Abstract
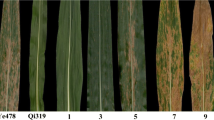
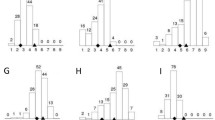
Gray leaf spot (GLS), caused by the causal fungal pathogen Cercospora zeae-maydis, is one of the most serious foliar diseases of maize worldwide. In the current study, a highly resistant inbred line Y32 and a susceptible line Q11 were used to produce segregating populations for both genetic analysis and QTL mapping. The broad-sense heritability (H 2) for GLS resistance was estimated to be as high as 0.85, indicating that genetic factors played key roles in phenotypic variation. In initial QTL analysis, four QTL, located on chromosomes 1, 2, 5, and 8, were detected to confer GLS resistance. Each QTL could explain 2.53–23.90 % of the total phenotypic variation, predominantly due to additive genetic effects. Two major QTL, qRgls1 and qRgls2 on chromosomes 8 and 5, were consistently detected across different locations and replicates. Compared to the previous results, qRgls2 is located in a ‘hotspot’ for GLS resistance; while, qRgls1 does not overlap with any other known resistance QTL. Furthermore, the major QTL-qRgls1 was fine-mapped into an interval of 1.4 Mb, flanked by the markers GZ204 and IDP5. The QTL-qRgls1 could enhance the resistance percentages by 19.70–61.28 %, suggesting its usefulness to improve maize resistance to GLS.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ayers JE, MW Johnson, RR Hill (1984) Identifying resistance to gray leaf spot. In: Proceedings of the Maize Sorghum Research Conference, 39th American Seed Trade Association, Washington, DC, pp 157–175
Bakr EM (2005) A new software for measuring leaf area, and area damaged by Tetranychus urticae Koch. J Appl Entomol 129:173–175
Balint-Kurti PJ, Wisser R, Zwonitzer JC (2008) Use of an advanced intercross line population for precise mapping of quantitative trait loci for gray leaf spot resistance in maize. Crop Sci 48:1696–1704
Basten CJ, Weir BS, Zeng ZB (1997) QTL cartographer: a reference manual and tutorial for QTL mapping. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, Raleigh, NC
Clements MJ, Dudley JW, White DG (2000) Quantitative trait loci associated with resistance to gray leaf spot of corn. Phytopathology 90:1018–1025
Danson J, Lagat M, Kimani M, Kuria A (2008) Quantitative trait loci (QTLs) for resistance to gray leaf spot and common rust diseases of maize. Afr J Biotechnol 7:3247–3254
Denazareno NRX, Lipps PE, Madden LV (1993) Effect of levels of corn residue on the epidemiology of gray leaf spot of corn in ohio. Plant Dis 77:67–70
Donahue PJ, Stromberg EL (1989) Hybrid performance and yield losses associated with gray leaf spot disease of corn in virginia USA. Phytopathology 79:1176
Donahue PJ, Stromberg EL, Myers SL (1991) Inheritance of reaction to gray leaf-spot in a diallel cross of 14 maize inbreds. Crop Sci 31:926–931
Elwinger GF, Johnson MW, Hill RR, Ayers JE (1990) Inheritance of resistance to gray leaf-spot of corn. Crop Sci 30:350–358
Gevers HO, Lake JK, Hohls T (1994) Diallel cross analysis of resistance to gray leaf-spot in maize. Plant Dis 78:379–383
Gordon SG, Bartsch M, Matthies I, Gevers HO, Lipps PE et al (2004) Linkage of molecular markers to Cercospora zeae-maydis resistance in maize. Crop Sci 44:628–636
Gordon SG, Lipps PE, Pratt RC (2006) Heritability and components of resistance to Cercospora zeae-maydis derived from maize inbred VO613Y. Phytopathology 96:593–598
Huff CA, Ayers JE, Hill RR (1988) Inheritance of resistance in corn (zea-mays) to gray leaf-spot. Phytopathology 78:790–794
Ininda J, Danson J, Lagat M, Wei Y, Ajanga S et al (2007) The use of simple sequence repeats markers to study genetic diversity in maize genotypes resistant to gray leaf spot disease. Afr J Biotechnol 6:1623–1628
Institute SAS (1999) SAS software. Cary, NC
Juliatti FC, Pedrosa MG, Silva HD, Correa Da Silva JV (2009) Genetic mapping for resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Euphytica 169:227–238
