Abuse Neglect 23(2):145–159
McGee R, Williams S, Poulton R (2000) Hallucinations in nonpsychotic children. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry 39(1):12–13
Drukker M, Kaplan CD, Feron FJM, Van Os J (2003) Children’s health-related quality of life, neighbourhood socio-economic deprivation and social capital. A contextual analysis. Soc Sci Med 57(5):825–841
Gunther N, Slavenburg B, Feron FJM, Van Os J (2003) Childhood social and early developmental factors associated with mental health service use. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 38(3):101–108
Costello A, Edelbrock C, Kalas R, Kessler M, Klaric S (1982) NIMH diagnostic interview for children child version. National Institute of Mental Health, Rockville: MD
APA (1980) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 3rd edn. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Henquet C, Krabbendam L, Spauwen J, Kaplan C, Lieb R, Wittchen HU, Van Os J (2005) Prospective cohort study of cannabis use, predisposition for psychosis, and psychotic symptoms in young people. Br Med J 330(7481):11–15
Van Os J, Hanssen M, Bijl RV, Ravelli A (2000) Strauss (1969) revisited: a psychosis continuum in the general population? Schizophr Res 45(1–2):11–20
Byrne M, Agerbo E, Eaton WW, Mortensen PB (2004) Parental socio-economic status and risk of first admission with schizophrenia—a Danish national register based study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 39(2):87–96
Mallett R, Leff J, Bhugra D, Pang D, Zhao JH (2002) Social environment, ethnicity and schizophrenia. A case-control study. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 37(7):329–335
Coulton CJ, Korbin JE, Su M (1999) Neighborhoods and child maltreatment: a multi-level study. Child Abuse Neglect 23(11):1019–1040
Coulton CJ, Korbin JE, Su M, Chow J (1995) Community level factors and child maltreatment rates. Childhood Dev 66(5): 1262–1276
Drukker M, Driessen G, Krabbendam L, Van Os J (2004) The wider social environment and mental health service use. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 110(2):119–129
Statacorp (2003) STATA Statistical Software: Release 8.0. Texas, College Station
Read J, Hammersley P (2005) Child sexual abuse and schizophrenia. Br J Psychiatry 186:76 (author reply 76)
Hill A (1965) The environment and disease: association or causation? J Royal Soc Med 58:295–300
Jones P, Rodgers B, Murray R, Marmot M (1994) Child development risk factors for adult schizophrenia in the British 1946 birth cohort. Lancet 344(8934):1398–1402
Van Os J, Sham P (2003) Gene–environment interactions. In: Murray RMJP, Susser E, Van Os J, Cannon M (eds) The epidemiology of schizophrenia. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 235–254
Bentall RP, Corcoran R, Howard R, Blackwood N, Kinderman P (2001) Persecutory delusions: a review and theoretical integration. Clin Psychol Rev 21(8):1143–1192
Walker EF, Diforio D (1997) Schizophrenia: a neural diathesis-stress model. Psychol Rev 104(4):667–685
Walker EF, Diforio D, Baum K (1999) Developmental neuropathology and the precursors of schizophrenia. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 395(supplement):12–19
Kapur S (2003) Psychosis as a state of aberrant salience: a framework linking biology, phenomenology, and pharmacology in schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 160(1):13–23
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A (1999) Dopamine as the wind of the psychotic fire: new evidence from brain imaging studies. J Psychopharmacol 13(4):358–371
Laruelle M, Abi-Dargham A, Gil R, Kegeles L, Innis R (1999) Increased dopamine transmission in schizophrenia: relationship to illness phases. Biol Psychiatry 46(1):56–72
Myin-Germeys I, Delespaul P, Van Os J (2005) Behavioural sensitization to daily life stress in psychosis. Psychol Med 35(5):733–741
Myin-Germeys I, Marcelis M, Krabbendam L, Delespaul P, Van Os J (2005) Subtle fluctuations in psychotic phenomena as functional states of abnormal dopamine reactivity in subjects at risk. Biol Psychiatry 58(2):105–110
Darves-Bornoz JM, Lemperiere T, Degiovanni A, Gaillard P (1995) Sexual victimization in women with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Soc Psychiatry Psychiatr Epidemiol 30(2):78–84
Dill DL, Chu JA, Grob MC, Eisen SV (1991) The reliability of abuse history reports: a comparison of two inquiry formats. Compr Psychiatry 32(2):166–169
Spauwen J, Krabbendam L, Lieb R, Wittchen H, Van Os J (2006) Impact of psychological trauma on the trajectory of psychosis proneness. Br J Psychiatry (In press)
Bak M, Krabbendam L, Janssen I, De Graaf R, Vollebergh W, Van Os J (2005) Early trauma increases the risk for psychotic experiences by impacting on emotional response and preception of control. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 112(5):360–366
Acknowledgements
Dr. Inez Myin-Germeys was supported by NARSAD (Young Investigator Award), by the Dutch Medical Council (VENI-GRANT), and especially by the Essel Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lataster, T., van Os, J., Drukker, M. et al. Childhood victimisation and developmental expression of non-clinical delusional ideation and hallucinatory experiences. Soc Psychiat Epidemiol 41, 423–428 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-006-0060-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00127-006-0060-4