Abstract
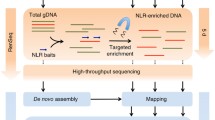
The conserved sequences in the nucleotide-binding sites of the nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat (NBS-LRR) class of disease resistance (R) genes have been used for PCR-based R-gene isolation and subsequent development of molecular markers. Here we present a PCR-based approach (NBS profiling) that efficiently targets R genes and R-gene analogs (RGAs) and, at the same time, produces polymorphic markers in these genes. In NBS profiling, genomic DNA is digested with a restriction enzyme, and an NBS-specific (degenerate) primer is used in a PCR reaction towards an adapter linked to the resulting DNA fragments. The NBS profiling protocol generates a reproducible polymorphic multilocus marker profile on a sequencing gel that is highly enriched for R genes and RGAs. NBS profiling was successfully used in potato with several restriction enzymes, and several primers targeted to different conserved motifs in the NBS. Across primers and enzymes, the NBS profiles contained 50–90% fragments that were significantly similar to known R-gene and RGA sequences. The protocol was similarly successful in other crops (including tomato, barley, and lettuce) without modifications. NBS profiling can thus be used to produce markers tightly linked to R genes and R-gene clusters for genomic mapping and positional cloning and to mine for new alleles and new sources of disease resistance in available germplasm.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarts MGM, Te Lintel Hekkert B, Holub EB, Beynon JL, Stiekema WJ, Pereira A (1998) Identification of R-gene homologous DNA fragments genetically linked to disease resistance loci in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:251–258
Altschul SF, Madden TL, Schäffer AA, Zhang J, Zhang Z, Miller W, Lipman DJ (1997) Gapped BLAST and PSI-BLAST: a new generation of protein database search programs. Nucleic Acids Res 25:3389–3402
Anderson PA, Lawrence GJ, Morrish BC, Ayliffe MA, Finnegan EJ, Ellis JG (1997) Inactivation of the flax rust resistance gene M associated with loss of a repeated unit within the leucine-rich repeat coding region. Plant Cell 9:641–651
Bent AF, Kunkel B, Dahlbeck D, Brown KL, Schmidt R, Giraudat J, Leung J, Staskawicz BJ (1997) RPS2 of Arabidopsis thaliana: a leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Science 265:1856–1860
Botella M A, Parker J E, Frost LN, Bittner-Eddy PD, Beynon JL, Daniels MJ, Holub EB, Jones JDG (1998) Three genes of the Arabidopsis RPP1 complex resistance locus recognize distinct Peronospora parasitica avirulence determinants. Plant Cell 10:1847–1860
Chen XM, Line RF, Leung H (1998) Genome scanning for resistance-gene analogs in rice, barley, and wheat by high-resolution electrophoresis. Theor Appl Genet 97:345–355
Collins NC, Webb CA, Seah S, Ellis JG, Hulbert SH, Pryor A (1998) The isolation and mapping of disease resistance gene analogs in maize. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:968–978
Collins NC, Park R, Spielmeyer W, Ellis J, Pryor T (2001) Resistance gene analogs in barley and their relationships to rust resistance genes. Genome 44:375–381
Deng Z, Huang S, Ling P, Chen C, Yu C, Weber CA, Moore GA, Gmitter FG Jr (2000) Cloning and characterization of NBS-LRR class resistance-gene candidate sequences in citrus. Theor Appl Genet 101:814–822
Ernst K, Kumar A, Kriseleit D, Kloos DU, Phillips MS, Ganal MW (2002) The broad-spectrum potato cyst nematode resistance gene (Hero) from tomato is the only member of a large gene family of NBS-LRR genes with an unusual amino acid repeat in the LRR region. Plant J 31:127–136
Fischer A, Saedler H, Theissen G (1995). Restriction fragment length polymorphism-coupled domain-directed differential display: a highly efficient technique for expression analysis of multigene families. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92:5331–5335
Flor HH (1971) Current status of the gene-for-gene concept. Annu Rev Phytopathol 9:275–276
