Abstract
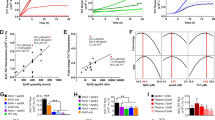
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) affects 10% of people older than 65 and is characterized by a progressive loss of cognitive function with an abnormal accumulation of amyloid β (Aβ) plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFT) in the brain. Efforts to reduce brain Aβ plaques continue to be investigated as a therapeutic approach for AD. We report here development of dual targeting agents with affinity for Aβ plaque/P-glycoprotein (Pgp) and Aβ plaque/α4β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChR). These novel dual agents may be able to efflux Aβ plaques via the paravascular (glymphatic) pathways. Ferulic acid (FA), ferulic acid ethyl ester (FAEE), and curcumin (CUR) were used for Aβ plaques, fexofenadine (FEX) was used as substrate for Pgp and nifrolidine (NIF) was used for α4β2* nAChRs. Aβ plaque/α4β2* nAChR dual agent, FA-NIF (GKS-007) exhibited IC50 = 3–6 nM for α4β2* nAChRs in [3H]cytisine-radiolabeled thalamus and frontal cortex in rat brain slices. In postmortem human AD frontal cortex, Aβ plaques labeled with [3H]PIB, FEX-CUR showed a 35% reduction in gray matter (GM)/white matter (WM) [3H]PIB binding, while CUR alone showed a 50% reduction. In vivo biodistribution studies are required of the Aβ−Pgp and Aβ-α4β2* nAChRs dual targeting agents in order to evaluate their potential as therapeutic approaches for reducing brain Aβ plaques.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aller SG, Yu J, Ward A, Weng Y, Chittaboina S, Zhuo R, Harrell PM, Trinh YT, Zhang Q, Urbatsch IL, Chang G (2009) Structure of P-glycoprotein reveals a molecular basis for poly-specific drug binding. Science 323:1718–1722
Ariza M, Kolb HC, Moechars D, Rombouts F, Andres JI (2015) Tau positron emission tomography (PET) imaging: past, present, and future. J Med Chem 58:4365–4382
Braak H, Braak E (1991) Neuropathological staging of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol 82:239–259
Bartels AL (2011) Blood brain barrier P-glycoprotein function in neurodenerative disease. Curr Pharm Des 17:2771–2777
Baranwal A, Patel HH, Mukherjee J (2014) [18F]Fluorodeoxyglycosylamines: Maillard reaction of 18F-FDG with biological amines. J Label Compds Radiopharm 57:86–91
Barten DM, Albright CF (2008) Therapeutic strategies for Alzheimer’s disease. Mol Neurobiol 37:171–186
Bacyinski A, Xu M, Wang W, Hu J (2017) The paravascular pathway for brain waste clearance: current understanding, significance and controversy. Front Neuroanat 11:101
Brendel M, Jaworska A, Greissinger E, Rotzer C, Burgold S, Gildehaus FJ, Carlsen J, Cumming P, Baumann K, Haass C, Steiner H, Bartenstein P, Hems J, Rominger A (2015) Cross-sectional comparison of small animal [18F]florbetaben amyloid-PET between transgenic AD mouse models. PLoS ONE 10(2):e0116678
Chattopadhyay S, Xue B, Pichika R, Collins D, Bagnera R, Leslie FM, Christian BT, Shi B, Narayanan TK, Potkin SG, Mukherjee J (2005) Synthesis and evaluation of nicotine α4β2 receptor ligand, 5-(3’-fluoropropyl)-3-(2-(S)-pyrrolidinyl)methoxy)pyridine (18F-nifrolidine) in rodents and imaging by PET in non-human primate. J Nucl Med 46:130–140
Coleman RA, Liang C, Patel R, Ali S, Mukherjee J (2017) Brain and brown adipose tissue metabolism in Tg 2576 transgenic mice models of Alzheimer’s disease assessed using 18F-FDG PET. Mol Imag 16:1–9
Deane R, Bell RD, Sagare A, Zlokovic BV (2009) Clearance of amyloid-b peptide across the blood-brain barrier: Implications for therapies in Alzheimer’s disease. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 8:16–30
