Abstract
Oncogenic PIK3CA mutations are common in endometrial cancers, and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is targetable by drugs. We sought to investigate whether the combination of an mTOR inhibitor, everolimus (RAD001), and an AKT inhibitor, terameprocol (M4N), exerts better antiproliferative effects in endometrial cancer. The molecular mechanisms underlying their pharmacological action were also examined. The combination of RAD001 and M4N exerted in vitro synergistic effects on cell viability, apoptosis, and expression of IGFBP2 in endometrial cancer cells. Mechanistically, the Sp1 site on the IGFBP2 promoter was required for RAD001- and M4N-induced downregulation. IGFBP2 protein expression was higher in endometrial cancer than in the normal endometrium (P < 0.001). Furthermore, elevated IGFBP2 histoscores were significantly associated with a lower overall survival (P = 0.021). In conclusion, our in vitro results demonstrate that RAD001 and M4N exert synergistic antiproliferative effects against endometrial cancer cells, which appeared to be mediated by the inhibition of IGFBP2, a key anti-apoptotic regulator. Further clinical studies of this drug combination in patients with endometrial cancer may be warranted, especially in the presence of PIK3CA and IGFBP2 aberrations.
Key messages
-
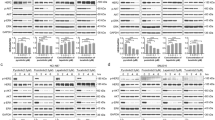
RAD001 and M4N synergistically suppress endometrial cancer growth.
-
IGFBP2 is overexpressed in endometrial cancer.
-
The combination of RAD001 and M4N significantly reduces IGFBP2 overexpression.
-
Sp1 binding site on the IGFBP2 promoter is required for RAD001- and M4N-induced downregulation.
-
High IGFBP2 histoscore in endometrial cancer portends a poor prognosis.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Ward EM, Johnson CJ, Cronin KA, Ma J, Ryerson B, Mariotto A, Lake AJ, Wilson R, Sherman RL et al (2017) Annual report to the nation on the status of cancer, 1975–2014, featuring survival. J Natl Cancer Inst 1:109(9)
Cancer Registry Annual Report, 2014 Taiwan: Ministry of Health and Welfare, Executive Yuan 2016 https://www.hpa.gov.tw/BHPNet/English/Index.aspx
Creasman WT, Miller DS (2012) Adenocarcinoma of the uterine corpus. In: Di Saia PJ, Creasman WT, Mannel RS, McMeekin DS, Mutch DG (eds) Clinical gynecologic oncology. Elsevier, Philadelphia, pp 121–154
Dedes KJ, Wetterskog D, Ashworth A, Kaye SB, Reis-Filho JS (2011) Emerging therapeutic targets in endometrial cancer. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 8:261–271
Hayes MP, Wang H, Espinal-Witter R, Douglas W, Solomon GJ, Baker SJ, Ellenson LH (2006) PIK3CA and PTEN mutations in uterine endometrioid carcinoma and complex atypical hyperplasia. Clin Cancer Res 12:5932–5935
Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Yan H, Gazdar A, Powell SM, Riggins GJ et al (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304:554
Salvesen HB, Carter SL, Mannelqvist M, Dutt A, Getz G, Stefansson IM, Raeder MB, Sos ML, Engelsen IB, Trovik J, Wik E, Greulich H, Bo TH, Jonassen I, Thomas RK, Zander T, Garraway LA, Oyan AM, Sellers WR, Kalland KH, Meyerson M, Akslen LA, Beroukhim R (2009) Integrated genomic profiling of endometrial carcinoma associates aggressive tumors with indicators of PI3 kinase activation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:4834–4839
Mireuta M, Darnel A, Pollak M (2010) IGFBP-2 expression in MCF-7 cells is regulated by the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through Sp1-induced increase in transcription. Growth Factors 28:243–255
Russo VC, Azar WJ, Yau SW, Sabin MA, Werther GA (2015) IGFBP-2: the dark horse in metabolism and cancer. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26:329–346
Hay N (2005) The Akt-mTOR tango and its relevance to cancer. Cancer Cell 8:179–183
Yuan R, Kay A, Berg WJ, Lebwohl D (2009) Targeting tumorigenesis: development and use of mTOR inhibitors in cancer therapy. J Hematol Oncol 2:45
Husseinzadeh N, Husseinzadeh HD (2014) mTOR inhibitors and their clinical application in cervical, endometrial and ovarian cancers: a critical review. Gynecol Oncol 133:375–381
