Abstract
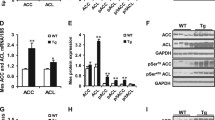
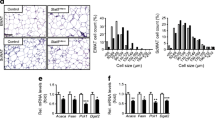
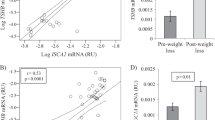
Transgenic overexpression of adipose tissue (AT) transducin-like enhancer of split 3 (TLE3) mimicked peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) agonists, improving insulin resistance in mice. This study aimed to investigate TLE3 gene expression (qRT-PCR) and protein (Western blot) in subjects with a wide spectrum of obesity and insulin sensitivity and in an independent cohort of obese subjects following surgery-induced weight loss. TLE3 was analyzed in human adipocytes and after treatment with rosiglitazone. Given the findings in humans, TLE3 was also investigated in mice after a high-fat diet (HFD) and in PPARγ knockout mice. Subcutaneous (SC) AT TLE3 was increased in subjects with type 2 diabetes (T2D). In fact, SC TLE3 was associated with increased fasting glucose (r = 0.25, p = 0.015) and S6K1 activity (r = 0.671, p = 0.003), and with decreased Glut4 (r = −0.426, p = 0.006) and IRS-1 expression (−31 %, p = 0.007) and activation (P-IRS-1/IRS-1, −17 %, p = 0.024). TLE3 was preferentially expressed in mature adipocytes and increased during in vitro differentiation in parallel to PPARγ. Weight loss led to improved insulin sensitivity, increased AT PPARγ and decreased TLE3 (−24 %, p = 0.0002), while rosiglitazone administration downregulated TLE3 gene expression in fully differentiated adipocytes (−45 %, p < 0.0001). The concept that TLE3 may act as a homeostatic linchpin in AT was also supported by its increased expression in HFD-fed mice (39 %, p = 0.013) and PPARγ knockout (74 %, p = 0.001). In summary, increased AT TLE3 in subjects with T2D and in AT from HFD-fed and PPARγ knockout mice suggest that TLE3 may play an adaptive regulatory role that improves AT function under decreased PPARγ expression.
Key message
-
TLE3 is expressed in mature adipocytes concomitantly with PPARγ.
-
Subcutaneous adipose TLE3 is increased in T2D patients.
-
Adipose TLE3 is upregulated in genetically ablated PPARγ and HFD-fed mice.
-
TLE3 may be a homeostatic linchpin in insulin resistance and defective PPARγ.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guilherme A, Virbasius JV, Puri V, Czech MP (2008) Adipocyte dysfunctions linking obesity to insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9(5):367–377
Qatanani M, Lazar MA (2007) Mechanisms of obesity-associated insulin resistance: many choices on the menu. Genes Dev 21(12):1443–1455
Farmer SR (2006) Transcriptional control of adipocyte formation. Cell Metab 4(4):263–273
MacDougald OA, Mandrup S (2002) Adipogenesis: forces that tip the scales. Trends Endocrinol Metab 13(1):5–11
Tontonoz P, Hu E, Graves RA, Budavari AI, Spiegelman BM (1994) mPPAR gamma 2: tissue-specific regulator of an adipocyte enhancer. Genes Dev 8(10):1224–1234
Tontonoz P, Spiegelman BM (2008) Fat and beyond: the diverse biology of PPARgamma. Annu Rev Biochem 77:289–312
Barak Y, Nelson MC, Ong ES, Jones YZ, Ruiz-Lozano P, Chien KR, Koder A, Evans RM (1999) PPAR gamma is required for placental, cardiac, and adipose tissue development. Mol Cell 4(4):585–595
Rosen ED, MacDougald OA (2006) Adipocyte differentiation from the inside out. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7(12):885–896
Rosen ED, Sarraf P, Troy AE, Bradwin G, Moore K, Milstone DS, Spiegelman BM, Mortensen RM (1999) PPAR gamma is required for the differentiation of adipose tissue in vivo and in vitro. Mol Cell 4(4):611–617
Semple RK, Chatterjee VK, O’Rahilly S (2006) PPAR gamma and human metabolic disease. J Clin Invest 116(3):581–589
Wu Z, Rosen ED, Brun R, Hauser S, Adelmant G, Troy AE, McKeon C, Darlington GJ, Spiegelman BM (1999) Cross-regulation of C/EBP alpha and PPAR gamma controls the transcriptional pathway of adipogenesis and insulin sensitivity. Mol Cell 3(2):151–158
Artavanis-Tsakonas S, Simpson P (1991) Choosing a cell fate: a view from the Notch locus. Trends Genet 7(11–12):403–408
Campos-Ortega JA (1993) Mechanisms of early neurogenesis in Drosophila melanogaster. J Neurobiol 24(10):1305–1327
Delidakis C, Preiss A, Hartley DA, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (1991) Two genetically and molecularly distinct functions involved in early neurogenesis reside within the Enhancer of split locus of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 129(3):803–823
Villanueva CJ, Waki H, Godio C, Nielsen R, Chou WL, Vargas L, Wroblewski K, Schmedt C, Chao LC, Boyadjian R et al (2011) TLE3 is a dual-function transcriptional coregulator of adipogenesis. Cell Metab 13(4):413–427
Ortega FJ, Mercader JM, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Sabater M, Pueyo N, Valdes S, Ruiz B, Luche E, Serino M, Naon D et al (2012) Targeting the association of calgranulin B (S100A9) with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. J Mol Med (Berl) 91(4):523–534
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Novelle MG, Catalan V, Ortega F, Moreno M, Gomez-Ambrosi J, Xifra G, Serrano M, Guerra E, Ricart W, Fruhbeck G, Dieguez C, Fernandez-Real JM (2014) Insulin resistance modulates iron-related proteins in adipose tissue. Diabetes Care
