Abstract
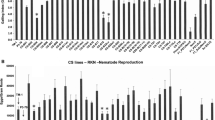
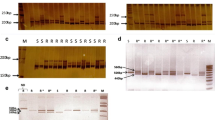
Host-plant resistance is the most economic and effective strategy for root-knot nematode (RKN) Meloidogyne incognita control in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Molecular markers linked to resistance are important for incorporating resistance genes into elite cultivars. To screen for microsatellite markers (SSR) closely linked to RKN resistance in G. hirsutum cv. Acala NemX, F1, F2, BC1F1, and F2:7 recombinant inbred lines (RILs) from intraspecific crosses and an F2 from an interspecific cross with G. barbadense cv. Pima S-7 were used. Screening of 284 SSR markers, which cover all the known identified chromosomes and most linkage groups of cotton, was performed by bulked segregant analysis, revealing informative SSRs. The informative SSRs were then mapped on the above populations. One co-dominant SSR marker CIR316 was identified tightly linked to a major resistance gene (designated as rkn1), producing amplified DNA fragments of approximately 221 bp (CIR316a) and 210 bp (CIR316c) in Acala NemX and susceptible Acala SJ-2, respectively. The linkage between CIR316a marker and resistance gene rkn1 in Acala NemX had an estimated distance of 2.1–3.3 cM depending on the population used. Additional markers, including BNL1231 with loose linkage to rkn1 (map distance 25.1–27.4 cM), BNL1066, and CIR003 allowed the rkn1 gene to be mapped to cotton linkage group A03. This is the first report in cotton with a closely linked major gene locus determining nematode resistance, and informative SSRs may be used for marker-assisted selection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abawi GS, Chen J (1998) Concomitant pathogen and pest interactions. In: Barker KR, Pederson GA, Windham GL (eds) Plant and nematode interactions. Am Soc Agron, Crop Sci Am, and Soil Sci Soc, Madison, pp 135–158
Abdalla AM, Reddy OUK, El-Zik KM, Pepper AE (2001) Genetic diversity and relationships of diploid and tetraploid cottons revealed using AFLP. Theor Appl Genet 102:222–229
Bezawada C, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Creech RG, McCarty JC (2003) SSR marker(s) associated with root-knot nematode resistance gene(s) in cotton. J Cotton Sci 7:179–184
Bridge J, Page SLJ (1980) Estimation of root-knot nematode infestation levels on roots using a rating chart. Trop Pest Manage 26:296–298
Frelichowski JE, Ulloa M, Tomkins JP, Palmer M, Main D, Stelly D, Cantrell RG (2004) New BAC-end derived microsatellite markers in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Acala ‘Maxxa’. In: ASA-CSSA-SSSA Annual Meeting Abstracts
Frelichowski JE, Ulloa M, Palmer MB, Main D, Tomkins JP, Stelly DM, Cantrell RG, Kohel RJ, Yu J (2005) Genetic, physical and QTL mapping assessments of BAC-end derived microsatellite markers developed from cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) Acala ‘Maxxa’. In: Plant and animal genome XIII conference, San Diego
Goodell PB, Montez GH (1994) Acala cotton tolerance to southern root-knot nematode, Meloidogyne incognita. In: Proceedings of Beltwide cotton production research conference, National Cotton Council of Am, Memphis, pp 265–267
He L, Du C, Covaleda L, Xu Z, Robinson AF, Yu JZ, Kohel RJ, Zhang H-B (2004) Cloning, characterization, and evolution of the NBS-LRR-encoding resistance gene analogue family in polyploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Mol Plant Microbe Interact 17:1234–1241
Hinchliffe DJ, Lu Y, Potenza C, Segupta-Gopalan C, Cantrell RG, Zhang J (2005) Resistance gene analogue markers are mapped to homeologous chromosomes in cultivated tetraploid cotton. Theor Appl Genet 110:1074–1085
Huang N, Angeles ER, Domingo J, Magpantay G, Singh S, Zhang G, Kumaravadivel N, Bennett J, Khush GS (1997) Pyramiding of bacterial blight resistance genes in rice: marker-assisted selection using RFLP and PCR. Theor Appl Genet 95:313–320
Hussey RS, Barker KR (1973) A comparision of methods of collecting inocula of Meloidogyne spp. including a new technique. Plant Dis Rep 57:1025–1028
Hyer AH, Jorgenson EC (1984) Root-knot nematode resistance in cotton breeding: techniques and results. In: Proceedings of Beltwide cotton production research conference, Natl Cotton Council of America, Memphis, pp 377–379
Jeffers DP, Roberts PA (1993) Effect of planting date and host genotype on the root-knot nematode-Fusarium wilt disease complex of cotton. Phytopathology 83:645–654
Kosambi DD (1944) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Lacape JM, Nguyen TB, Thibivilliers S, Bojinov B, Courtois B, Cantrell RG, Burr B, Hau B (2003) A combined RFLP-SSR-AFLP map of tetraploid cotton based on a Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense backcross population. Genome 46:612–626
McPherson MG, Jenkins JN, Watson CE, McCarty JC (2004) Inheritance of root-knot nematode resistance in M-315 RNR and M78-RNR cotton. J Cotton Sci 8:154–161
Michelmore RW, Paran I, Kesseli RV (1991) Identification of markers linked to disease resistance genes by bulked segregant analysis: a rapid method to detect markers in specific genomic regions by using segregating populations, Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:9828–9832