Fulton TM, Chunwongse J, Tanksley SD (1995) Microprep protocol for extraction of DNA from tomato and other herbaceous plants. Plant Mol Biol Rep 13:207–209
Goff SA, Ricke D, Lan TH, Presting G, Wang R, Dunn M, Glazebrook J, Sessions A, Oeller P, Varma H, Hadley D, Hutchison D, Martin C, Katagiri F, Lange BM, Moughamer T, Xia Y, Budworth P, Zhong J, Miguel T, Paszkowski U, Zhang S, Colbert M, Sun WL, Chen L, Cooper B, Park S, Wood TC, Mao L, Quail P, Wing R, Dean R, Yu Y, Zharkikh A, Shen R, Sahasrabudhe S, Thomas A, Cannings R, Gutin A, Pruss D, Reid J, Tavtigian S, Mitchell J, Eldredge G, Scholl T, Miller RM, Bhatnagar S, Adey N, Rubano T, Tusneem N, Robinson R, Feldhaus J, Macalma T, Oliphant A, Briggs S (2002) A draft sequence of the rice genome (Oryza sativa L. ssp. japonica). Science 296:92–100
Hayes AJ, Saghai Maroof MA (2000) Targeted resistance gene mapping in soy bean using modified AFLPs. Theor Appl Genet 100:1279–1283
Hornstra IK, Yang TP (1993) In vivo footprinting and genomic sequencing by ligation-mediated PCR. Anal Biochem 213:179–193
Jia Y, McAdams SA, Bryan GT, Hershey HP, Valent B (2000) Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J 19:4004–4014
Jones DA, Jones JDG (1997) The role of leucine-rich repeat proteins in plant defenses. Adv Bot Res 24:89–167
Keen NT (1990) Gene-for-gene complementarity in plant-pathogen interactions Annu Rev Genet 24:447–463
Kobe B, Deisenhofer J (1994) The leucine-rich repeat: a versatile binding motif. Trends Biochem Sci 19:415–421
Lawrence GJ, Finnegan EJ, Ayliffe MA, Ellis JG (1995) The L6 gene for flax rust resistance is related to the Arabidopsis bacterial resistance gene RPS2 and the tobacco viral resistance gene N. Plant Cell 7:1195–206
Leister D, Ballvora A, Salamini F, Gebhardt C (1996) A PCR-based approach for isolating pathogen resistance genes from potato with potential for wide application in plants. Nat Genet 14:421–429
Leister D, Kurth J, Laurie DA, Yano M, Sasaki T, Devos K, Graner A, Schulze-Lefert P (1998) Rapid reorganization of resistance gene homologues in cereal genomes Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:370–375
Mago R, Nair S, Mohan M (1999). Resistance gene analogues from rice: cloning, sequencing and mapping. Theor Appl Genet 99:50–57
Meyers BC, Chin DB, Shen KA, Sivaramakrishnan S, Lavelle DO, Zhang Z, Mitchelmore RW (1998) The major resistance gene cluster in lettuce is highly duplicated and spans several megabases. Plant Cell 10:1817–1832
Meyers BC, Dickerman AW, Michelmore RW, Sivaramakrishnan S, Sobral B, Young ND (1999) Plant disease resistance genes encode members of an ancient and diverse protein family within the nucleotide-binding superfamily. Plant J 20:317–332
Michelmore RW, Meyers BC (1998) Clusters of resistance genes in plants evolve by divergent selection and a birth-and-death process. Genome Res 8:1113–1130
Milligan SB, Bodeau J, Yaghoobi J, Kaloshian I, Zabel P, Williamson VM (1998) The root knot nematode resistance gene Mi from tomato is a member of the leucine zipper, nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat family of plant genes. Plant Cell 10:1307–1319
Noir S, Combes M-C, Anthony F, Lashermes P (2001) Origin, diversity and evolution of NBS-type disease-resistance gene homologues in coffee trees (Coffea L.). Mol Genet Genom 265:654–662
Ori N, Eshed Y, Paran I, Presting G, Aviv D, Tanksley S, Zamir D, Fluhr R (1997) The I2C family from the wilt disease resistance locus I2 belongs to the nucleotide-binding, leucine-rich repeat superfamily of plant resistance genes. Plant Cell 9:521–532
Pan Q, Wendel J, Fluhr R (2000) Divergent evolution of plant NBS-LRR resistance gene homologues in dicot and cereal genomes. J Mol Evol 50:203–213
Parker JE, Coleman MJ, Szabo V, Frost LN, Schmidt R, van der Biezen EA, Moores T, Dean C, Daniels MJ, Jones JDG (1997) The Arabidopsis downy mildew resistance gene RPP5 shares similarity to the Toll and interleukin-1 receptors with N and L6. Plant Cell 9:879–894.