Ray-Coquard I, Favier L, Weber B, Roemer-Becuwe C, Bougnoux P, Fabbro M, Floquet A, Joly F, Plantade A, Paraiso D, Pujade-Lauraine E (2013) Everolimus as second- or third-line treatment of advanced endometrial cancer: ENDORAD, a phase II trial of GINECO. Br J Cancer 108:1771–1777
Tibes R, McDonagh KT, Lekakis L, Bogenberger JM, Kim S, Frazer N, Mohrland S, Bassett D, Garcia R, Schroeder K et al (2015) Phase I study of the novel Cdc2/CDK1 and AKT inhibitor terameprocol in patients with advanced leukemias. Investig New Drugs 33:389–396
Huang RC, Chang CC, Mold D (2006) Survivin-dependent and -independent pathways and the induction of cancer cell death by tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid. Semin Oncol 33:479–485
Smolewski P (2008) Terameprocol, a novel site-specific transcription inhibitor with anticancer activity. IDrugs 11:204–214
Chang CC, Heller JD, Kuo J, Huang RC (2004) Tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid induces growth arrest and cellular apoptosis by inhibiting Cdc2 and survivin expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:13239–13244
Park R, Chang CC, Liang YC, Chung Y, Henry RA, Lin E, Mold DE, Huang RC (2005) Systemic treatment with tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid suppresses the growth of human xenograft tumors. Clin Cancer Res 11:4601–4609
Grossman SA, Ye X, Peereboom D, Rosenfeld MR, Mikkelsen T, Supko JG, Desideri S, Adult Brain Tumor C (2012) Phase I study of terameprocol in patients with recurrent high-grade glioma. Neuro-Oncology 14:511–517
Lin CY, Chao A, Wang TH, Lee LY, Yang LY, Tsai CL, Wang HS, Lai CH (2016) Nucleophosmin/B23 is a negative regulator of estrogen receptor alpha expression via AP2gamma in endometrial cancer cells. Oncotarget 7:60038–60052
Lin CY, Chao A, Wang TH, Hsueh S, Lee YS, Wu TI, Chao AS, Huang HJ, Chou HH, Chang TC, Lai CH (2014) A dual tyrosine kinase inhibitor lapatinib suppresses overexpression of matrix metallopeptidase 1 (MMP1) in endometrial cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 92:969–981
Nishida M (2002) The Ishikawa cells from birth to the present. Hum Cell 15:104–117
Zhao S, Choi M, Overton JD, Bellone S, Roque DM, Cocco E, Guzzo F, English DP, Varughese J, Gasparrini S, Bortolomai I, Buza N, Hui P, Abu-Khalaf M, Ravaggi A, Bignotti E, Bandiera E, Romani C, Todeschini P, Tassi R, Zanotti L, Carrara L, Pecorelli S, Silasi DA, Ratner E, Azodi M, Schwartz PE, Rutherford TJ, Stiegler AL, Mane S, Boggon TJ, Schlessinger J, Lifton RP, Santin AD (2013) Landscape of somatic single-nucleotide and copy-number mutations in uterine serous carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:2916–2921
Li Y, Yang X, Su LJ, Flaig TW (2011) Pazopanib synergizes with docetaxel in the treatment of bladder cancer cells. Urology 78(233):e237–e213
Hirashima K, Baba Y, Watanabe M, Karashima RI, Sato N, Imamura Y, Nagai Y, Hayashi N, Iyama KI, Baba H (2012) Aberrant activation of the mTOR pathway and anti-tumour effect of everolimus on oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Br J Cancer 106:876–882
Heller JD, Kuo J, Wu TC, Kast WM, Huang RC (2001) Tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid induces G2 arrest in mammalian cells and exhibits tumoricidal activity in vivo. Cancer Res 61:5499–5504
Reagan-Shaw S, Nihal M, Ahmad N (2008) Dose translation from animal to human studies revisited. FASEB J 22:659–661
USFDA (2005) Guidance for industry: estimating the maximum safe starting dose in adult healthy volunteer. US Food and Drug Administration, Rockville, MD
Chao A, Chang TC, Lapke N, Jung SM, Chi P, Chen CH, Yang LY, Lin CT, Huang HJ, Chou HH et al (2016) Prevalence and clinical significance of BRCA1/2 germline and somatic mutations in Taiwanese patients with ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 7:85529–85541
Youden WJ (1950) Index for rating diagnostic tests. Cancer 3:32–35
Wei Y, To KK, Au-Yeung SC (2015) Synergistic cytotoxicity from combination of imatinib and platinum-based anticancer drugs specifically in Bcr-Abl positive leukemia cells. J Pharmacol Sci 129:210–215
Chou TC (2010) Drug combination studies and their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer Res 70:440–446
