Abstract
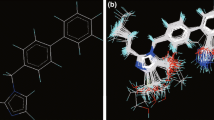
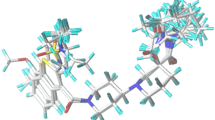
Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitors are currently considered as potential drugs for treating high low-density lipoprotein cholesterol. In this work, we developed a receptor-based quantitative structure–activity relationship (QSAR) models based on a series of tetrahydronaphthyridines derivatives to support the design of new CETP inhibitors. Multivariate adaptive regression spline and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system were employed to select the best subset of descriptors and mapping tool. The obtained QSAR model indicates that the inhibitory activity can be described by relative negative charge, Moriguchi octanol–water partition coefficient, topological electronic indices, steric interaction, and hydrogen bonding energies between the receptor and the inhibitors. In addition, the docking analysis showed that the interaction of the inhibitors with residues of the ARG201 and ASP460 residues plays an important role in the activities of the inhibitors. The results of validation and applicability domain techniques show that the models exhibited optimum stability and good predictive power which can be used in prediction of activity of new CETP inhibitors.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asadollahi-Baboli M (2012) Quantitative structure–activity relationship analysis of human neutrophil elastase inhibitors using shuffling classification and regression trees and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference systems. SAR QSAR Environ Res 23:505–520
Asadollahi-Baboli M, Mani-Varnosfaderani A (2013) Molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation and QSAR model on potent thiazolidine-4-carboxylic acid inhibitors of influenza neuraminidase. Med Chem Res 22:1700–1710
Azimi JG, Afiuni-Zadeh S, Karami A (2012) A QSAR study for modeling of thyroid receptors β1 selective ligands by application of adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system and radial basis function. J Chemom 26:135–142
Castilho MS, Guido RVC, Andricopulo AD (2007) 2D Quantitative structure–activity relationship studies on a series of cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 15:6242–6252
Escribano A, Mateo AI, Martin EM, Mayhugh DR, Cockerham SL (2012) Design and synthesis of new tetrahydroquinolines derivatives as CETP inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:3671–3675
Fernandez M, Escribano A, Mateo AI, Parthasarathy S (2012) Design, synthesis and structure–activity-relationship of 1,5-tetrahydronaphthyridines as CETP inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22:3056–3062
Friedman JH (1991) Multivariate adaptive regression splines. Annal Statist 19:1–141
Ghasemi JB, Pirhadi S, Ayati M (2011) 3D-QSAR studies of 2-arylbenzoxazoles as novel cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors. Bull Korean Chem Soc 32:645–650
Jalali-Heravi M, Asadollahi-Baboli M, Mani-Varnosfaderani A (2009) Shuffling multivariate adaptive regression splines and adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system as tools for QSAR study of SARS inhibitors. J Pharm Biomed Anal 50:853–860
LaRosa JC, He J, Vupputuri S (1999) Effect of statins on risk of coronary disease. JAMA 282:2340–2346
McCarthy PA (1993) New approaches to atherosclerosis: an overview. Med Res Rev 13:139–159
Nissen SE, Tardif JC, Nicholls SJ, Revkin JH, Shear CL, Duggan WT (2007) Effect of torcetrapib on the progression of coronary atherosclerosis. Engl J Med 356:1304–1316
Roy P, Roy K (2002) On some aspects of variable selection for partial least squares regression models. QSAR Comb Sci 27:302–313
Weaver S, Gleeson MP (2008) The importance of the domain of applicability in QSAR modeling. J Mol Graph Model 26:1315–1326
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asadollahi-Baboli, M. Docking and receptor-based QSAR approaches for modeling of CETP inhibitors. Med Chem Res 23, 1162–1169 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0722-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-013-0722-1