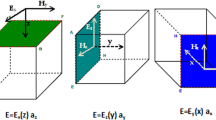
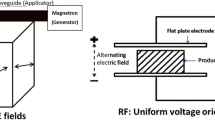
Abstract
The research aimed to establish whether dielectric heating of wood at high frequency could be accomplished fast, without excessive temperature fluctuations and no wood degrade. The intention was to develop optimized dielectric heating schedules in order to effectively pasteurize green timbers and logs for export—an eco-friendly substitute to currently used toxic chemical method. Data analysis revealed that the electric field distribution within the specimen was a strong function of its dielectric properties. Specifically, homogeneous moisture contents generated constant electric field values while heterogeneous distributions generated sudden drops and raises of the electric field strength with heating uniformly dispersed due to a fast redistribution from hot to colder areas. Convection losses through air contact may reduce the average heating rate of the timber shell by about 50%.
Zusammenfassung
In dieser Studie wurde untersucht, ob Hochfrequenzerhitzung von Holz schnell und ohne übermäßige Temperaturschwankungen und ohne Beeinträchtigung der Holzqualität durchgeführt werden kann. Ziel war es, ein optimiertes Erhitzungsprogramm zur effektiven phytosanitären Behandlung von für den Export bestimmtem Schnitt- und Rundholz zu entwickeln – als umweltfreundliche Alternative zu den gegenwärtig verwendeten toxischen chemischen Verfahren. Die Versuchsergebnisse zeigten, dass die Verteilung des elektrischen Feldes im Prüfkörper stark von dessen dielektrischen Eigenschaften abhing. Eine homogene Holzfeuchte ergab konstante elektrische Feldwerte. Eine heterogene Holzfeuchteverteilung führte zu plötzlichen Ab- und Anstiegen der elektrischen Feldstärke, jedoch wegen einer schnellen Umverteilung zwischen heißen und kalten Bereichen zu einer gleichmäßigen Aufheizung. Wärmeverluste durch Luftkontakt können die mittlere Aufheizrate der Schnittholzoberfläche um bis zu 50 % verringern.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avramidis S, Liu F, Neilson BJ (1994) Radio-frequency/vacuum drying of softwoods: drying of thick western red cedar with constant electrode voltage. For Prod J 44(1):41–47
Constant T, Moyne C, Perré P (1996) Drying with internal heat generation: theoretical aspects and application to microwave heating. AIChE J 42(2):359–368
Elustondo D, Avramidis S, Zwick R (2005) The demonstration of increased lumber value using optimized lumber sorting and radio frequency vacuum drying. For Prod J 55(1):76–83
Halbach K, Holsinger RF (1976) Superfish—a computer program for evaluation of RF cavities with cylindrical symmetry. Part Accel 7:213–222
Jiao S, Tang J, Johnson JA, Tiwari G, Wang S (2010) Determining radio frequency heating uniformity in mixed beans for disinfestations. In: Proceedings of 2010 IMPI 44th annual microwave power symposium, 14–16 July 2010, Denver, Colorado, USA
Johnson JA, Wang S, Tang J (2010) Radio frequency treatments for insect disinfestation of dried legumes. In: Proceedings of 10th international working conference on stored product protection (IWCSPP), June 27–July 2, 2010, Estoril, Portugal, 20 p
Lazarescu C, Avramidis S (2011) Radio—frequency heating kinetics of softwood logs. Dry Technol 29(6):673–681
Lazarescu C, Dale A, Uzunovic A, Breuil C, Avramidis S (2010) Radio frequency heating pasteurization of pine wood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus) infected wood. Eur J Wood Prod. doi:10.1007/s00107-010-0515-x
Lazarescu C, Plattner A, Hart F, Breuil C, Avramidis S (2009) Pasteurization of hemlock by radio frequency heating: a preliminary study. For Prod J 59(4):79–83
Norimoto M (1976) Dielectric properties of wood. Wood Res 59/60:106–152
Norimoto M, Hayashi S, Yamada T (1971) Anisotropy of dielectric constant in coniferous wood. Holzforschung 51:12–32
Norimoto M, Hayashi S, Yamada T (1978) Anisotropy of dielectric constant in coniferous wood. Holzforschung 32:167–172
Peyskens E, de Pourcq M, Stevens M, Schalck J (1984) Dielectric properties of softwood species at microwave frequencies. Wood Sci Technol 18(4):267–280
Resch H (2006) High-frequency electric current for drying of wood—historical perspectives. Maderas Cienc Tecnol 8(2):67–82
Salas WA, Ranson KJ, Rock BN, Smith KT (1994) Temporal and spatial variations in dielectric constant and water status of dominant forest species from New England. Remote Sens Environ 47:109–119
Skaar C (1948) The dielectric properties of wood at several radio frequencies. Technical publication Nr 69, New York State, Syracuse
Torgovnikov GI (1993) Dielectric properties of wood and wood-based materials. Springer, Berlin, 194 pp
USDA (1999) Wood handbook. Wood as an engineering material. US Dept agric. General technical report FPL-GTR-113, Chapter 3–22
Venkateswaran A (1972) A comparison of the electrical properties of milled wood, milled wood cellulose and milled wood lignin. Wood Sci 4(4):248–253
Zhou B, Avramidis S (1999) On the loss factor of wood during radio frequency heating. Wood Sci Technol 33(4):299–310
Acknowledgements
This work is financially supported by a Strategic Grant from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council (NSERC) of Canada. The input regarding the experimental design and technical information about the RF-heating by Dr. Terry Enegren is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazarescu, C., Avramidis, S. Heating characteristics of western hemlock (Tsuga heterophylla) in a high frequency field. Eur. J. Wood Prod. 70, 489–496 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-011-0579-2
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00107-011-0579-2