Nguyen TB, Giband M, Brottier P, Risterucci AM, Lacape JM (2004) Wide coverage of the tetraploid cotton genome using newly developed microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 109:167–175
Oakley SR (1995) CPCSD Acala C-225: a new nematode-resistant Acala variety for California’s San Joaquin Valley. In: Proceedings of Beltwide cotton production research conference, Natl Cotton Council of Am, Memphis, p 39
Ogallo JL, Goodell PB, Eckert J, Roberts PA (1997) Evaluation of NemX, a new cultivar of cotton with high resistance to Meloidogyne incognita. J Nematol 29:531–537
Park YH, Alabady MS, Sickler B, Wilkins TA, Yu J, Stelly DM, Kohel RJ, El-Shihy OM, Cantrell RG, Ulloa M (2005) Genetic mapping of new cotton fiber loci using EST-derived microsatellites in an interspecific recombinant inbred line (RIL) cotton population. Mol Gen Genomics (in press)
Reinisch A, Dong J, Brubaker CL, Stelly DM, Wendel JF, Paterson AH (1994) A detailed RFLP map of cotton, Gossypium hirsutum × Gossypium barbadense: chromosome organization and evolution in a disomic polyploid genome. Genetics 138:829–847
Roberts PA, Matthews WC, Veremis JC (1998) Genetic mechanisms of host-plant resistance to nematodes. In: Barker KR, Pederson GA, Windham GL (eds) Plant and nematode interactions. Am Soc Agron, Crop Sci Am, and Soil Sci Soc, Madison, pp 209–238
Rong J , Abbey C, Bowers JE, Brubaker CL, Chang C, Chee PW, Delmonte TA, Ding X, Garza JJ, Marler BS, Park C, Pierce GJ, Rainey KM, Rastogi VK, Schulze SR, Trolinder NL, Wendel JF, Wilkins TA, Williams-Coplin TD, Wing RA, Wright RJ, Zhao X, Zhu L, Paterson AH (2004) A 3347-locus genetic recombination map of sequence-tagged sites reveals features of genome organization, transmission and evolution of cotton (Gossypium). Genetics 166:389–417
Rungis D, Llewellyn D, Dennis ES, Lyon BR (2005) Simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers reveal low levels of polymorphism between cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) cultivars. Aust J Agric Res 56:301–307
Sanchez AC, Brar DS, Huang N, Li Z, Khush GS (2000) Sequence tagged site marker-assisted selection for three bacterial blight resistance genes in rice. Crop Sci 40:792–797
Sasser JN (1977) Worldwide dissemination and importance of the root-knot nematodes, Meloidogyne spp. J Nematol 9:26–29
Shappley ZW, Jenkins JN, Meredith WR, McCarty JC (1998) An RFLP linkage map of upland cotton, Gossypium hirsutum L. Theor Appl Genet 97:756–761
Shepherd RL (1974) Transgressive segregation for root-knot nematode resistance in cotton. Crop Sci 14:872–875
Shepherd RL (1982) Registration of three germplasm lines of cotton. Crop Sci 22:692
Shepherd RL, McCarty JC, Jenkins JN, Parrott WL (1988) Registration of twelve nonphotoperiodic lines with root-knot nematode resistant primitive cotton germplasm. Crop Sci 28:868–869
Shepherd RL, McCarty JC, Jenkins JN, Parrott WL (1989) Notice of release of nine root-knot nematode resistant germplasm lines of upland cotton Gossypium hirsutum L. USDA Miss Agric and Forestry Exp Stn Memo
Tan H, Callahan FE, Zhang X-D, Karaca M, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Creech RG, Ma D-P (2003) Identification of resistance gene analogs in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Euphytica 134:1–7
Ulloa M, Meredith WR Jr (2000) Genetic linkage map and QTL analysis of agronomic and fiber quality traits in an intraspecific population. J Cotton Sci 4:161–170
Ulloa M, Meredith WR, Shappley ZW, Kahler AL (2002) RFLP genetic linkage maps from four F2:3 populations and a joinmap of Gossypium hirsutum L. Theor Appl Genet 104:200–208
Ulloa M, Saha S, Jenkins JN, Meredith WR Jr, McCarty JC, Stelly DM (2005) Chromosomal assignment of RFLP linkage groups harboring important QTLs on an intraspecific cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) joinmap. J Hered 96:132–144
Van Ooijen JW, Voorrips RE (2001) JoinMap® 3.0, software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Zhang J, Guo W, Zhang T (2002) Molecular linkage map of allotetraploid cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L. × Gossypium barbadense L.) with a haploid population. Theor Appl Genet 105:1166–1174
Acknowledgement
This study was funded in part by a Cooperative Research Agreement from Cotton Incorporated and a grant from the University of California Discovery Grant (BioSTAR) Program. The authors thank Steven Oakley, California Planting Cotton Seed Distributors for providing cotton seed; Mikeal Roose for helpful advice; and William Matthews, Kathie Carter, and Teresa Mullens for technical help.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Langridge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, C., Ulloa, M. & Roberts, P.A. Identification and mapping of microsatellite markers linked to a root-knot nematode resistance gene (rkn1) in Acala NemX cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.). Theor Appl Genet 112, 770–777 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0183-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0183-0