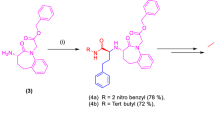
Abstract
Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors have emerged as a revolution in antihypertensive therapy. Introduction of captopril, the first rationally designed ACE inhibitor, has encouraged researchers all over the world to design and synthesize target molecules controlling hypertension based on these lines. It has been observed that replacing proline part of captopril with 4-substituted prolines or 5-oxo-prolines led to significant enhancement in ACE inhibitory activity, and this observation prompted us to design and synthesize N-acyl 4-substituted pyroglutamates and prolinates with the objective of developing therapeutically better ACE inhibitors. Herein we describe an easy approach for N-acylation of 4-α(S)-(phenylmethyl) pyroglutamates with the aim of synthesizing N-[3′-(acetylthio)alkanoyl] and N-[3′-mercaptoalkanoyl]-4-α-(s)-(phenylmethyl) pyroglutamic acids and prolines as ACE inhibitors.
Graphical Abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexandrou EN, Liakopoulou-Kyriakides M (1990) Inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme by l-alanyl-4 or 5-substituted l-prolines and their N-alpha-phosphoryl-derivatives. Biochem Int 21(2):271–278
Biollaz J, Burnier M, Turini GA, Brunner DB, Porchet M, Gomez HJ, Jones KH, Ferber F, Abrams WB, Gavras H, Bruner HR (1981) Three new long acting angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors; relationship between plasma converting enzyme activity and pressor response to angiotensin-I. Clin Pharmacol Ther 29:665–670
Caubert V, Langlois N (2006) Studies toward the synthesis of salinosporamide A, a potent proteasome inhibitor Tetrahedron Lett 47:4473–4475. doi:10.1016/j.tetlet.2006.04.070 (and references cited therein)
Chen X, Du D-M, Hua W-T (2002) Pyroglutamic acid: a versatile building block in asymmetric synthesis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 13:43–46. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(02)00052-6
Cushman DW, Cheung HS (1971) Spectroscopic assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem Pharmacol 20:1637–1648. doi:10.1016/0006-2952(71)90292-9
Cushman DW, Ondetti MA (1980) Inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme. In: Ellis GP, West GB (eds) Progress in Medical Chemistry. Elsevier/North Holland, Amsterdam, pp 17–41
Dikshit DK, Panday SK (1992) Aldol reactions of pyroglutamates: chiral synthesis of 4-α(S)- and 4-β(R)-arylmethyl pyroglutamates. J Org Chem 57:1920–1924. doi:10.1021/jo00032a056 (and references cited therein)
Dikshit DK, Maheshwari A, Panday SK (1995) Self reproduction of chirality in pyroglutamates; Reactions at α-position with electrophiles. Tetrahedron Lett 36:6131–6134. doi:10.1016/0040-4039(95)01160-J
Herdeis C, Kelm B (2003). A stereoselective synthesis of 3-substituted(S)-pyroglutamic and glutamic acids via OBO ester derivatives. Tetrahedron 59:217–219. doi:10.1016/S0040-4020(02)01490-4 (and references cited therein)
Imaki K, Sakuyama S, Okada T, Toda M, Hayashi M, Miyamoto T, Kawasaki A, Okegawa T (1981) Potent orally active inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo) 29:2210–2214
Krapcho J, Turk C, Cushman DW, Powell JR, Deforrest JM, Spitzmiller ER, Karanewsky DS, Duggan M, Rovnyak G, Schwartz J, Natrajan S, Godfrey JD, Ryono DE, Neubeck R, Atwal KS, Petrillo EW Jr (1988) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors, mercaptan, carboxyalkyl dipeptide and phosphinic acid inhibitors incorporating 4-substituted prolines. J Med Chem 31(6):1148–1160. doi:10.1021/jm00401a014
Ksander GM (1984) Abstracts, 19th National Med. Chem. Symposium, Tucson, AZ, June 17–21, 1984, p 20
Laragh JH (1980) In: Case DB (ed) Captopril and hypertension. Plenum, New York, p 173
Najera C, Yus M (1999) Pyroglutamic acid: a versatile building block in asymmetric Synthesis. Tetrahedron Asymmetry 10:2245–2303. doi:10.1016/S0957-4166(99)00213-X
Ohfune Y, Tomita M (1982) Total synthesis of (−)-domoic acid. A revision of original structure. J Am Chem Soc 104:3511–3513. doi:10.1021/ja00376a048