Doody RS, Thomas RG, Farlow MD (2014) Phase 3 trials of solanezumab for mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. N Engl J Med 370:311–321
Filser S, Ovsepian SV, Masana M, Blazquez-Llorca L, Brandt Elvang A, Volbracht C, Muller MB, Jung CK, Hems J (2015) Pharmacological inhibition of BACE1 impairs synaptic plasticity and cognitive functions. Biol Psych 77:729–739
Garcia-Alloza M, Borrelli LA, Rozkalne B, Hyman T, Bacskai BJ (2007) Curcumin labels amyloid pathology in vivo, disrupts existing plaques, and partially restores distorted neurites in an Alzheimer’s mouse model. J Neurochem 102:1095–1104
Gerenu G, Liu K, Chojnacki JE et al. (2015) Curcumin/melatonin hybrid 5-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-3-oxo-pentanoic acid [2-(5-methoxy-1H-indol-3-yl)-ethyl]-amide ameliorates AD-like pathology in the APP/PS1 mouse mode. ACS Chem Neurosci 6:1393–1399
Hu S, Maiti P, Ma X, Jones MR, Cole GM, Frautschy SA (2015) Clinical development of curcumin in neurodegenerative disease. Expert Rev Neurother 15:629–637
Jessen NA, Munk AS, Lundgaard I, Nedergaard M (2015) The glymphatic system: a beginners guide. Neurochem Res 40:2583–2599
Krishnamurthy S, Tichenor MD, Satish AG, Lehman DB (2014) A proposed role for efflux transporters in the pathogenesis of hydrocephalus. Croat Med J 55:66–76
Leinenga G, Gotz J (2015) Scanning ultrasound removes amyloid-beta and restores memory in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Sci Transl Med 7(278):278ra33
Mancuso C, Santangelo R (2014) Pharmacological and toxicological aspects. Food Chem Toxicol 65:185–195
Moghbel MC, Saboury B, Basu S, Metzler SD, Torigian DA, Langstrom B, Alavi A (2012) Amyloid-b imaging with PET in Alzheimer’s disease: is it feasible with current radiotracers and technologies? Eur J Nucl Mol Imag 39:202–208
Mukherjee J, Lao P, Betthauser T, Samra GK, Pan ML, Patel IH, Liang C, Metherate R, Christian BT (2018) Human brain imaging of nicotinic acetylcholine α4β2* receptors using [18F]Nifene: selectivity, functional activity, toxicity, aging effects, gender effects and extrathalamic pathways. J Comp Neurol 526:80–96
Pan ML, Mukherjee MT, Patel HH, Patel B, Constantinescu CC, Mirbolooki MR, Liang C, Mukherjee J (2016) Evaluation of [11C]TAZA for amyloid Aβ plaque imaging in postmortem Alzheimer’s disease brain region and whole body distribution in rodent PET/CT. Synapse 70:163–176
Pahnke J, Wolkenhauer O, Krohn M, Walker LC (2008) Clinico-pathologic function of cerebral ABC transporters-implications for the pathogenesis of Alzheimers disease. Curr Alzheimers Res 5:396–405
Posadas I, Lopez-Hernandez B, Cena V (2013) Nicotinic receptors in neurodegeneration. Curr Neuropharmacol 11:298–314
Pichika R, Easwaramoorthy B, Christian BT, Shi B, Narayanan TK, Collins D, Mukherjee J (2011) Nicotine α4β2 receptor imaging agents. Part III. Synthesis and evaluation of 18F-Nifzetidine in rodents and imaging by PET in non-human primate. Nucl Med Biol 38:1183–1192
Pichika R, Kuruvilla SA, Patel N, Vu K, Sinha S, Easwaramoorthy B, Narayanan TK, Shi B, Christian B, Mukherjee J (2013) Nicotine α4β2 receptor imaging agents. Part IV. Synthesis and evaluation of 18F-nifrolene in rodents and non-human primate by PET imaging. Nucl Med Biol 40:117–125
Pi R, Mao X, Chao X, Cheng Z, Liu M, Duan XX, Ye M, Chen X, Mei Z, Liu P, Li W, Han Y (2012) Tacrine-6-ferulic acid, a novel multifunctional dimer, inhibits amyloid-β mediated Alzheimer’s disease associated pathogenesis in vitro and in vivo. PLoS ONE 7:e31921
