Abstract
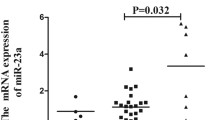
Previous studies have identified miR-182, miR-27a, FoxO1, and IL2RA as regulatory factors for Treg cell development and function. In order to investigate the association of miR-182, miR-27a, FoxO1, and IL2RA gene polymorphisms with Behçet’s disease (BD) and Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada (VKH) syndrome in a Chinese Han population, a two-stage association study was performed in 820 BD, 900 VKH patients, and 1,800 controls using polymerase chain reaction restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP) assay. In the first stage study, association analysis of 10 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) was performed in 400 BD, 400 VKH patients, and 600 controls. The results showed significantly decreased frequencies of the miR-182/rs76481776 CC genotype and C allele in BD (P = 3.36 × 10−4, OR = 0.55; P = 4.74 × 10−4, OR = 0.59) and VKH patients (P = 1.11 × 10−4, OR = 0.53; P = 1.26 × 10−4, OR = 0.56). No significant association of the other nine SNPs with BD or VKH was observed. In the second stage study, association analysis of miR-182/rs76481776 was performed in 420 BD, 500 VKH patients, and 1,200 controls. The second stage and combined studies confirmed the association of miR-182/rs76481776 with BD (CC genotype: P = 3.25 × 10−7, OR = 0.58; C allele: P = 1.81 × 10−7, OR = 0.60) and VKH (CC genotype: P = 7.89 × 10−8, OR = 0.57; C allele: P = 2.52 × 10−8, OR = 0.59). Real-time PCR analysis showed a significantly increased expression of miR-182 in TT/CT cases compared to CC cases in anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies-stimulated CD4+ T cells (P = 2.1 × 10−2). In conclusion, this study suggests that miR-182, but not miR-27a, FoxO1, and IL2RA, contributes to the genetic susceptibility of BD and VKH.
Key Message
-
MiR-182 contributes to genetic susceptibility of BD and VKH.
-
No significant association of miR-27a, FoxO1, and IL2RA with BD or VKH was observed.
-
Significantly increased expression of miR-182 in TT/CT cases compared to CC cases was observed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yang P, Fang W, Meng Q, Ren Y, Xing L, Kijlstra A (2008) Clinical features of chinese patients with Behcet's disease. Ophthalmology 115:312–318
Khairallah M, Accorinti M, Muccioli C, Kahloun R, Kempen JH (2012) Epidemiology of Behcet disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 20:324–335
Yang P, Ren Y, Li B, Fang W, Meng Q, Kijlstra A (2007) Clinical characteristics of Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome in Chinese patients. Ophthalmology 114:606–614
Gul A, Inanc M, Ocal L, Aral O, Konice M (2000) Familial aggregation of Behcet's disease in Turkey. Ann Rheum Dis 59:622–625
Jiang Z, Yang P, Hou S, Du L, Xie L, Zhou H, Kijlstra A (2010) IL-23R gene confers susceptibility to Behcet's disease in a Chinese Han population. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1325–1328
Zhou Q, Hou S, Liang L, Li X, Tan X, Wei L, Lei B, Kijlstra A, Yang P (2014) MicroRNA-146a and Ets-1 gene polymorphisms in ocular Behcet's disease and Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 73:170–176
Xavier JM, Krug T, Davatchi F, Shahram F, Fonseca BV, Jesus G, Barcelos F, Vedes J, Salgado M, Abdollahi BS et al (2013) Gene expression profiling and association studies implicate the neuregulin signaling pathway in Behcet's disease susceptibility. J Mol Med 91:1013–1023
Du L, Yang P, Hou S, Lin X, Zhou H, Huang X, Wang L, Kijlstra A (2008) Association of the CTLA-4 gene with Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome. Clin Immunol 127:43–48
Shu Q, Yang P, Hou S, Li F, Chen Y, Du L, Jiang Z (2010) Interleukin-17 gene polymorphism is associated with Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome but not with Behcet's disease in a Chinese Han population. Hum Immunol 71:988–991
