Abstract
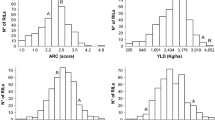
Advanced backcross QTL analysis was used to identify quantitative trait loci (QTL) for agronomic performance in a population of BC2F3:5 introgression lines created from the cross of a Colombian large red-seeded commercial cultivar, ICA Cerinza, and a wild common bean accession, G24404. A total of 157 lines were evaluated for phenological traits, plant architecture, seed weight, yield and yield components in replicated trials in three environments in Colombia and genotyped with microsatellite, SCAR, and phaseolin markers that were used to create a genetic map that covered all 11 linkage groups of the common bean genome with markers spaced at an average distance of every 10.4 cM. Segregation distortion was most significant in regions orthologous for a seed coat color locus (R-C) on linkage group b08 and two domestication syndrome genes, one on linkage group b01 at the determinacy (fin) locus and the other on linkage group b02 at the seed-shattering (st) locus. Composite interval mapping analysis identified a total of 41 significant QTL for the eight traits measured of which five for seed weight, two for days to flowering, and one for yield were consistent across two or more environments. QTL were located on every linkage group with b06 showing the greatest number of independent loci. A total of 13 QTL for plant height, yield and yield components along with a single QTL for seed size showed positive alleles from the wild parent while the remaining QTL showed positive alleles from the cultivated parent. Some QTL co-localized with regions that had previously been described to be important for these traits. Compensation was observed between greater pod and seed production and smaller seed size and may have resulted from QTL for these traits being linked or pleiotropic. Although wild beans have been used before to transfer biotic stress resistance traits, this study is the first to attempt to simultaneously obtain a higher yield potential from wild beans and to analyze this trait with single-copy markers. The wild accession was notable for being from a unique center of diversity and for contributing positive alleles for yield and other traits to the introgression lines showing the potential that advanced backcrossing has in common bean improvement.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanador LK, Hadley SD (1993) Adoption of a mini-prep DNA extraction method for RAPD marker analysis in common bean. Bean Improv Coop 35:10–11
Anthony JL, Vorder RA, Hall TC (1990) Nucleotide sequence of an alpha-phaseolin gene from Phaseolus vulgaris. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3396
Bassett MJ (1991) A revised linkage map of common bean. HortScience 26:834–836
Basten C, Weir BS, Zeng Z-B (2001) Windows QTL Cartographer v 1.21. Software. Department of Statistics, North Carolina State University, USA
Beaver JS (1999) Improvement of large-seeded race Nueva Granada cultivars. In: Singh SP (ed) Common bean improvement in the twenty-first century. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Beaver JS, Rosas JCM, Myers J, Acosta J, Kelly JD, Nchimbi-Msolla S, Misangu R, Bokosi J, Temple S, Aranud-Santana E, Coyne DP (2003) Contributions of the bean/cowpea CRSP to cultivar and germplasm development in common bean. Field Crops Res 82:87–102
Becerra-Velazquez L, Gepts P (1994) RFLP diversity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in its centres of origin. Genome 37:256–263
Beebe S, Toro O, González AV, Chacón MI, Debouck DG (1997) Wild-weed-crop complexes of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L., Fabaceae) in the Andes of Peru and Colombia, and their implications for conservation and breeding. Genet Resour Crop Evol 44:73–91
Beebe SE, Réngifo J, Gaitán-Solis E, Duque MC, Tohme J (2001) Diversity and origin of Andean landraces of common bean. Crop Sci 41:854–862
Blair MW, Pedraza F, Buendía HF, Gaitán-Solís E, Beebe SE, Gepts P, Tohme J (2003) Development of a genome-wide anchored microsatellite map for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 107:1362–1374
Broughton WJ, Hernandez G, Blair MW, Beebe SE, Gepts P, Vanderleyden J (2003) Beans (Phaseolus spp.)—model food legumes. Plant Soil 252:55–128
Buendia HF, Beebe SE, Blair MW, Teran H, Pedraza F (2003) Identificación de marcadores moleculares asociados a genes de rendimiento en una población RC2F3.7 de frijol común Phaseolus vulgaris L. (DOR390 × G19892). Fitotecnia Colombiana 3:57–64
Cattan-Toupance I, Michalakis Y, Neema C (1998) Genetic structure of wild bean populations in their South-Andean centre of origin. Theor Appl Genet 96:844–851