Qosa H, Abuznait AH, Hill RA, Kaddoumi A (2012) Enhanced brain amyloid beta clearance by rifamycin and caffeine as a possible protective mechanism against Alzheimers disease. J Alz Dis 31:151–156
Ryu EK, Choe YS, Lee K, Choi Y, Kim B (2006) Curcumin and dehydrozingerone derivatives: synthesis, radiolabeling, and evaluation for β-amyloid plaque imaging. J Med Chem 49:6111–6119
Salloway S, Sperling R, Fox NC, Bapineuzumab 301 and 302 Clinical Trial Investigators (2014) Two phase 3 trials of bapineuzumab in mild-to-moderate Alzheimers disease. N Engl J Med 370:322–333
Samra GK, Intskirveli I, Govind AP, Liang C, Lazar R, Green WN, Metherate R, Mukherjee J (2018) Development of fluorescent probes for imaging α4β2* nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 28:371–377
Schenk D, Barbour R, Dunn W et al. (1999) Immunization with amyloid-beta attenuates Alzheimer’s disease like pathology in the PDAPP mouse. Nature 402:537–540
Siemers ER, Sundell KL, Carlson C, Case M, Sethuraman G, Liu-Seifert H, Dowsett SA, Pontecorvo MJ, Dean RA, Demattos R (2016) Phase 3 solanezumab trials: secondary outcomes in mild Alzheimer’ disease patients. Alzheimers Dement 12:110–120
Sultana R (2012) Ferulic acid ethyl ester as a potential therapy in neurodegenerative disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1822:748–752
Sgarbossa A, Giacomazza D, Di Carlo M (2015) Ferulic acid: a hope for Alzheimer’s disease therapy from plants. Nutrients 7:5764–5782
Syvanen S, Eriksson (2013) Advances in PET imaging of P-glycoprotein function at the blood-brain barrier. ACS Chem Neurosci 4:225–237
Tahara H, Kusuhara H, Fuse E, Sugiyama Y (2005) P-glycoprotein plays a major role in the efflux of fexofenadine in the small intestine and blood brain barrier, but only a limited role in its biliary excretion. Drug Metab Dis 33:963–968
Tampellini D (2015) Synaptic activity and Alzheimer’s disease: a critical update. Front Neurosci 9:423
Vassar R (2014) BACE1 inhibitor drugs in clinical trials for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res & Ther 6:89
Venigalla M, Sonego S, Gyengesi E, Sharman MJ, Munch G (2016) Novel promising therapeutics against chronic inflammation and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Int 95:63–74
Vlaming MLH, Lappchen T, Jansen HT et al. (2015) PET-CT imaging with [18F]-gefitinib to measure Abcd1a/1b (P-gp) and Abcg2 (Bcrp1) mediated drug-drug interactions at the murine blood-brain barrier. Nucl Med Biol 42:833–841
Yan J-J, Jung J-S, Kim T-K, Hasan MA, Hong C-W, Nam J-S, Song D-K (2013) Protective effects of ferulic acid in amyloid precursor protein plus presenilin-1 transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Biol Pharm Bull 36:140–143
Zhao R, Kalvass C, Yanni SB, Bridges AS, Pollack GM (2009) Fexofenadine brain exposure and the influence of blood brain barrier P-glycoprotein after fexofenadine and terfenadine administration. Drug Metab Disp 37:529–535
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by a grant from NIH/NIA AG029479 (J.M.). We like to thank Banner Sun Health Research Institute, Sun City, Arizona for the postmortem human brain tissue samples, and Christopher Liang for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Samra, G.K., Dang, K., Ho, H. et al. Dual targeting agents for Aβ plaque/P-glycoprotein and Aβ plaque/nicotinic acetylcholine α4β2* receptors—potential approaches to facilitate Aβ plaque removal in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Med Chem Res 27, 1634–1646 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2178-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-018-2178-9