Abstract.
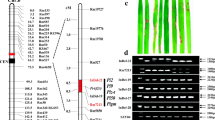
Rice blast disease is a major constraint for rice breeding. Nevertheless, the genetic basis of resistance remains poorly understood for most rice varieties, and new resistance genes remain to be identified. We identified the resistance gene corresponding to the cloned avirulence gene ACE1 using pairs of isogenic strains of Magnaporthe grisea differing only by their ACE1 allele. This resistance gene was mapped on the short arm of rice chromosome 8 using progenies from the crosses IR64 (resistant) × Azucena (susceptible) and Azucena × Bala (resistant). The isogenic strains also permitted the detection of this resistance gene in several rice varieties, including the differential isogenic line C101LAC. Allelism tests permitted us to distinguish this gene from two other resistance genes [Pi11 and Pi-29(t)] that are present on the short arm of chromosome 8. Segregation analysis in F2 populations was in agreement with the existence of a single dominant gene, designated as Pi33. Finally, Pi33 was finely mapped between two molecular markers of the rice genetic map that are separated by a distance of 1.6 cM. Detection of Pi33 in different semi-dwarf indica varieties indicated that this gene could originate from either one or a few varieties.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Böhnert HU, Fudal I, Dioh W, Tharreau D, Notteghem JL, Lebrun MH (2001) A fungal polyketide synthase is controlling recognition of avirulent Magnaporthe grisea by resistant rice. In: 10th Int Congress on Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions. 10–14th July, 2001, Madison, Wisconsin, USA, (Abstract): http://www.plantpath.wisc.edu/mpmi/
Bryan GT, Wu KS, Farrall L, Jia Y, Hershey HP, McAdams SA, Faulk KN, Donaldson GK, Tarchini R, Valent B (2000) A single amino-acid difference distinguishes resistant and susceptible alleles of the rice blast gene Pi-ta. Plant Cell 12:2033–2045
Causse MA, Fulton TM, Cho YG, Ahn SN, Chunwongse J, Wu K, Xiao J, Yu Z, Ronald PC, Harrington SE, Second G, McCouch SR, Tanksley SD (1994) Saturated molecular map of the rice genome based on an interspecific backross population. Genetics 138:1251–1274
Chen X, Temnykh S, Xu Y, Cho YG, McCouch SR (1997) Development of a microsatellite framework map providing genome-wide coverage in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 94:553–567
Dangl JL, Jones JDG (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833
Devic M, Albert S, Delseny M, Roscoe TJ (1997) Efficient PCR walking on plant genomic DNA. Plant Physiol Biochem 35:331–339
Dioh W, Tharreau D, Notteghem JL, Orbach M, Lebrun MH (2000) Mapping of avirulence genes in the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe grisea, with RFLP and RAPD markers. Mol Plant-Microbe Interact 13:217–27
Dixon MS, Hatzixanthis K, Jones DA, Harrison K, Jones JD (1998) The tomato Cf-5 disease resistance gene and six homologs show pronounced allelic variation in leucine-rich repeat copy number. Plant Cell 10:1915–1925
Ezuka A (1979) Breeding for and genetics of blast resistance in Japan. In: Proce Rice Blast Workshop, IRRI, Los Baños, The Philippines, pp 27–48
Filloux D, Brasseleur G, Leborgne L, Madelon E, Berger A, Garsmeur O, Grivet L, Glaszmann JC, Mathieu T, Lorieux M, Guesquière A (2000) An extended population of IR64 × Azucena RILS from the EGRAM European Program. In: 4th Int Rice Genet Symp, p 279 (Abstract)
Guiderdoni E, Galinato E, Louistro J, Vergara G (1992) Anther culture of tropical japonica × indica hybrids of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Euphytica 62:219–224
Hoisington D, Khairallah M, González-de-León D (1994) Laboratory protocols: CIMMYT applied molecular genetics laboratory, 2nd edn. CIMMYT, Mexico City, Mexico
Huang N, Parco A, Mew T, Magpantay G, McCouch S, Guiderdoni E, Xu J, Subudi P, Angeles ER, Khush G (1997) RFLP mapping of isosymes, RAPD and QTLs for grain shape, brown planthopper resistance in a doubled-haploid rice population. Mol Breed 3:105–113
Hulbert SH, Webb CA, Smith SM, Sun Q (2001) Resistance gene complexes: evolution and utilisation. Annu Rev Phytopathol 39:312–331
Imbe T, Matsumoto S (1985) Inheritance of resistance of rice varieties to the blast fungus strains virulent to the variety "Reiho" (in Japanese with English summary). Japan J Breed 35:332–339
Inukai T, Nelson RJ, Zeigler RS, Sarkarung S, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Takamure I, Kinoshita T (1994) Allelism of blast resistance genes in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 84:1278–1283
IRRI (2002) International rice information system. http://www.iris.irri.org/
Jia Y, McAdams SA, Bryan GT, Hershey HP, Valent B (2000) Direct interaction of resistance gene and avirulence gene products confers rice blast resistance. EMBO J 19:4004–4014
Kinoshita T (1998) Report of the committee of gene symbolization, nomenclature and linkage groups. Rice Genet Newslett 14:57–59
Kiyosawa S (1971) Genetical approach to the biochemical nature of plant disease resistance. Japan Agric Res Quart 6:72–80
Kiyosawa S (1984) Establishment of differential varieties for pathogenicity test of rice blast fungus. Rice Genet Newslett 1:95–97
