Abstract
Purpose
The evaluation of carotid-cavernous fistulas (CCFs) and the intracranial vasculature has been predominantly carried out using conventional digital subtraction angiography (DSA). Recent developments in time-resolved magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) provide the opportunity to assess both multiple arterial and venous phases with high temporal and spatial resolution. Here, we investigated the feasibility of this technique to functionally assess CCF prior to intervention.
Methods
Six consecutive patients with clinical symptoms of a CCF were scheduled for clinically indicated MRA and underwent a protocol that comprised conventional imaging sequences and high resolution time-resolved MRA with interleaved stochastic trajectories (TWIST). The location of the fistulous communication, the flow pattern, and venous drainage were determined by time-resolved MRA and compared with DSA which was available in five out of six patients.
Results
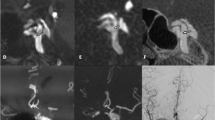
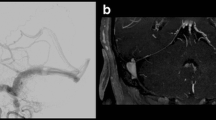
Typical morphological findings (including enlargement of the superior ophthalmic vein, exophthalmos) were found in all cases in both conventional MRI and time-resolved MRA source data. The temporal resolution of time-resolved MRA enabled a good separation of the early filling of the cavernous sinus during the arterial phase. Direct fistulous communication was assessed in three patients with good correlation to DSA, whereas indirect CCF could not definitely be visualized. The time-resolved MRA provided information about the flow pattern and the venous drainage of the fistula in all patients, which is essential for therapy planning.
Conclusion
Time-resolved MRA provides important morphological and functional information in patients with CCF. Although DSA remains the gold standard for diagnosis and exact classification of fistulas, time-resolved MRA can provide the relevant hemodynamic information to plan interventional treatment as a one-step procedure with a focused diagnostic workup.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Debrun GM. Angiographic workup of a carotid cavernous sinus fistula (CCF) or what information does the interventionalist need for treatment? Surg Neurol. 1995;44(1):75–9.
Ringer AJ, Salud L, Tomsick TA. Carotid cavernous fistulas: anatomy, classification, and treatment. Neurosurg Clin North Am. 2005;16(2):279–95.
Barrow DL, Spector RH, Braun IF, Landman JA, Tindall SC, Tindall GT. Classification and treatment of -cavernous sinus fistulas. J Neurosurg. 1985;62(2):248–56.
Gemmete JJ, Ansari SA, Gandhi DM. Endovascular techniques for treatment of carotid-cavernous fistula. J neuro-ophthalmology: Off J North Am Neuro-Ophthalmology Soc. 2009;29(1):62–71.
Ellis JA, Goldstein H, Connolly ES Jr., Meyers PM. Carotid-cavernous fistulas. Neurosurg Focus. 2012;32(5):E9.
Kramer U, Ernemann U, Fenchel M, Seeger A, Laub G, Claussen CD et al. Pretreatment evaluation of peripheral vascular malformations using low-dose contrast-enhanced time-resolved 3D MR angiography: initial results in 22 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2011;196(3):702–11.
Unlu E, Temizoz O, Albayram S, Genchellac H, Hamamcioglu MK, Kurt I et al. Contrast-enhanced MR 3D angiography in the assessment of brain AVMs. Eur J Radiol. 2006;60(3):367–78.
Stracke CP, Spuentrup E, Reinacher P, Thron A, Krings T. Time Resolved 3D MRA. Applications for Interventional Neuroradiology. Interv Neuroradiol: J Peritherapeutic Neuroradiol, Surg Proced Relat Neurosci. 2006;12(3):223–31.
Vattoth S, Cherian J, Pandey T. Magnetic resonance angiographic demonstration of carotid-cavernous fistula using elliptical centric time resolved imaging of contrast kinetics (EC-TRICKS). Magn Reson Imaging. 2007;25(8):1227–31.
Lim RP, Shapiro M, Wang EY, Law M, Babb JS, Rueff LE et al. 3D time-resolved MR angiography (MRA) of the carotid arteries with time-resolved imaging with stochastic trajectories: comparison with 3D contrast-enhanced Bolus-Chase MRA and 3D time-of-flight MRA. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008;29(10):1847–54.
Meyers PM, Halbach VV, Dowd CF, Lempert TE, Malek AM, Phatouros CC et al. Dural carotid cavernous fistula: definitive endovascular management and long-term follow-up. Am J Ophthalmol. 2002;134(1):85–92.
Coskun O, Hamon M, Catroux G, Gosme L, Courtheoux P, Theron J. Carotid-cavernous fistulas: diagnosis with spiral CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000;21(4):712–6.
Korkmazer B, Kocak B, Tureci E, Islak C, Kocer N, Kizilkilic O. Endovascular treatment of carotid cavernous sinus fistula: A systematic review. World J Radiol. 2013;5(4):143–55.
Halbach VV, Hieshima GB, Higashida RT, Reicher M. Carotid cavernous fistulae: indications for urgent treatment. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1987;149(3):587–93.
Gemmete JJ, Chaudhary N, Pandey A, Ansari S. Treatment of carotid cavernous fistulas. Curr Treat Options Neurol. 2010;12(1):43–53.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Data
Supplementary Data
The supplementary movies show the time-resolved MRA of patient 3 in coronal angulation (ESM_1) and sagittal angulation (ESM_2) as well as transversal reconstructions (ESM_3) and MIP reconstructions (ESM_4).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no actual or potential conflicts of interest in relation to this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seeger, A., Kramer, U., Bischof, F. et al. Feasibility of Noninvasive Diagnosis and Treatment Planning in a Case Series with Carotid-Cavernous Fistula using High-Resolution Time-Resolved MR-Angiography with Stochastic Trajectories (TWIST) and Extended Parallel Acquisition Technique (ePAT 6) at 3 T. Clin Neuroradiol 25, 241–247 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0298-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00062-014-0298-2