Abstract
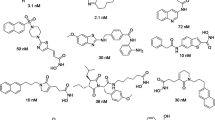
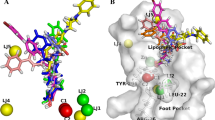
The World Cancer Report 2014 shows that cancer is a leading cause of death globally, and cancer related death is likely to go up by about 70 % in the next two decades. Among several target receptors of cancer, histone deacetylases are the promising therapeutic target for many cancers. The current study deals with a primary goal of identification of novel non-hydroxamic acid histone deacetylase 8 inhibitors. In this context, six featured pharmacophoric hypotheses with hydrogen bond acceptors (A), hydrogen bond donor (D), and aromatic ring (R) were generated using 36 reported histone deacetylase 8 inhibitors. Virtual screening of database using two pharmacophore hypothesis AAAADR.161 and AAADDR.189 resulted 2000 hits each having fitness score >1.503. The pharmacophore AAADDR.189 yielded statistically significant three-dimensional quantitative structure-activity relationship model with training set (R 2: 0.9756, SD: 0.0680, F: 151.6, N: 26) and test set (Q 2: 0.6922, Pearson R: 0.8705, N: 10) molecules. The R 2 pred value of the model was 0.6951, which confirmed the good predictive ability of the model for external data set. Hits resulted from virtual screening and known inhibitors were subjected to molecular docking study to identify the binding affinity of inhibitors with active site amino acid residues. Finally, absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion study were undertaken to determine the drug likeness properties of identified hits. On the basis of fitness score, predicted activities, XP Glide score, interacting amino acid residues of known inhibitors and absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion properties, ten structurally diverse hits are reported in this paper as potential histone deacetylase 8 inhibitors which reduce the cost of histone deacetylase 8 inhibitor discovery and enhance the process prior synthesis.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balasubramanian S, Ramos J, Luo W, Sirisawad M, Verner E, Buggy JJ (2008) A novel histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8)-specific inhibitor PCI-34051 induces apoptosis in T-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 22:1026–1034
Boyd DB (1990) Successes of computer-assisted molecular design, in: Reviews in computational chemistry, vol 4. VCH, New York, pp 355–371
Debnath S, Nath P, Nath RK (2014) Identification of novel HDAC8 inhibitors using pharmacophore based virtual screening, 3D QSAR and molecular docking approach. Am. J PharmTech Res 4:253–267
Debnath T, Majumder S, Arunasree MK, Aparna V, Debnath S (2015) Identification of potent histone deacetylase 8 inhibitors using pharmacophore based virtual screening, 3D QSAR and docking study. Res Rep Med Chem 5:21–39
Di Marcotullio L, Canettieri G, Infante P, Greco A, Gulino A (2011) Protected from the inside: endogenous histone deacetylase inhibitors and the road to cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 18:241–252
Dixon SL, Smondyrev AM, Knoll EH, Rao SN, Shaw DE, Friesner RA (2006) PHASE: a new engine for pharmacophore perception, 3D QSAR model development, and 3D database screening. 1. Methodology and preliminary results. J Comput Aided Mol Des 20:647–671
Dowling DP, Gantt SL, Gattis SG, Fierke CA, Christianson DW (2008) Structural studies of human histone deacetylase 8 and its site-specific variants complexed with substrate and inhibitors. Biochemistry 47:13554–13563
Feng JH, Jing FB, Fang H, Gu LC, Xu WF (2011) Expression, purification, and S-nitrosylation of recombinant histone deacetylase 8 in Escherichia coli. Biosci Trends 5:17–22
Finnin MS, Donigian JR, Cohen A, Richon VM, Rifkind RA, Marks PA, Breslow R, Pavletich NP (1999) Structures of a histone deacetylase homologue bound to the TSA and SAHA inhibitors. Nature 401:188–93
Friesner RA, Banks JL, Murphy RB, Halgren TA, Klicic JJ, Mainz DT, Repasky MP, Knoll EH, Shelley M, Perry JK, Shaw DE, Francis P, Shenkin PS (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 1. Method and assessment of docking accuracy. J Med Chem 47:1739–1749
