Abstract
Key message
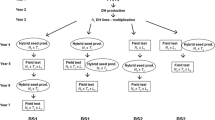
We investigated associations between line per se and testcross performance in rye and suggested that selection for per se performance is valuable for several traits in multi-stage selection programs.
Abstract
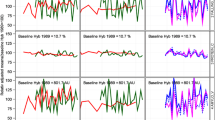
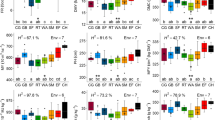
Genotypic correlation between line per se and testcross performance is an important quantitative-genetic parameter for optimizing hybrid breeding programs. The main goal of this survey was to study the association of line per se and testcross performance at the phenotypic level. We used experimental data from the line per se and testcross performance of two segregating winter rye populations (A, B) with each of 220 progenies tested in six environments for eight agronomic and quality traits. Genotypic variances were considerably larger for per se than for testcross performance of all investigated traits resulting in higher heritabilities of the former in most instances. Genotypic correlations (r g) between testcross and line per se performance decreased with increasing complexity of the trait as shown by the respective heritabilities. They were highest (r g ≥ 0.7) for plant height and test weight in population B, and thousand-kernel weight, falling number and starch content in both populations. A selection of these traits for line per se performance in early generations will save field plots in further testing testcross performance and increase efficiency of hybrid breeding.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker H (2011) Pflanzenzüchtung. P. 110. E. Ulmer, Stuttgart, Germany
Falconer DS, Mackay TFC (1996) Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edn. Longmans Green, Harlow
Falke KC, Wilde P, Wortmann H, Müller B, Piepho HP, Miedaner T (2010) Correlation between per se and testcross performance in rye (Secale cereale L.) introgression lines estimated with a bivariate mixed linear model. Crop Sci 50:1863–1873
Geiger HH, Miedaner T (1999) Hybrid rye and heterosis. In: Coors JG, Pandey S (eds) Genetics and exploitation of heterosis in crops. Crop Sci. Soc. America, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, pp 439–450
Geiger HH, Miedaner T (2009) Rye breeding. In: Carena MJ (ed) Cereals (Handbook of plant breeding), 1st edn. Springer, New York, pp 157–181
Geiger HH, Schnell FW (1970) Die Züchtung von Roggensorten aus Inzuchtlinien. I. Selbstungsanteile in Polycross-Nachkommenschaften. Theor Appl Genet 40:305–311
Geiger HH, Wahle G (1978) Struktur der Heterosis von Komplexmerkmalen bei Winterroggen-Einfachhybriden. Z Pflanzenzüchtung 80:198–210
Grieder C, Dhillon BS, Schipprack W, Melchinger AE (2012) Breeding maize as biogas substrate in Central Europe: II. Quantitative-genetic parameters for inbred lines and correlations with testcross performance. Theor Appl Gen 124:981–988
Hallauer AR, Carena MJ, Miranda Filho JB (2010) Quantitative genetics in maize breeding. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Köhler KL (1986) Experimentelle Untersuchungen zur Aufspaltungsvariation und -kovariation der Linieneigenleistung und Kombinationsfähigkeit bei Roggen. PhD, University of Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany
Miedaner T, Hübner M (2010) Qualitätsansprüche für unterschiedliche Verwendungszwecke bei Hybridroggen. Ber. 61. Tag. Vereinig. Pflanzenzücht. Saatgutkaufl. Österr. Gumpenstein 2010:45–49
Miedaner T, Müller BU, Piepho H-P, Falke KC (2011) Genetic architecture of plant height in winter rye introgression libraries. Plant Breed 130:209–216
Miedaner T, Hübner M, Korzun V, Schmiedchen B, Bauer E, Haseneyer G, Wilde P, Reif JC (2012) Genetic architecture of complex agronomic traits examined in two testcross populations of rye (Secale cereale L.). BMC Genomics 13:706
Mihaljevic R, Schön CC, Utz HF, Melchinger AE (2005) Correlations and QTL correspondence between line per se and testcross performance for agronomic traits in four populations of European maize. Crop Sci 45:114–122
Mode CJ, Robinson HF (1959) Pleiotropism and the genetic variance and covariance. Biometrics 15:518–537
Rode J (2008) Züchtung von Industrieroggen zur Bioethanolgewinnung. PhD, University of Halle/Saale, Germany
Schnell FW (1961) On some aspects of reciprocal recurrent selection. Euphytica 10:24–30
Schutz WM, Cockerham CC (1962) The effect of field blocking on gain from selection. NC State Univ Inst Statist Mimeogr Ser 328:86
Schwegler DD, Gowda M, Schulz B, Miedaner T, Liu W, Reif JC (2013) Genotypic correlations and QTL correspondence between line per se and testcross performance in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.). Mol Breed (submitted)
Smith OS (1986) Covariance between line per se and testcross performance. Crop Sci 26:540–543
Snedecor GW, Cochran WG (1980) Statistical methods, 7th edn. Iowa State University Press, Ames
Tomerius A-M, Miedaner T, Geiger HH (2008) A model calculation approach towards the optimization of a standard scheme of seed-parent line development in hybrid rye breeding. Plant Breed 127:433–440
Utz HF (2011) PLABSTAT. A computer program for statistical analysis of plant breeding experiments. Version 3A: Univ. Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany
Wahle G, Geiger HH (1978) Vergleich der phänotypischen Stabilität von Inzuchtlinien, Einfachhybriden und Populationen bei Winterroggen. Z Pflanzenzüchtung 80:211–222
Wilde P (1987) Schätzung von Populationsparametern und Untersuchungen zur Effizienz verschiedener Verfahren der Rekurrenten Selektion bei Winterroggen. PhD, University Hohenheim, Stuttgart, Germany
Acknowledgments
We highly appreciate the contribution of M.Sc. Brigitta Schmiedchen and M.Sc. Pawel Dopierala, both KWS LOCHOW GMBH, concerning the technical realization of the experiments in Petkus and Walewice/PL, respectively. This research was conducted within the project “Genetische Architektur der Eigen- versus Testkreuzungsleistung für wichtige agronomische Merkmale beim Roggen” financially supported by the “Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft”, Bonn (DFG Grant ID:MI 519/1-1).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
The experiments reported in this study comply with the current laws of Germany.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by T. Lubberstedt.
T. Miedaner and D. D. Schwegler contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miedaner, T., Schwegler, D.D., Wilde, P. et al. Association between line per se and testcross performance for eight agronomic and quality traits in winter rye. Theor Appl Genet 127, 33–41 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2198-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-013-2198-2