Karczewska-Kupczewska M, Lelental N, Adamska A, Nikolajuk A, Kowalska I, Gorska M, Zimmermann R, Kornhuber J, Straczkowski M, Lewczuk P (2013) The influence of insulin infusion on the metabolism of amyloid beta peptides in plasma. Alzheimers Dement 9(4):400–405
DeFronzo RA, Tobin JD, Andres R (1979) Glucose clamp technique: a method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am J Physiol 237(3):E214–E223
Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Carobbio S, Velagapudi VR, Barbarroja N, Moreno-Navarrete JM, Tinahones FJ, Fernandez-Real JM, Oresic M, Vidal-Puig A (2012) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma-dependent regulation of lipolytic nodes and metabolic flexibility. Mol Cell Biol 32(8):1555–1565
Arner P (1995) Differences in lipolysis between human subcutaneous and omental adipose tissues. Ann Med 27(4):435–438
Rodriguez-Cuenca S, Carobbio S, Vidal-Puig A (2012) Ablation of Pparg2 impairs lipolysis and reveals murine strain differences in lipolytic responses. FASEB J 26(5):1835–1844
Medina-Gomez G, Virtue S, Lelliott C, Boiani R, Campbell M, Christodoulides C, Perrin C, Jimenez-Linan M, Blount M, Dixon J et al (2005) The link between nutritional status and insulin sensitivity is dependent on the adipocyte-specific peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma2 isoform. Diabetes 54(6):1706–1716
Villanueva CJ, Vergnes L, Wang J, Drew BG, Hong C, Tu Y, Hu Y, Peng X, Xu F, Saez E et al (2013) Adipose subtype-selective recruitment of TLE3 or Prdm16 by PPARgamma specifies lipid storage versus thermogenic gene programs. Cell Metab 17(3):423–435
Pfaffl MW, Tichopad A, Prgomet C, Neuvians TP (2004) Determination of stable housekeeping genes, differentially regulated target genes and sample integrity: BestKeeper–Excel-based tool using pair-wise correlations. Biotechnol Lett 26(6):509–515
White MF (2002) IRS proteins and the common path to diabetes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 283(3):E413–E422
Moreno-Navarrete JM, Ortega F, Sanchez-Garrido MA, Sabater M, Ricart W, Zorzano A, Tena-Sempere M, Fernandez-Real JM (2013) Phosphorylated S6K1 (Thr389) is a molecular adipose tissue marker of altered glucose tolerance. J Nutr Biochem 24(1):32–38
Shepherd PR, Kahn BB (1999) Glucose transporters and insulin action—implications for insulin resistance and diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 341(4):248–257
Maggard-Gibbons M, Maglione M, Livhits M, Ewing B, Maher AR, Hu J, Li Z, Shekelle PG (2013) Bariatric surgery for weight loss and glycemic control in nonmorbidly obese adults with diabetes: a systematic review. JAMA 309(21):2250–2261
Ibrahim MM (2010) Subcutaneous and visceral adipose tissue: structural and functional differences. Obes Rev 11(1):11–18
Daniels DL, Weis WI (2005) Beta-catenin directly displaces Groucho/TLE repressors from Tcf/Lef in Wnt-mediated transcription activation. Nat Struct Mol Biol 12(4):364–371
Albrektsen T, Frederiksen KS, Holmes WE, Boel E, Taylor K, Fleckner J (2002) Novel genes regulated by the insulin sensitizer rosiglitazone during adipocyte differentiation. Diabetes 51(4):1042–1051
Camp HS, Whitton AL, Tafuri SR (1999) PPARgamma activators down-regulate the expression of PPARgamma in 3 T3-L1 adipocytes. FEBS Lett 447(2–3):186–190
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the technical assistance of Isabel Alonso, Oscar Rovira and Emili LosHuertos (Unit of Diabetes, Endocrinology and Nutrition, Institut d’Investigació Biomèdica de Girona, Hospital Universitari de Girona Dr. Josep Trueta). This study was supported by the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation (FIS 2011–00214) and CIBER de la Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y la Nutrición (CIBERobn). The CIBER de la Fisiopatología de la Obesidad y Nutrición (CIBERobn) is an initiative from the Instituto de Salud Carlos III (ISCIII).
Disclosures
The authors have nothing to disclose.
Author contribution
All authors of this manuscript have directly participated in the execution and analysis of the study. FJO and MS designed the study, analyzed the biochemical variables, performed the statistical analysis, and wrote the manuscript. JMM-N, MG-S, and MS analyzed biochemical variables. JIR-H, GX, and WR obtained the samples, anthropometrical characteristics, and the written consent of participants. SR-C and AV-P provided samples from HFD and PPARγ2-KO mouse models. BP and AV-P provided important intellectual content. JMF-R carried out the conception and coordination of this study and helped with the writing of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Francisco José Ortega and Marta Serrano contributed equally to this manuscript.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 473 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ortega, F.J., Serrano, M., Rodriguez-Cuenca, S. et al. Transducin-like enhancer of split 3 (TLE3) in adipose tissue is increased in situations characterized by decreased PPARγ gene expression. J Mol Med 93, 83–92 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1207-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1207-5