Background and Purpose:
Recurrences of glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) within previously irradiated volumes pose a serious therapeutic challenge. This retrospective study evaluates the long-term tumor control of recurrent GBM treated with interstitial high-dose-rate brachytherapy (HDR-BRT).
Patients and Methods:
Between 1995 and 2003, 84 patients were treated for recurrent cerebral GBM located within previously irradiated volumes. All patients had received adjuvant external radiotherapy following primary surgery, with a focal dose up to 60 Gy. The median recurrent tumor volume was 51 cm3 (3–207cm3), and the HDR-BRT consisted of an afterloading 192Ir implant which delivered a median dose of 40 Gy (30–50 Gy). Catheter implantation was implemented using interactive computed tomography (CT) guidance under local anesthesia and sedoanalgesia.
Results:
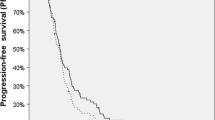
After a median follow-up of 61 months, 5/84 patients (6%) were alive. The median post-BRT survival was 37 weeks, and the median overall survival 78 weeks. Moderate to severe complications occurred in 5/84 cases (6%).
Conclusion:
For patients with recurrences of GBM within previously irradiated volumes, CT-guided interstitial HDR-BRT is a feasible treatment option that can play an important role in providing palliation.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Glioblastoma-multiforme-(GBM-)Rezidive innerhalb vorbestrahlter Volumina stellen eine therapeutische Herausforderung dar. Ziel dieser Studie ist die Vorstellung der CT-gestützten interstitiellen High-Dose-Rate-Brachytherapie (HDRBRT) bei der Behandlung zerebraler GBM-Rezidive.
Patienten und Methodik:
Von 1995 bis 2003 wurden insgesamt 84 Patienten mit rezidiviertem GBM mittels interstitieller HDR-BRT behandelt. Alle Patienten waren voroperiert und hatten im Rahmen der Primärtherapie eine adjuvante perkutane Teilhirnbestrahlung bis 60 Gy erhalten. In der Rezidivsituation erhielten alle eine fraktionierte interstitielle 192Ir-HDR-BRT bis zu einer medianen Gesamtdosis von 40 Gy (30–50 Gy). Die Implantation der BRT-Katheter wurde bei einem medianen Tumorvolumen von 51 cm3 (3–207 cm3) unter CT-Kontrolle in Sedoanalgesie und Lokalanästhesie durchgeführt.
Ergebnisse:
Bei einer medianen Nachbeobachtung von 61 Monaten betrug das mediane Überleben 37 Wochen vom Zeitpunkt der Brachytherapie sowie 78 Wochen ab Diagnosestellung. Moderate bis schwerwiegende Komplikationen ereigneten sich in 5/84 Fällen (6%).
Schlussfolgerung:
Die CT-gestützte interstitielle HDR-BRT ist ein wertvolles Instrument für die palliative Behandlung von Patienten mit rezidiviertem GBM.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tselis, N., Kolotas, C., Birn, G. et al. CT-Guided Interstitial HDR Brachytherapy for Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme. Strahlenther Onkol 183, 563–570 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1721-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-007-1721-2