Kerdiles YM, Stone EL, Beisner DR, McGargill MA, Ch'en IL, Stockmann C, Katayama CD, Hedrick SM (2010) Foxo transcription factors control regulatory T cell development and function. Immunity 33:890–904
Ouyang W, Liao W, Luo CT, Yin N, Huse M, Kim MV, Peng M, Chan P, Ma Q, Mo Y et al (2012) Novel Foxo1-dependent transcriptional programs control T(reg) cell function. Nature 491:554–559
Guttilla IK, White BA (2009) Coordinate regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast cancer cells. J Biol Chem 284:23204–23216
O'Neill LA (2010) Outfoxing Foxo1 with miR-182. Nat Immunol 11:983–984
Stittrich AB, Haftmann C, Sgouroudis E, Kuhl AA, Hegazy AN, Panse I, Riedel R, Flossdorf M, Dong J, Fuhrmann F et al (2010) The microRNA miR-182 is induced by IL-2 and promotes clonal expansion of activated helper T lymphocytes. Nat Immunol 11:1057–1062
Kelada S, Sethupathy P, Okoye IS, Kistasis E, Czieso S, White SD, Chou D, Martens C, Ricklefs SM, Virtaneva K et al (2013) miR-182 and miR-10a are key regulators of Treg specialisation and stability during Schistosome and Leishmania-associated inflammation. PLoS pathogens 9:e1003451
Mussig K, Staiger H, Machicao F, Stancakova A, Kuusisto J, Laakso M, Thamer C, Machann J, Schick F, Claussen CD et al (2009) Association of common genetic variation in the FOXO1 gene with beta-cell dysfunction, impaired glucose tolerance, and type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:1353–1360
Sun Q, Gu H, Zeng Y, Xia Y, Wang Y, Jing Y, Yang L, Wang B (2010) Hsa-mir-27a genetic variant contributes to gastric cancer susceptibility through affecting miR-27a and target gene expression. Cancer Sci 101:2241–2247
Klinker MW, Schiller JJ, Magnuson VL, Wang T, Basken J, Veth K, Pearce KI, Kinnunen L, Harjutsalo V, Wang X et al (2010) Single-nucleotide polymorphisms in the IL2RA gene are associated with age at diagnosis in late-onset Finnish type 1 diabetes subjects. Immunogenetics 62:101–107
Kawasaki E, Awata T, Ikegami H, Kobayashi T, Maruyama T, Nakanishi K, Shimada A, Uga M, Kurihara S, Kawabata Y et al (2009) Genetic association between the interleukin-2 receptor-alpha gene and mode of onset of type 1 diabetes in the Japanese population. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:947–952
Saus E, Soria V, Escaramis G, Vivarelli F, Crespo JM, Kagerbauer B, Menchon JM, Urretavizcaya M, Gratacos M, Estivill X (2010) Genetic variants and abnormal processing of pre-miR-182, a circadian clock modulator, in major depression patients with late insomnia. Hum Mol Genet 19:4017–4025
Hinks A, Cobb J, Sudman M, Eyre S, Martin P, Flynn E, Packham J, Barton A, Worthington J, Langefeld CD et al (2012) Investigation of rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility loci in juvenile idiopathic arthritis confirms high degree of overlap. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1117–1121
Li T, Wu X, Zhu X, Li J, Pan L, Li P, Xin Z, Liu Y (2011) Association analyses between the genetic polymorphisms of HNF4A and FOXO1 genes and Chinese Han patients with type 2 diabetes. Mol Cell Biochem 353:259–265
Karim MA, Craig RL, Wang X, Hale TC, Elbein SC (2006) Analysis of FOXO1A as a candidate gene for type 2 diabetes. Mol Genet Metab 88:171–177
Chen L, Yang P, Zhou H, He H, Ren X, Chi W, Wang L, Kijlstra A (2008) Diminished frequency and function of CD4 + CD25high regulatory T cells associated with active uveitis in Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 49:3475–3482
Read RW, Holland GN, Rao NA, Tabbara KF, Ohno S, Arellanes-Garcia L, Pivetti-Pezzi P, Tessler HH, Usui M (2001) Revised diagnostic criteria for Vogt–Koyanagi–Harada disease: report of an international committee on nomenclature. Am J Ophthalmol 131:647–652