Ohta T, Hosoi A, Nozoe S (1988) Stereoselective hydroxylation of N-carbamoyl-l-pyroglutamate. Synthesis of (−)-bulgecinine. Tetrahedron Lett 29:329–332. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(00)80087-8
Ondetti MA, Cushman DW (1981) In: Soffer RL (ed) Biochemical regulation of blood pressure. Wiley, New York, pp 165–204
Ondetti MA, Cushman DW (1982) Enzymes of the rennin-angiotensin system and their inhibitors. Ann Rev Biochem 51:283–308. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001435
Ondetti MA, Cushman DW (1984) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: biochemical properties and biological actions. CRC Crit Rev Biochem 16:381–411. doi:10.3109/10409238409108720
Panday SK, Langlois N (1997) An efficient straight forward synthesis of (−)-bulgecinine. Syn Comm 27(8):1373–1384. doi:10.1080/00397919708006067
Patchett AA, Harris EW, Tristram EW, Wyvratt MJ, Wu MT, Taub D, Peterson ER, Ikeler TJ, Broeke JL, Payne LG, Ondeyka DL, Thorsett ED, Greenlee WJ, Lohr NS, Hoffsommer RD, Joshua H, Ruyle WV, Rothroch JW, Aster SD, Maycock AL, Robinson FM, Hirschmann R, Sweet CS, Ulm EM, Gross DM, Vassil TC, Stone CA (1980) A new class of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Nature 288:280–283
Peterson JS, Fels G, Rapoport H (1984) Chirospecific synthesis of (+) and (−)-anatoxin a. J Am Chem Soc 106:4539–4547. doi:10.1021/ja00328a040
Petrillo EW Jr, Ondetti MA (1982) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: medicinal chemistry and biological actions. Med Res Rev 2:1–41. doi:10.1002/med.2610020103
Potts D, Stevenson PJ, Thomson N (2000) Expedient synthesis of (+)-trans-5-allyl hexahydroindolizidin-3-one. Tetrahedron Lett 41:275–278. doi:10.1016/S0040-4039(99)02034-1
Rigo B, Lespagnol C, Pauly M (1988) Studies on pyrrolidinones; synthesis of N-acyl pyroglutamic esters with bactericide and fungicide properties. J Heterocycl Chem 25(1):49–59
Smith EM, Swiss GF, Gold Neustadt BR, EH Sommer JA, Brown AD, Chiu PJS, Moran R, Sybertz EJ, Baum TJ (1988) Synthesis and pharmacological activity of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: N-(mercaptoalkanoyl)-4-substituted-(S)-prolines. Med Chem 31(4):875–885. doi:10.1021/jm00399a033
Smith EM, Swiss GF, Neustadt BR, McNamara P, Gold EH, Sybertz EJ, Baum T (1989) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors: spirapril and related compounds. J Med Chem 32:1600–1606. doi:10.1021/jm00127a033 (and references cited therein)
Suh JT, Skiles JA, Williams BE, Youssefyeh RD, Jones H, Love B, Neiss ES, Schwab A, Mann WS, Khandwala A, Wolf PS, Weinryb MA (1985) Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. New orally active anti hypertensive (mercaptoalkanoyl) and [(acylthio) alkanoyl] glycine derivatives. J Med Chem 28(1):57–66. doi:10.1021/jm00379a013
Thottahil JK, Moniot JL, Mueller RH, Wong MKY, Kissick TPJ (1986) Conversion of l-pyroglutamic acid to 4-alkyl substituted-l-prolines: The synthesis of trans-4-cyclohexyl-l-proline. J Org Chem 51:3140–3143. doi:10.1021/jo00366a011
Wiecek A, Grzeszczak W (1986) Poly Arch Med Wewn 76(5–6/11–12):291–297
Wyratt MA, Patchett AA (1985) Recent developments in the design of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors. Med Res Rev 5:483–531. doi:10.1002/med.2610050405
Wyvratt MJ, Tristram EW, Ikeler TJ, Lohr NS, Joshua H, Springer JP, Arison BH, Patchett AA (1984) Chirality in drug research. J Org Chem 49:2816–2819. doi:10.1021/jo00189a036
Zhang X, Jiang W, Schmitt AC (2001) A convenient and versatile synthesis of 6,5 and 7,5-fused bicyclic lactams as peptidomimetics. Tetrahedron Lett 42:4943–4945
Acknowledgements
The corresponding author is thankful to the Central Drug Research Institute, Lucknow, India, for providing infrastructural facilities to carry out above work and to SAIF, CDRI, Lucknow for providing analytical data.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Panday, S.K., Dikshit, M. & Dikshit, D.K. Synthesis of N-[3′-(acetylthio)alkanoyl] and N-[3′-mercaptoalkanoyl]-4-α(s)-(phenylmethyl) pyroglutamic acids and prolines as potent ACE inhibitors. Med Chem Res 18, 566–578 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-008-9150-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-008-9150-z