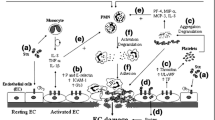
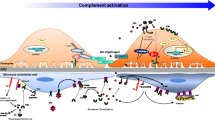
Abstract
The two major Shiga toxin (Stx) types, Stx1 and Stx2, produced by enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) in particular injure renal and cerebral microvascular endothelial cells after transfer from the human intestine into the circulation. Stxs are AB5 toxins composed of an enzymatically active A subunit and the pentameric B subunit, which preferentially binds to the glycosphingolipid globotriaosylceramide (Gb3Cer/CD77). This review summarizes the current knowledge on Stx-caused cellular injury and the structural diversity of Stx receptors as well as the initial molecular interaction of Stxs with the human endothelium of different vascular beds. The varying lipoforms of Stx receptors and their spatial organization in lipid rafts suggest a central role in different modes of receptor-mediated endocytosis and intracellular destiny of the toxins. The design and development of tailored Stx neutralizers targeting the oligosaccharide–toxin recognition event has become a very real prospect to ameliorate or prevent life-threatening renal and neurological complications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sahni SK (2007) Endothelial cell infection and hemostasis. Thromb Res 119:531–549
Chi JT, Chang HY, Haraldsen G, Jahnsen FL, Troyanskaya OG, Chang DS, Wang Z, Rockson SG, van de Rijn M, Botstein D, Brown PO (2003) Endothelial cell diversity revealed by global expression profiling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10623–10628
Pober JS, Min W, Bradley JR (2009) Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction, injury, and death. Annu Rev Pathol 4:71–95
Schnittler H, Preissner KT (2009) Between microbial attack and defence: the endothelium as a vulnerable player in infectious diseases. Thromb Haemost 102:1011–1013
Lemichez E, Lecuit M, Nassif X, Bourdoulous S (2010) Breaking the wall: targeting of the endothelium by pathogenic bacteria. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:93–104
Opitz B, Hippenstiel S, Eitel J, Suttorp N (2007) Extra- and intracellular innate immune recognition in endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 98:319–326
Cardoso FL, Brites B, Brito MA (2010) Looking at the blood-brain barrier: molecular anatomy and possible investigation approaches. Brain Res Rev 64:328–363
Ballermann BJ (2007) Contribution of the endothelium to the glomerular permselectivity barrier in health and disease. Nephron Physiol 106:19–25
Satchell SC, Braet F (2009) Glomerular endothelial cell fenestrations: an integral component of the glomerular filtration barrier. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296:F947–F956
Chiang CK, Inagi R (2010) Glomerular diseases: genetic causes and future therapeutics. Nat Rev Nephrol 6:539–554
Patrakka J, Tryggvason K (2010) Molecular make-up of the glomerular filtration barrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 396:164–169
Pate M, Damarla V, Chi DS, Negi S, Krishnaswamy G (2010) Endothelial cell biology: role in the inflammatory response. Adv Clin Chem 52:109–130
Harding M, Kubes P (2012) Innate immunity in the vasculature: interactions with pathogenic bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 15:85–91
Vestweber D (2007) Adhesion and signaling molecules controlling the transmigration of leukocytes through endothelium. Immunol Rev 218:178–196
Tesfamariam B, DeFelice AF (2007) Endothelial injury in the initiation and progression of vascular disorders. Vasc Pharmacol 46:229–237
Nataro JP, Kaper JB (1998) Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:142–201
Johnson TJ, Nolan LK (2009) Pathogenomics of virulence plasmids of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 73:750–774
Farfan MJ, Torres AG (2012) Molecular mechanisms that mediate colonization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains. Infect Immun 80:903–913
Melton-Celsa A, Mohawk K, Teel L, O’Brien A (2012) Pathogenesis of Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 357:67–103
Schmidt MA (2010) LEEways: tales of EPEC, ATEC and EHEC. Cell Microbiol 12:1544–1552
Lingwood CA (1996) Role of verotoxin receptors in pathogenesis. Trends Microbiol 4:147–153