Kiyosawa S, Mackill DS, Bonman JM, Tanak Y, Ling ZZ (1986) An attempt of classification of world's rice varieties based on reaction pattern to blast fungus strains. Bull Natl Inst Agrobiol Resources 2:13–39
Kurata N, Nagamura Y, Yamamoto K, Harushima Y, Sue N, Wu J, Antonio BA, Shomura A, Shimizu T, Lin SY, et al. (1994) A 300 kilobases interval genetic map of rice including 883 expressed sequences. Nature Genet 8:365–372
Mackill DJ, Bonman JM (1992) Inheritance of blast resistance in near-isogenic lines of rice. Phytopathology 82:746–749
McCouch SR, Kochert G, Yu ZH, Wang ZY, Khush GS, Coffman WR, Tanksley SD (1988) Molecular mapping of rice chromosomes. Theor Appl Genet 76:815–829
Monna L, Kitazawa N, Yoshino R, Suzuki J, Masuda H, Maehara Y, Tanji M, Sato M, Nasu S, Minobe Y (2002) Positional cloning of rice semi-dwarfing gene, sd-1: rice "green revolution gene" encodes a mutant enzyme involved in gibberellin synthesis. DNA Res 9:11–17
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high-molecular-weight plant DNA. Nucleic Acids Res 8:4321–4325
Price AH, Thomos AD (1997) Genetic dissection of root growth in rice (Oryza sativa L.). II. Mapping quantitative trait loci using molecular markers. Theor Appl Genet 95:143–152
Price AH, Steele KA, Moore BJ, Barraclough PB, Clarck LJ (2000) A combinated RFLP and AFLP linkage map of upland rice (Oryza sativa, L.) used to identify QTLs for root-penetration ability. Theor Appl Genet 100:49–56
Sallaud C, Lorieux M, Roumen E, Tharreau D, Berruyer R, Svestasrani P, Garsmeur O, Guesquiere A, Notteghem JL (2003) Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast resistant variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Theor Appl Genet 106:794–803
Saji S, Umehara Y, Antonio BA, Yamane H, Tanoue H, Baba T, Aoki H, Ishige N, Wu J, Koike K, Matsumoto T, Sasaki T (2001) A physical map with yeast artificial chromosome (YAC) clones covering 63% of the 12 rice chromosomes. Genome 44:32–37
Silué D, Tharreau D, Notteghem JL (1992) Identification of Magnaporthe grisea avirulence genes to seven rice cultivars. Phytopathology 82:1462–1467
Takahashi Y (1965) Genetics of resistance to the rice blast disease. In: The Rice Blast Disease. Proc Symp Int Rice Research Institute, Los Baños, The Philippines. The Johns Hopkins press, Baltimore, Maryland, pp 303–329
Temnykh S, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S, Hauch N, Lipovich L, Cho YC, Ishii T, McCouch SR (2000) Mapping and genome organisation of microsatellite sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:697–712
Temnykh S, DeClerck G, Lukashova A, Lipovich L, Cartinhour S, McCouch S (2001) Computational and experimental analysis of microsatellites in rice (Oryza sativa L.): frequency, length variation, transposon associations, and genetic marker potential. Genome Res 11:1441–1452
Umehara Y, Inagaki A, Tanoue H, Yasukoshi Y, Nagamura Y, Saji S, Otsuki Y, Fujimura T, Kurata N, Minobe Y (1995) Construction and characterization of a rice YAC library for physical mapping. Mol Breed 1:79–89
Van der Hoorn RA, Kruijt M, Roth R, Brandwagt BF, Joosten MH, De Wit PJ (2001) Intragenic recombination generated two distinct Cf genes that mediate AVR9 recognition in the natural population of Lycopersicon pimpinellifolium. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:10,493–10,498
Wang GL, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, McCouch SR, Champoux MC, Nelson RJ (1994) RFLP mapping of genes conferring complete and partial resistance to blast in a durably resistant rice cultivar. Genetics 136:1421–1434
Wang ZX, Yano M, Yamanouchi U, Iwamoto M, Monna L, Hayasaka H, Sasaki T (1999) The Pi-b gene for blast resistance belongs to the nucleotide binding and leucine-rich repeat class of plant disease resistance genes. Plant J 19:55–64
Wu KS, Tanksley SD (1993) Abundance, polymorphism and genetic mapping of microsatellites in rice. Mol Gen Genet 241:225–235
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley (1991a) Tagging genes for blast resistance in rice via linkage to RFLP markers. Theor Appl Genet 81:471–476
Yu ZH, Mackill DJ, Bonman JM, Tanksley (1991b) RFLP tagging of blast resistance genes in rice. In: Rice Genetics II. IRRI, Manila, The Philippines, pp 451–458
Zhu LH, Chen Y, Xu YB, Xu JC, Cai HW, Ling ZZ (1993) Construction of a molecular map of rice and gene mapping using a double-haploid population of a cross between indica and japonica varieties. Rice Genet Newslett 10:132–135
Acknowledgements.
We thank Claudia Kaye, Nourollah Ahmadi and Michel Peterschmitt for a critical review of the manuscript. YAC clones were obtained from the Japanese Ministry of Agriculture, Forestry and Fisheries (MAFF) DNA bank.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by D.J. Mackill
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berruyer, R., Adreit, H., Milazzo, J. et al. Identification and fine mapping of Pi33, the rice resistance gene corresponding to the Magnaporthe grisea avirulence gene ACE1 . Theor Appl Genet 107, 1139–1147 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1349-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-003-1349-2