Knapp SJ, Stroup WW, Ross WM (1985) Exact confidence-intervals for heritability on a progeny mean basis. Crop Sci 25:192–194
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugenics 12:172–175
Latterell FM, Rossi AE (1983) Gray leaf-spot of corn—a disease on the move. Plant Dis 67:842–847
Lehmensiek A, Esterhuizen AM, Van Staden D, Nelson SW, Retief AE (2001) Genetic mapping of gray leaf spot (GLS) resistance genes in maize. Theor Appl Genet 103:797–803
Lincoln S, M Daly, E Lander (1992) Mapping genetic mapping with MAPMAKER/EXP3.0. Whitehead Institute Technical Report, Cambridge
Mcgee DC (1988) Maize diseases a reference source for seed technologists. American Phytopathological Society, St Paul
Menkir A, Ayodele M (2005) Genetic analysis of resistance to gray leaf spot of midaltitude maize inbred lines. Crop Sci 45:163–170
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Payne GA, Adkins CR (1987) Influence of tillage on development of gray leaf-spot and number of airborne conidia of Cercospora-zeae-maydis. Plant Dis 71:329–332
Pozar G, Butruille D, Silva HD, Mccuddin ZP, Viglioni Penna JC (2009) Mapping and validation of quantitative trait loci for resistance to Cercospora zeae-maydis infection in tropical maize (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 118:553–564
Rupe JC, Siegel MR, Hartman JR (1982) Influence of environment and plant maturity on gray leaf-spot of corn caused by Cercospora-zeae-maydis. Phytopathology 72:1587–1591
Saghai Maroof MA, Yue YG, Xiang ZX, Stromberg EL, Rufener GK (1996) Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling resistance to gray leaf spot disease in maize. Theor Appl Genet 93:539–546
Shi L, Li X, Hao Z, Xie C, Ji H et al (2007) Comparative QTL mapping of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize based on bioinformatics. Agric Sci China 6:1411–1419
Stormberg EL, PJ Donahue (1986) Hybrid performance of yield losses associated with gray leaf spot disease. In: Proceedings of the Maize Sorghum Research Conference, 41st American Seed Trade Association, Washington, DC, pp 92–104
Thompson DL, Bergquist RR, Payne GA, Bowman DT, Goodman MM (1987) Inheritance of resistance to gray leaf-spot in maize. Crop Sci 27:243–246
Ulrich JF, Hawk JA, Carroll RB (1990) Diallel analysis of maize inbreds for resistance to gray leaf-spot. Crop Sci 30:1198–1200
Wang J, Levy M, Dunkle LD (1998) Sibling species of Cercospora associated with gray leaf spot of maize. Phytopathology 88:1269–1275
Ward JMJ, Laing MD, Cairns ALP (1997a) Management practices to reduce gray leaf spot of maize. Crop Sci 37:1257–1262
Ward JMJ, Laing MD, Rijkenberg FHJ (1997b) Frequency and timing of fungicide applications for the control of gray leaf spot in maize. Plant Dis 81:41–48
Ward JMJ, Stromberg EL, Nowell DC, Nutter FW (1999) Gray leaf spot—a disease of global importance in maize production. Plant Dis 83:884–895
Yang Q, Zhang DF, Xu ML (2012) A sequential QTL fine-mapping strategy using recombinant-derived progeny. J Integr Plant Biol 54:228–237
Zeng ZB (1994) Precision mapping of quantitative trait loci. Genetics 136:1457–1468
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Mr. Kun Wang, Shiqiang Li, and Fuyan Jiang and Miss Haiyan Li from Yunnan Academy of Agricultural Sciences for their technical assistance in the experimental field. We greatly appreciate the efforts of Prof. Siquan Shao, Xinyi Pang and Bihua Huang from Baoshan and Dehong Institute of Agricultural Sciences for their help in symptom diagnose in the field. This study was financially supported by the national ‘973’ basic research program; the national ‘863’ high-tech program of China; and the ‘outstanding PhD thesis foundation’ of Beijing municipal authorities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Geiger.
Y. Zhang and L. Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Xu, L., Fan, X. et al. QTL mapping of resistance to gray leaf spot in maize. Theor Appl Genet 125, 1797–1808 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1954-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1954-z