Chacón MI, Pickersgill SB, Debouck DG (2005) Domestication patterns in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and the origin of the Mesoamerican and Andean cultivated races. Theor Appl Genet 110:432–444
Churchill GA, Doerge RW (1994) Empirical threshold values for quantitative trait mapping. Genetics 138:963–971
Coyne DP (1967) Photoperiodism: inheritance and linkage studies in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Hered 58:313–314
Coyne DP (1970) Genetic control of a photoperiod-temperature response for time of flowering in beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Crop Sci 10:246–248
Debouck DG, Smartt J (1995) Beans: Phaseolus spp. (Leguminosae-papilionoideae). In: Smartt J, Simmonds NW (eds) Evolution of crop plants. 2nd edn. Longman, London, pp 297–294
Debouck DG, Tohme J (1989) Implications for bean breeders of studies on the origins of common beans, Phaseolus vulgaris L. In: Beebe S (ed) Current topics in breeding of common bean, vol 47. Bean program, (CIAT), Cali, Colombia, pp 3–42
Debouck DG, Toro O, Paredes M, Johnson WC, Gepts P (1993) Genetic diversity and ecological distribution of Phaseolus vulgaris (Fabaceae) in northwestern South America. Econ Bot 47:408–423
Freyre R, Ríos R, Guzmán L, Debouck D, Gepts P (1996) Ecogeographic distribution of Phaseolus spp. (Fabaceae) in Bolivia. Econ Bot 50:195–215
Freyre R, Skroch PW, Geffroy V, Adam-Blondon A, Shirmohamadali A, Johnson WC, Llaca V, Nodari RO, Pereira PA, Tsai S, Tohme J, Dron M, Nienhuis J, Vallejos C, Gepts P (1998) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. 4. Development of a core linkage map alignment of RFLP maps. Theor Appl Genet 97:847–856
Gaitán-Solís E, Duque MC, Edwards KJ, Tohme J (2002) Microsatellite repeats in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris): isolation, characterization, and cross-species amplification in Phaseolus ssp. Crop Sci 42:2128–2136
Gepts P (1988) Phaseolin as an evolutionary marker. In: Gepts P (ed) Genetic resources of Phaseolus beans; their maintenance, domestication, evolution, and utilization. Current plant science and biotechnology in agriculture. Kluwer, Dordrecht, 624 pp
Gepts P (1998) Origin and evolution of common bean: past events and recent trends. HortScience 33:1124–1130
Gepts P (2002) A comparison between crop domestication, classical plant breeding, and genetic engineering. Crop Sci 42:1780–1790
Gepts P, Bliss FA (1986) Phaseolin variability among wild and cultivated common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) from Colombia. Econ Bot 40:469–478
Gepts P, Debouck D (1991) Origin, domestication, and evolution of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). In: Schoonhoven AV (ed) Common beans: research for crop improvement. CIAT, Cali, pp 7–53
Gu W, Zhu JQ, Wallace DH, Singh SP, Weeden NF (1998) Analysis of genes controlling photoperiod sensitivity in common bean using DNA markers. Euphytica 102:125–132
Johnson WC, Gepts P (2002) The role of epistasis in controlling seed yield and other agronomic traits in an Andean × Mesoamerican cross of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Euphytica 125:69–72
Kami J, Becerra Velázquez V, Debouck DG, Gepts P (1995) Identification of presumed ancestral DNA sequences of phaseolin in Phaseolus vulgaris. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:1101–1104
Kelly JD, Schneider KA, Kolkman JM (1999) Breeding to improve yield. In: Singh SP (ed) Developments in plant breeding. Common bean improvement in the twenty-first century. Kluwer, Dordrecht
Kelly JD, Gepts P, Miklas PN, Coyne DP (2003) Tagging and mapping of genes and QTL and molecular-marker assisted selection for traits of economic importance in bean and cowpea. Field Crops Res 82:135–154
Khairallah M, Sears B, Adams M (1992) Mitochondrial restriction fragment length polymorphisms in wild Phaseolus vulgaris L.: insights on the domestication of the common bean. Theor Appl Genet 84:915–922
Koenig RL, Gepts P (1989) Allozyme diversity in wild Phaseolus vulgaris: further evidence for two major centers of genetic diversity. Theor Appl Genet 78:809–817
Koenig RL, Singh SP, Gepts P (1990) Novel phaseolin types in wild and cultivated common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae). Econ Bot 44:50–60
Koinange EMK, Singh SP, Gepts P (1996) Genetic control of the domestication syndrome in common bean. Crop Sci 36:1037–1045
Kornegay J, Cardona C, Posso CE (1993) Inheritance of resistance to Mexican bean weevil in common bean, determined by bioassay and biochemical tests. Crop Sci 33:589–984
