Abstract
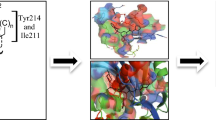
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder involving the dysregulation of glucose metabolism, β-cell dysfunction, and impaired insulin sensitivity. Glucokinase (GK) promotes glycogen synthesis, while it enhances insulin secretion from pancreatic β-cells. In this study, we focused on molecular modeling study of 3-alkoxy-5-phenoxy-N-thiazolyl benzamide analogs with reference to structural requirements. The amalgamated best fit consensus scoring function showed coefficient of determination (0.927), leave-one-out cross-validated squared correlation coefficient (0.865), and external predictivity value (0.763). The binding of 3-alkoxy-5-phenoxy-N-thiazolyl benzamide analogs to glucokinase enzyme was explored with the help of docking. The most stable ligand–enzyme complex of compound TR-2 showed that the NH of the benzamide make key hydrogen bonds with the backbone C=O of Arg63. The phenoxy moiety on the 5th position of benzene ring occupies the hydrophobic space on the allosteric binding site constituted from Met210, Met235, Cys220, and Tyr214. One of the oxygen of methylsulfonyl group forms hydrogen bond with NE2 of Gln98 and phenyl ring and the aromatic ring of Tyr215 are perpendicular to each other, which probably increase potency due to van der Waals interactions.The structural insights gleaned from the study could be usefully employed to design activators with a much more enhanced potency.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham MH (1993) Scales of solute hydrogen-bonding: their construction and application to physicochemical and biochemical processes. Chem Soc Rev 22:73–83
Abraham MH, Al-Hussaini AJM (2001) Solvation descriptors for the polychloronaphthalenes: estimation of some physicochemical properties. J Environ Monit 3:377–381
AutoDock Version 4.0 (2007) The Scripps Research Institute, 10550 North Torrey Pines Road, La Jolla, CA 92037-(858) 784-1000, USA
Bell DSH (2004) A comparison of agents used to manage type 2 diabetes mellitus: need for reappraisal of traditional approaches. Treat Endocrinol 3:67–76
Bertram LS, Black D, Briner PH, Chatfield R, Cooke A, Fyfe MCT, Murray PJ, Naud F, Nawano M, Procter MJ, Rakipovski G, Rasamison CM, Reynet C, Schofield KL, Shah VK, Spindler F, Taylor A, Turton R, Williams GM, Wong-Kai-In P, Yasuda K (2008) SAR, pharmacokinetics, safety, and efficacy of glucokinase activating 2-(4-sulfonylphenyl)-N-thiazol-2-ylacetamides: discovery of PSN-GK1. J Med Chem 51:4340–4345
Civcir PU (2001) A theoretical study of tautomerism of 6-thiopurine in the gas and aqueous phases using AM1 and PM3. J Mol Struct THEOCHEM 535:121–129
Coghlan M, Leighton B (2008) Glucokinase activators in diabetes management. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 17:145–167
CS ChemOffice, Version 11.0 (2008) Cambridge Soft Corporation, Software Publishers Association, 1730 M Street, Suite 700, Washington DC, 20036 (202) 452-1600, USA
Daniewski AR, Liu W, Radinov RN (2007) WO Patent 2007/115968
Dewar MJS, Zoebisch EG, Healey EF, Stewart JJP (1985) AM1: a new general purpose quantum mechanical molecular model. J Am Chem Soc 107:3902–3909
Dewar MJS, Hwang JC, Kuhn DR (1991) An AM1 study of the reactions of ozone with ethylene and 2-butene. J Am Chem Soc 113:735–741
Fedorowicz A, Zheng L, Singh H, Demchuk E (2004) QSAR study of skin sensitization using local lymph node assay data. Int J Mol Sci 5:56–66
Futamura M, Hosaka H, Kadotani A, Shimazaki H, Sasaki K, Ohyama S, Nishimura T, Eiki J, Nagata Y (2006) An allosteric activator of glucokinase impairs the interaction of glucokinase and glucokinase regulatory protein and regulates glucose metabolism. J Biol Chem 281:37668–37674
Fyfe MCT, White JR, Taylor A, Chatfield R, Wargent E, Printz RL, Sulpice T, McCormack JG, Procter MJ, Reynet C, Widdowson PS, Wong-Kai-In P (2007) Glucokinase activator PSN-GK1 displays enhanced antihyperglycaemic and insulinotropic actions. Diabetologia 50:1277–1287
Gershell L (2005) Type 2 diabetes market. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:367–368
Gloyn AL, Odili S, Zelent D, Buettger C, Castleden HAJ, Steele AM, Stride A, Shiota C, Magnuson MA, Lorini R, d’Annunzio G, Stanley CA, Kwagh J, Schaftingen EV, Veiga-da-Cunha M, Barbetti F, Dunten P, Han Y, Grimsby J, Taub R, Ellard S, Hattersley AT, Matschinsky FM (2005) Insights into the structure and regulation of glucokinase from a novel mutation (V62M), which causes maturity-onset diabetes of the young. J Biol Chem 280:14105–14113
Gonzalez MP, Teran C, Teijeira M, Gonzalez-Moa MJ (2005) GETAWAY descriptors to predicting A2A adenosine receptors agonists. Eur J Med Chem 40:1080–1086