Friesner RA, Murphy RB, Repasky MP, Frye LL, Greenwood JR, Halgren TA, Sanschagrin PC, Mainz DT (2006) Extra precision glide: docking and scoring incorporating a model of hydrophobic enclosure for protein-ligand complexes. J Med Chem 49:6177–6196
Giannini G, Marzi M, Pezzi R, Brunetti T, Battistuzzi G, Marzo MD, Cabri W, Vesci L, Pisano C (2009) N-Hydroxy-(4-oxime)-cinnamide: a versatile scaffold for the synthesis of novel histone deacetylase [correction of deacetilase] (HDAC) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:2346–2349
Gryder BE, Rood MK, Johnson KA, Patil V, Raftery ED, Yao LP, Rice M, Azizi B, Doyle DF, Oyelere AK (2013) Histone deacetylase inhibitors equipped with estrogen receptor modulation activity. J Med Chem 56:5782–5796
Gryder BE, Sodji QH, Oyelere AK (2012) Targeted cancer therapy: giving histone deacet7ylase inhibitors all they need to succeed. Future Med Chem 4:505–524
Halgren TA, Murphy RB, Friesner RA, Beard HS, Frye LL, Pollard WT, Banks JL (2004) Glide: a new approach for rapid, accurate docking and scoring. 2. Enrichment factors in database screening. J Med Chem 47:1750–1759
Huang WJ, Chen CC, Chao SW, Yu CC, Yang CY, Guh JH, Lin YC, Kuo CI, Yang P, Chang CI (2011) Synthesis and evaluation of aliphatic-chain hydroxamates capped with osthole derivatives as histone deacetylase inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 46:4042–4049
Islam S (2011) Study on the inhibition mechanism of histone deacetylases by design of inhibitors with various functional groups, Dissertation [http://hdl.handle.net/10228/4887] Kyushu Institute of Technology Academic Repository, Japan.
Kim HJ, Bae SC (2011) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: molecular mechanisms of action and clinical trials as anti-cancer drugs. Am J Transl Res 3:166–179
Krennhrubec K, Marshall BL, Hedglin M, Verdin E, Ulrich SM (2007) Design and evaluation of “Linkerless” hydroxamic acids as selective HDAC8 inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 17:2874–2878
Liu T, Kapustin G, Etzkorn FA (2007) Design and synthesis of a potent histone deacetylase inhibitor. J Med Chem 50:2003–2006
Mulder GJ, Meerman JH (1983) Sulfation and glucuronidation as competing pathways in the metabolism of hydroxamic acids: the role of N,O-sulfonation in chemical carcinogenesis of aromatic amines. Environ Health Perspect 49:27–32
Oehme I, Deubzer HE, Wegener D, Pickert D, Linke JP, Hero B, Kopp-Schneider A, Westermann F, Ulrich SM, von Deimling A, Fischer M, Witt O (2009) Histone deacetylase 8 in neuroblastoma tumorigenesis. Clin Cancer Res 15:91–99
Ortore G, Di Colo F, Martinelli A (2009) Docking of hydroxamic acids into HDAC1 and HDAC8:a rationalization of activity trends and selectivities. J Chem Inf Model 49:2774–2785
Robey RW, Chakraborty AR, Basseville A, Luchenko V, Bahr J, Zhan Z, Bates SE (2011) Histone deacetylase inhibitors: emerging mechanisms of resistance. Mol Pharm 8:2021–2031
Roy DR, Sarkar U, Chattaraj PK, Mitra A, Padmanabhan J, Parthasarathi R, Subramanian V, Van Damme S, Bultinck P (2006) Analyzing toxicity through electrophilicity. Mol Divers 10:119–131
San Juan AA, Cho SJ (2007) 3D-QSAR study of microsomal prostaglandin E2 synthase (mPGES-1) inhibitors. J Mol Model 13:601–610
Sodji QH, Patil V, Kornacki JR, Mrksich M, Oyelere AK (2013) Synthesis and structure-activity relationship of 3-hydroxypyridine-2-thione-based histone deacetylase inhibitors. J Med Chem 56:9969–9981
Somoza JR, Skene RJ, Katz BA, Mol C, Ho JD, Jennings AJ, Luong C, Arvai A, Buggy JJ, Chi E, Tang J, Sang BC, Verner E, Wynands R, Leahy EM, Dougan DR, Snell G, Navre M, Knuth MW, Swanson RV, McRee DE, Tari LW (2004) Structural snapshots of human HDAC8 provide insights into the class I histone deacetylases. Structure 12:1325–1334
Song J, Noh JH, Lee JH, Eun JW, Ahn YM, Kim SY, Lee SH, Park WS, Yoo NJ, Lee JY, Nam SW (2005) Increased expression of histone deacetylase 2 is found in human gastric cancer. APMIS 113:264–268