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly M, Lincoln SE, Newburg L (1987) MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1:174–181
López CE, Acosta IF, Jara C, Pedraza F, Gaitán-Solís E, Gallego G, Beebe S, Tohme J (2003) Identifying resistance gene analogs associated with resistances to different pathogens in common bean. Phytopathology 93:88–95
Lynch M, Walsh B (1998) Genetics and analysis of quantitative traits. Sinauer Associates, Sunderland, 980 pp
McClean PE, Lee RK, Otto C, Gepts P, Bassett MJ (2002) Molecular and phenotypic mapping of genes controlling seed coat pattern and color in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 93:148–152
Métais I, Hamon B, Jalouzot R, Peltier D (2002) Structure and level of genetic diversity in various bean types evidenced with microsatellite markers isolated from a genomic enriched library. Theor Appl Genet 104:1346–1352
Miklas PN, Coyne DP, Grafton KF, Mutlu N, Reiser J, Lindgren DT, Singh SP (2003) A major QTL for common bacterial blight resistance derives from the common bean great northern landrace cultivar Montana No. 5. Euphytica 131:137–146
Motto M, Sorresi GP, Salamini F (1978) Seed size inheritance in a cross between wild and cultivated common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Genetica 49:31–36
Nodari RO, Tsai SM, Gilbertson RL, Gepts P (1993) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. II. Development of an RFLP based linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 85:513–520
Park SO, Coyne DP, Jung G, Skroch PW, Arnaud-Santana E, Steadman JR, Ariyarathne HM, Nienhuis J (2000) Mapping of QTL for seed size and shape traits in common bean. J Am Soc Hort Sci 125:466–475
Singh SP (2001) Broadening the genetic base of common bean cultivars: a review. Crop Sci 41:659–1675
Singh SP, Gepts P, Debouck DG (1991a) Races of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae). Econ Bot 45:379–396
Singh S, Nodari R, Gepts P (1991b) Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean. II. Marker-based analysis of morphological and agronomic traits. Crop Sci 31:19–23
Singh SP, Molina A, Gepts P (1995) Potential of wild common bean for seed yield improvement of cultivars in the tropics. Can J Plant Sci 75:807–812
Sullivan JG, Bliss FA (1983) Expression of enhanced seed protein content in inbred backcross lines of common bean. J Am Soc Hort Sci 108:787–791
Tanksley SD, McCouch SR (1997) Seed banks and molecular maps: unlocking genetic potential from the wild. Science 277:1063–1066
Tanksley SD, Nelson JC (1996) Advanced backcross QTL analysis: a method for the simultaneous discovery and transfer of valuable QTL from germplasm into elite breeding lines. Theor Appl Genet 92:191–203
Tar’an B, Michaels TE, Pauls KP (2002) Genetic mapping of agronomic traits in common bean. Crop Sci 42:544–556
Tohme J, Gonzlez DO, Beebe S, Duque MC (1996) AFLP analysis of gene pools of a wild bean core collection. Crop Sci 36:1375–1384
Vallejos C, Sakiyama NS, Chase CD (1992) A molecular marker based linkage map of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Genetics 131:733–740
Voysest O (2000) Mejoramiento genético del frijol (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): Legado de variedades de América Latina 1930–1999. CIAT, Cali
Xu Y, Zhu L, Xiao J, Huang N, McCouch SR (1997) Chromosomal regions associated with segregation distortion of molecular markers in F2, backcross, doubled haploid, and recombinant inbred populations in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 253:535–545
Yu K, Park SJ, Poysa V, Gepts P (2000) Integration of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers into a molecular linkage map of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 91:429–434
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Didier Peltier for providing selected microsatellite markers, to Alcides Hincapie for hybridizations between wild and cultivated parents, to Agobardo Hoyos for help with data analysis, to Yercil Viera for field trial management, to Gustavo Vallejo, Daniel Debouck and César Martinez for helpful reviewing of the manuscript or drafts and P. Zamorano for formatting.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by F. J. Muehlbauer
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blair, M.W., Iriarte, G. & Beebe, S. QTL analysis of yield traits in an advanced backcross population derived from a cultivated Andean × wild common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) cross. Theor Appl Genet 112, 1149–1163 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0217-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0217-2