Guertin KR, Grimsby J (2006) Small molecule glucokinase activators as glucose lowering agents: a new paradigm for diabetes therapy. J Curr Med Chem 13:1839–1843
Gupta AK, Arockia BM, Kaskhedikar SG (2004) VALSTAT: validation program for quantitative structure activity relationship studies. Indian J Pharm Sci 66:396–402
Hansch C, Leo A (1979) Substituent constants for correlation analysis in chemistry and biology. John Wiley, New York
Hemmer MC, Gasteiger J (2000) Prediction of three-dimensional structure using information from infrared spectra. Anal Chim Acta 420:145–154
Hemmer MC, Steinhauer V, Gasteiger J (1999) The prediction of the 3D structure of organic molecules from their infrared spectra. J Vib Spectrosc 19:151–164
Hill JO, Wyatt HR, Reed GW, Peters JC (2003) Obesity and the environment: where do we go from here? Science 299:853–855
Iino T, Tsukahara D, Kamata K, Sasaki K, Ohyama S, Hosaka H, Hasegawa T, Chiba M, Nagata Y, Eiki J, Nishimura T (2009) Discovery of potent and orally active 3-alkoxy-5-phenoxy-N-thiazolyl benzamides as novel allosteric glucokinase activators. Bioorg Med Chem 17:2733–2743
Kier LB (1971) Molecular orbital theory in drug research. Academic Press, New York
Leighton B, Atkinson A, Coghlan MP (2005) Small molecule glucokinase activators as novel anti-diabetic agents. Biochem Soc Trans 33:371–374
Matschinsky FM (1996) A lesson in metabolic regulation inspired by the glucokinase glucose sensor paradigm. Diabetes 45:223–241
Matschinsky FM (2002) Regulation of pancreatic beta-cell glucokinase: from basics to therapeutics. Diabetes 51:S394–S404
Matschinsky FM, Magnuson MA (2004) Glucokinase and glycemic disease: from basics to novel therapeutics. Karger, Basel
McKerrecher D, Allen JV, Caulkett PWR, Donald CS, Fenwick ML, Grange E, Johnson KM, Johnstone C, Jones CD, Pike KG, Rayner JW, Walker RP (2006) Design of a potent, soluble glucokinase activator with excellent in vivo efficacy. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 16:2705–2709
Mitsuya M, Kamata K, Bamba M, Watanabe H, Sasaki Y, Sasaki K, Ohyama S, Hosaka H, Nagata Y, Eiki J, Nishimura T (2009) Discovery of novel 3,6-disubstituted 2-pyridinecarboxamide derivatives as GK activators. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 19:2718–2721
Moore MC, Cherrington AD, Wasserman DH (2003) Regulation of hepatic and peripheral glucose disposal. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 17:343–364
Nathan DM (2002) Initial management of glycemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 347:1342–1349
Sarabu R, Grimsby J (2005) Targeting glucokinase activation for the treatment of type 2 diabetes—a status review. Curr Opin Drug Discov Dev 8:631–637
Schaper KJ (1999) Free-Wilson-type analysis of non-additive substituent effects on THPB dopamine receptor affinity using artificial neural networks. Quant Struct Act Relatsh 18:354–360
Skagerberg B, Bonelli D, Clementi S, Cruciani G, Ebert C (1989) Principal properties for aromatic substituents. A multivariate approach for design in QSAR. Quant Struct Act Relatsh 8:32–38
Takahashi K, Hashimoto N, Nakama C, Kamata K, Sasaki K, Yoshimoto R, Ohyama S, Hosaka H, Maruki H, Nagata Y, Eiki J, Nishimura T (2009) The design and optimization of a series of 2-(pyridin-2-yl)-1H-benzimidazole compounds as allosteric glucokinase activators. Bioorg Med Chem 17:7042–7051
Todeschini R, Consonni V (2001) DRAGON-software for the calculation of molecular descriptors, rel. 1.12 for Windows
Todeschini R, Gramatica P (1997) 3D-modelling and prediction by WHIM descriptors. Part 5. Theory development and chemical meaning of WHIM descriptors. Quant Struct Act Relatsh 16:113–119
Todeschini R, Lasagni M, Marengo E (1994) New molecular descriptors for 2D and 3D structures. Theory. J Chemom 8:263–273
Wold S, Eriksson L (1995) Chemometric methods in molecular design. VCH Weinheim, New York
Wolff ME (1994) Burger’s medicinal chemistry and drug discovery. Wiley, New York
Zelent D, Najafi H, Odili S, Buettger C, Weik-Collins H, Li C, Doliba N, Grimsby J, Matschinsky FM (2005) Glucokinase and glucose homeostasis: proven concepts and new ideas. Biochem Soc Trans 33:306–310
Zimmet P, Alberti KG, Shaw J (2001) Global and societal implications of the diabetes epidemic. Nature 414:782–787
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, A.K., Sabarwal, N., Patidar, A. et al. Rationalization of physicochemical characters and docking of 3-alkoxy-5-phenoxy-N-thiazolyl benzamide analogs toward glucokinase activator activity. Med Chem Res 21, 2196–2207 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9740-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-011-9740-z