Salmeron J, Oldroyd G, Rommens C, Scofield S, Kim H, Lavelle D, Dahlbeck D, Staskawicz B (1996) Tomato Prf is a member of the leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes and lies embedded within the Pto kinase gene cluster. Cell 86:123–133
Saraste M, Sibbald PR, Wittinghofer A (1990). The P-loop: a common motif in ATP- and GTP-binding proteins. Trends Biochem Sci 15:430–434
Sela-Buurlage MB, Budai-Hadrian O, Pan Q, Carmel-Goren L, Vunsch R, Zamir D, Fluhr R (2001) Genome-wide dissection of fusarium resistance in tomato reveals multiple complex loci. Mol Genet Genom 265:1104–1111
Shen KA, Meyers BC, Islam-Faridi MN, Chin DB, Stelly DM, Michelmore RW (1998) Resistance gene candidates identified by PCR with degenerate oligonucleotide primers map to clusters of resistance genes in lettuce. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 11:815–823
Sicard D, Woo S-S, Arroyo-Garcia R, Ochoa O, Nguyen D, Korol A, Nevo E, Mitchelmore R (1999) Molecular diversity at the major cluster of disease resistance genes in cultivated and wild Lactuca spp. Theor Appl Genet 99:405–418
The Arabidopsis Genome Initiative (TAGI) (2000) Analysis of the genome sequence of the flowering plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Nature 6814:796–815
Tienderen PH van, De Haan AA, Van der Linden CG, Vosman B (2002) Biodiversity assessment using markers for ecologically important traits. Trends Ecol Evol 17:577–582
Timmerman-Vaughan GM, Frew TJ, Weerden NF (2000) Characterization and linkage mapping of R-gene analogous DNA sequences in pea (Pisum sativum L). Theor Appl Genet 101:241–247
Traut TW (1994) The functions and conserved motifs of nine types of peptide segments that form different types of nucleotide-binding sites. Eur J Biochem 229: 9–19
Trognitz F, Manosalva M, Gysin R, Nino-Liu D, Simon R, Herrera MR, Trognitz B, Ghislain M, Nelson R (2002) Plant defense genes associated with quantitative resistance to potato late blight in Solanum phujera × dihaploid S. tuberosum hybrids. Mol Plant Microbe Interact 15:587–597
Vicente JG, King GJ (2001) Characterisation of disease gene-like sequences in Brassica oleracea L. Theor Appl Genet 102:555–563
Vos P, Simons G, Jesse T, Wijbrandi J, Heinen L, Hogers R, Frijters A, Groenendijk J, Diergaarde P, Reijans M, Fierens-Onstenk J, de Both M, Peleman J, Liharska T, Hontelez J, Zabeau M (1998) The tomato Mi-1 gene confers resistance to both root knot nematodes and potato aphids. Nature Biotechnol 16:1365–1369
Vossen EAG van der, Rouppe van der Voort JNAM, Kanyuka K, Bendahmane A, Sandbrink S, Baulcombe DC, Bakker J, Stiekema WJ, Klein-Lankhorst RM (2000) Homologues of a single resistance-gene cluster in potato confer resistance to distinct pathogens: a virus and a nematode. Plant J 23:567–576
Walker JE, Saraste M, Runswick MJ, Gay NJ (1982) Distantly related genes in the α- and β-subunits of ATP synthetase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide-binding fold. EMBO J 1:945–951
Waugh R, McLean K, Flavell AJ, Pearce SR, Kumar A, Thomas BBT, Powell W (1997) Genetic distribution of Bare-1-like retrotransposable elements in the barley genome revealed by sequence-specific amplification polymorphisms (SSAP). Mol Gen Genet 253:687–694
Whitham S, Dinesh-Kumar SP, Choi D, Hehl R, Corr C, Baker B (1994). The product of the tobacco mosaic virus resistance gene N: Similarity to Toll and the interleukin-1 receptor. Cell 78:1101–1115.
Young ND (2000) The genetic architecture of resistance. Curr Opin Plant Biol 3:285–290
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank Dr. Edwin van der Vossen for critically reading the manuscript. This study has been carried out with financial support from the Ministry of Agriculture, Nature Management and Fisheries of The Netherlands (DLO program 283) and from the Commission of the European Communities, contract BIO4-98-033. It does not necessarily reflect its views and in no way anticipates the Commission’s future policy in this area.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H.F. Linskens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Linden, C.G., Wouters, D.C.A.E., Mihalka, V. et al. Efficient targeting of plant disease resistance loci using NBS profiling. Theor Appl Genet 109, 384–393 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1642-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-004-1642-8