Introduction:
Different concepts and applications of teleradiology systems have been realised. However, their cost-effectiveness is still questionable. Therefore, a cost-benefit anylsis of three different scenarios of the new teleradiology system Kamedin (Kooperatives Arbeiten und rechnergestützte Medizinische Diagnostik auf innovativen Netzen der Deutschen Telekom) was performed.
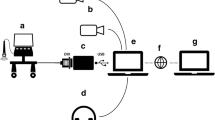
Methods: CT examinations were transmitted from an Advantage Windows (GE) workstation to a Kamedin workstation using DICOM 3 protocol. Afterwards a teleconference was established with a Kamedin workstation in the intensive care unit within the hospital via FDDI/Ethernet, with an external workstation in a radiology department 6 km away via ISDN and with a Kamedin PC located with radiologist on duty 22 km away via ISDN. On average, 36 CT slices per patient were transferred. A break-even analysis was performed with respect to costs of hardware, software, support, use of ISDN and staff, as well as benefits like the decrease in transportation or film documentation costs.
Results: Owing to the different reductions in transportation costs, two applications (intensive care unit and external PC) showed a break-even of 1817 and 528 teleconferences/year, respectively. Further optimisation of cost-effectiveness is possible on condition that existing hardware can be used and an automatic data transfer without staff control is available. When all optimisation factors were combined, the break-even decreased to a minimum of 167 and 77 teleconferences/year, respectively.
Conclusion: Teleconferences with high image quality can be set up between workstations and PCs using the Kamedin system. Depending on the possible decrease in transportation costs, teleconferencing is cost-effective under certain conditions. Teleradiology has additional advantages, such as the acceleration and optimisation of patient management.
Zusammenfassung
Fragestellung: Eine weiterentwickelte Softwareversion des Teleradiologiesystems KAMEDIN wird in 3 Anwendungsszenarien evaluiert und einer Wirtschaftlichkeitsanalyse unterzogen.
Methodik: In die Break-even-Analyse wird eine klinikinterne Übertragung zu einer Workstation auf der anästhesistischen Intensivstation, eine externe Übertragung zu der Workstation einer 6 km entfernten radiologischen Außenstelle und eine externe Übertragung zu einem 22 km entfernten PC (Bereitschaftsdienst) einbezogen. Den Gesamtkosten (Investitionskosten, Support, ISDN-Gebühren, Personalkosten) wird die mögliche Reduktion der Patiententransporte, der Arztwegezeiten und der Filmkosten gegenübergestellt.
Ergebnisse: In 2 der 3 Szenarien wird ein Break-even bei 1817 bzw. 528 Telekonferenzen/Jahr erreicht, die Unterschiede zwischen den Szenarien werden u. a. durch die Höhe der entfallenden Transportkosten verursacht. Eine Verbesserung der Wirtschaftlichkeit kann durch die Einbeziehung bereits bestehender Hardwarekapazitäten und einen reduzierten Supportumfang erzielt werden. Bei einer Kombination aller Einsparpotentiale kann der Break-even auf 167 bzw. 77 Telekonferenzen/Jahr abgesenkt werden.
Schlußfolgerungen: Unter geeigneten Rahmenbedingungen kann die Teleradiologie auch bei moderaten Einsatzfrequenzen kostensparend betrieben werden.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Eingegangen am 10. Januar 1997 Angenommen am 11. Februar 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lehmann, K., Walz, M., Bolte, R. et al. Concept and applicability of the KAMEDIN teleradiology system in view of a cost-benefit analysis. Radiologe 37, 278–284 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001170050212
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001170050212