Ceribelli A, Satoh M, Chan EK (2012) MicroRNAs and autoimmunity. Curr Opin Immunol 24:686–691
Zhu S, Pan W, Qian Y (2013) MicroRNA in immunity and autoimmunity. J Mol Med 91:1039–1050
Remmers E, Cosan F, Kirino Y, Ombrello M, Abaci N, Satorius C, Julie M, Yang B, Korman B, Cakiris A et al (2010) Genome-wide association study indentifies variants in the MHC class I, IL 10, and IL23R/IL12RB2 regions associated with Behçet’s disease. Nat Genet 42:698–702
Hou S, Yang Z, Du L, Jiang Z, Shu Q, Chen Y, Li F, Zhou Q, Ohno S, Chen R et al (2012) Identification of a susceptibility locus in STAT4 for Behçet’s disease in Han Chinese in a genome-wide association study. Arthritis Rheum 64:4104–4113
Kirino Y, Bertsias G, Ishigatsubo Y, Mizuki N, Tugal-Tutkun I, Seyahi E, Ozyazgan Y, Sacli F, Erer B, Inoko H et al (2013) Genome-wide association study indentifies new susceptibility loci for Behçet’s disease and epistasis between HLA-B*51 and ERAP1. Nat Genet 45:202–207
Xu S, Witmer P, Lumayag S, Kovacs B, Valle D (2007) MicroRNA (miRNA) transcriptome of mouse retina and indentification of a sensory organ-specific miRNA cluster. J Biol Chem 282:25053–25066
Shi D, Li P, Ma L, Zhong D, Chu H, Yan F, Lv Q, Qin C, Wang W, Wang M et al (2012) A genetic variant in pre-miR-27a is associated with a reduced renal cell cancer risk in a Chinese population. PLoS ONE 7:e46566
Schmied MC, Zehetmayer S, Reindl M, Ehling R, Bajer-Kornek B, Leutmezer F, Zebenholzer K, Hotzy C, Lichtner P, Meitinger T et al (2012) Replication study of multiple sclerosis (MS) susceptibility alleles and correlation of DNA-variants with disease features in a cohort of Austrian MS patients. Neurogenetics 13:181–187
Knevel R, de Rooy DP, Zhernakova A, Grondal G, Krabben A, Steinsson K, Wijmenga C, Cavet G, Toes RE, Huizinga TW et al (2013) Association of variants in IL2RA with progression of joint destruction in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 65:1684–1693
Cenit MC, Marquez A, Cordero-Coma M, Fonollosa A, Adan A, Martinez-Berriotxoa A, Llorenc V, Diaz Valle D, Blanco R, Canal J et al (2013) Evaluation of the IL2/IL21, IL2RA and IL2RB genetic variants influence on the endogenous non-anterior uveitis genetic predisposition. BMC Med Gen 14:52
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all donors enrolled in the present study. This work was supported by Natural Science Foundation Major International (Regional) Joint Research Project (81320108009), National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (2011CB510200), Key Project of Natural Science Foundation (81130019), National Natural Science Foundation Project (31370893, 81200678), Basic Research program of Chongqing (cstc2013jcyjC10001), Chongqing Key Laboratory of Ophthalmology (CSTC, 2008CA5003), National Clinical Key Department Construction Program, Key Project of Health Bureau of Chongqing (2012-1-003), and Fund for PAR-EU Scholars Program.
Conflict if interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Fig. S1
Comparison of the relative expression levels of miR-182 variants. PBMCs and LPS-stimulated PBMCs samples of 12 CC genotype, 12 CT and TT genotype of rs76481776 were freshly obtained from healthy controls in the study (GIF 10 kb)
Fig. S2
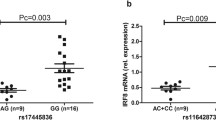
The influence of various rs76481776 genotypes on expression of FoxO1. Purified CD4+ T cells and anti-CD3/CD28 antibodies-stimulated CD4+ T cells of 12 CC genotypes, 8 CT and TT genotypes of rs76481776 were freshly obtained from healthy controls in the study (GIF 19 kb)
ESM 1
(DOC 220 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, H., Liu, Y., Bai, L. et al. Predisposition to Behçet’s disease and VKH syndrome by genetic variants of miR-182. J Mol Med 92, 961–967 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1159-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-014-1159-9