Boisclair YR, Brown AL, Casola S, Rechler MM (1993) Three clustered Sp1 sites are required for efficient transcription of the TATA-less promoter of the gene for insulin-like growth factor-binding protein-2 from the rat. J Biol Chem 268:24892–24901
Solomon SS, Majumdar G, Martinez-Hernandez A, Raghow R (2008) A critical role of Sp1 transcription factor in regulating gene expression in response to insulin and other hormones. Life Sci 83:305–312
Li A, Fan S, Xu Y, Meng J, Shen X, Mao J, Zhang L, Zhang X, Moeckel G, Wu D, Wu G, Liang C (2017) Rapamycin treatment dose-dependently improves the cystic kidney in a new ADPKD mouse model via the mTORC1 and cell-cycle-associated CDK1/cyclin axis. J Cell Mol Med 21:1619–1635
Oh SH, Jin Q, Kim ES, Khuri FR, Lee HY (2008) Insulin-like growth factor-I receptor signaling pathway induces resistance to the apoptotic activities of SCH66336 (lonafarnib) through Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin-mediated increases in survivin expression. Clin Cancer Res 14:1581–1589
Alshaker H, Wang Q, Bohler T, Mills R, Winkler M, Arafat T, Kawano Y, Pchejetski D (2017) Combination of RAD001 (everolimus) and docetaxel reduces prostate and breast cancer cell VEGF production and tumour vascularisation independently of sphingosine-kinase-1. Sci Rep 7:3493
Thul PJ, Akesson L, Wiking M, Mahdessian D, Geladaki A, Ait Blal H, Alm T, Asplund A, Bjork L, Breckels LM et al (2017) A subcellular map of the human proteome. Science:356
Li J, Lu Y, Akbani R, Ju Z, Roebuck PL, Liu W, Yang JY, Broom BM, Verhaak RG, Kane DW et al (2013) TCPA: a resource for cancer functional proteomics data. Nat Methods 10:1046–1047
Lee YS, Chen CH, Tsai CN, Tsai CL, Chao A, Wang TH (2009) Microarray labeling extension values: laboratory signatures for Affymetrix GeneChips. Nucleic Acids Res 37:e61
Gymnopoulos M, Elsliger MA, Vogt PK (2007) Rare cancer-specific mutations in PIK3CA show gain of function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:5569–5574
Slomovitz BM, Lu KH, Johnston T, Coleman RL, Munsell M, Broaddus RR, Walker C, Ramondetta LM, Burke TW, Gershenson DM, Wolf J (2010) A phase 2 study of the oral mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor, everolimus, in patients with recurrent endometrial carcinoma. Cancer 116:5415–5419
Slomovitz BM, Jiang Y, Yates MS, Soliman PT, Johnston T, Nowakowski M, Levenback C, Zhang Q, Ring K, Munsell MF, Gershenson DM, Lu KH, Coleman RL (2015) Phase II study of everolimus and letrozole in patients with recurrent endometrial carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 33:930–936
Kimura K, Huang RC (2016) Tetra-O-methyl nordihydroguaiaretic acid broadly suppresses cancer metabolism and synergistically induces strong anticancer activity in combination with etoposide, rapamycin and UCN-01. PLoS One 11:e0148685
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Ms. Jung-Erh Yang for her excellent technical assistance. Formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded specimens were kindly provided by the Tumor Bank. We also acknowledge the statistical assistance provided by the Clinical Trial Center (Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Linkou, Taiwan), which was founded by the Taiwanese Ministry of Health and Welfare (grant MOHW106-TDU-B-212-113005).
Funding
This study was financially supported by grants from the Chang Gung Foundation (CMRPG3C1351/2/3, CMRPG3G1781, CRRPG3D0041-3, and CMRPG3F2111/2) and the Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST 105-2320-B-182A-005).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
SJC is an employee of ACT Genomics Co., Ltd.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 10214 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chao, A., Lin, CY., Wu, RC. et al. The combination of everolimus and terameprocol exerts synergistic antiproliferative effects in endometrial cancer: molecular role of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2. J Mol Med 96, 1251–1266 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1699-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-018-1699-5