Tang H, Wang XS, Huang XP, Roth BL, Butler KV, Kozikowski AP, Jung M, Tropsha A (2009) Novel inhibitors of human histone deacetylase (HDAC) identified by QSAR modeling of known inhibitors, virtual screening, and experimental validation. J Chem Inf Model 49:461–476
Tetko IV, Tanchuk VY, Villa AE (2001) Prediction of n-octanol/water partition coefficients from PHYSPROP database using artificial neural networks and E-state indices. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 41:1407–1421
Thangapandian S, John S, Lee Y, Kim S, Lee KW (2011) Dynamic structure-based pharmacophore model development: a new and effective addition in the histone deacetylase 8 (HDAC8) inhibitor discovery. Int J Mol Sci 12:9440–9462
Thangapandian S, John S, Sakkiah S, Lee KW (2010) Ligand and structure based pharmacophore modeling to facilitate novel histone deacetylase 8 inhibitor design. Eur J Med Chem 45:4409–4417
Thangapandian S, John S, Sakkiah S, Lee KW (2010) Docking-enabled pharmacophore model for histone deacetylase 8 inhibitors and its application in anti-cancer drug discovery. J Mol Graph Model 29:382–395
Thurn KT, Thomas S, Moore A, Munster PN (2011) Rational therapeutic combinations with histone deacetylase inhibitors for the treatment of cancer. Future Oncol 7:263–283
Vannini A, Volpari C, Gallinari P, Jones P, Mattu M, Carfí A, De Francesco R, Steinkühler C, Di Marco S (2007) Substrate binding to histone deacetylases as shown by the crystal structure of the HDAC8-substrate complex. EMBO Rep 8:879–884
Vassiliou S, Mucha A, Cuniasse P, Georgiadis D, Lucet-Levannier K, Beau F, Kannan R, Murphy G, Knaeuper V, Rio MC, Basset P, Yiotakis A, Dive V (1999) Phosphinic pseudo-tripeptides as potent inhibitors of matrix metalloproteinases: a structure-activity study. J Med Chem 42:2610–2620
Veerasamy R, Rajak H, Jain A, Sivadasan S, Varghese CP, Agrawal RK (2011) Int J Drug Design Discov 2: 511–519.
Vijayakumar B, Umamaheswari A, Puratchikody A, Velmurugan D (2011) Selection of an improved HDAC8 inhibitor through structure-based drug design. Bioinformation 7:134–141
Wang H, Yu N, Song H, Chen D, Zou Y, Deng W, Lye PL, Chang J, Ng M, Sun ET, Sangthongpitag K, Wang X, Wu X, Khng HH, Fang L, Goh SK, Ong WC, Bonday Z, Stünkel W, Poulsen A, Entzeroth M (2009) N-Hydroxy-1,2-disubstituted-1H-benzimidazol-5-yl acrylamides as novel histone deacetylase inhibitors: design, synthesis, SAR studies, and in vivo anti-tumor activity. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:1403–1408
Whitehead L, Dobler MR, Radetich B, Zhu Y, Atadja PW, Claiborne T, Grob JE, McRiner A, Pancost MR, Patnaik A, Shao W, Shultz M, Tichkule R, Tommasi RA, Vash B, Wang P, Stams T (2011) Human HDAC isoform selectivity achieved via exploitation of the acetate release channel with structurally unique small molecule inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 19:4626–4634
Zhang Y, Feng J, Liu C, Fang H, Xu W (2011) Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of tyrosine-based hydroxamic acid analogs as novel histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 19:4437–4444
Zhang Y, Feng J, Liu C, Zhang L, Jiao J, Fang H, Su L, Zhang X, Zhang J, Li M, Wang B, Xu W (2010) Design, synthesis and preliminary activity assay of 1,2,3,4 tetrahydroisoquinoline-3-carboxylic acid derivatives as novel Histone deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 18:1761–1772
Zhu P, Martin E, Mengwasser J, Schlag P, Janssen KP, Göttlicher M (2004) Induction of HDAC2 expression upon loss of APC in colorectal tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell 5:455–463
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Department of Biotechnology, New Delhi, Govt. of India for providing financial support [F.No.BT/327/NE/TBP/2012] for this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Debnath, S., Debnath, T., Majumdar, S. et al. A combined pharmacophore modeling, 3D QSAR, virtual screening, molecular docking, and ADME studies to identify potential HDAC8 inhibitors. Med Chem Res 25, 2434–2450 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1652-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-016-1652-5