Karch H, Tarr PI, Bielaszewska M (2005) Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli in human medicine. Int J Med Microbiol 295:405–418
Karch H, Friedrich AW, Gerber A, Zimmerhackl LB, Schmidt MA, Bielaszewska M (2006) New aspects in the pathogenesis of enteropathic hemolytic uremic syndrome. Semin Thromb Hemost 32:105–112
Tarr PI, Gordon CA, Chandler WL (2005) Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli and haemolytic uraemic syndrome. Lancet 365:1073–1086
Zoja C, Buelli S, Morigi M (2010) Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: pathophysiology of endothelial dysfunction. Pediatr Nephrol 25:2231–2240
Friedrich AW, Zhang W, Bielaszewska M, Mellmann A, Köck R, Fruth A, Tschäpe H, Karch H (2007) Prevalence, virulence profiles, and clinical significance of Shiga toxin-negative variants of enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157 infection in humans. Clin Infect Dis 45:39–45
Mellmann A, Bielaszewska M, Karch H (2009) Intrahost genome alterations in enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Gastroenterology 136:1925–1938
Tsai HM (2006) The molecular biology of thrombotic microangipathy. Kidney Int 70:16–23
Karpman D, Sartz L, Johnson S (2010) Pathophysiology of typical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:575–585
Obata F (2010) Influence of Escherichia coli Shiga toxin on the mammalian central nervous system. Adv Appl Microbiol 71:1–19
Karmali MA, Gannon V, Sargeant JM (2010) Verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli (VTEC). Vet Microbiol 140:360–370
Ferens WA, Hovde CJ (2011) Escherichia coli O157:H7: animal reservoir and sources of human infection. Foodborne Pathog Dis 8:465–487
Hoey DEE, Currie C, Else RW, Nutikka A, Lingwood CA, Gally DL, Smith DGE (2002) Expression of receptors for verotoxin 1 from Escherichia coli O157 on bovine intestinal epithelium. J Med Microbiol 51:143–149
Pennington H (2010) Escherichia coli O157. Lancet 376:1428–1435
Wong CS, Mooney JC, Brandt JR, Staples AO, Jelacic S, Boster DR, Watkins SL, Tarr PI (2012) Risk factors for the hemolytic uremic syndrome in children infected with Escherichia coli O157:H7: a multivariable analysis. Clin Infect Dis 55:33–41
Hunt JM (2010) Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC). Clin Lab Med 30:21–45
Mellmann A, Bielaszewska M, Köck R, Friedrich AW, Fruth A, Middendorf B, Harmsen D, Schmidt MA, Karch H (2008) Analysis of collection of hemolytic uremic syndrome-associated enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Emerg Infect Dis 14:1287–1290
Zimmerhackl LB, Rosales A, Hofer J, Riedl M, Jungraithmayr T, Mellmann A, Bielaszewska M, Karch H (2010) Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O26:H11-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: bacteriology and clinical presentation. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:586–593
Jenke C, Lindstedt BA, Harmsen D, Karch H, Brandal LT, Mellmann A (2011) Comparison of multilocus variable-number tandem-repeat analysis and multilocus sequence typing for differentiation of hemolytic-uremic syndrome-associated Escherichia coli (HUSEC) collection strains. J Clin Microbiol 49:3644–3646
Kunzendorf U, Karch H, Werber D, Haller H (2011) Recent outbreak of hemolytic uremic syndrome in Germany. Kidney Int 80:900–902
Frank C, Werber D, Cramer JP, Askar M, Faber M, an der Heiden M, Bernard H, Fruth A, Prager R, Spode A, Wadl M, Zoufaly A, Jordan S, Kemper MJ, Follin P, Müller L, King LA, Rosner B, Buchholz U, Stark K, Krause G, HUS Investigation Team (2011) Epidemic profile of Shiga-toxin-producing Escherichia coli O104:H4 outbreak in Germany. N Engl J Med 365:1771–1780
Frank C, Faber MS, Askar M, Bernard H, Fruth A, Gilsdorf A, Höhle M, Karch H, Krause G, Prager R, Spode A, Stark K, Werber D (2011) Large and ongoing outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome, Germany, May 2011. Euro Surveill 16(21). pii:19878
Bielaszewska M, Mellmann A, Zhang W, Köck R, Fruth A, Bauwens A, Peters G, Karch H (2011) Characterisation of the Escherichia coli strain associated with an outbreak of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Germany, 2011: a microbiological study. Lancet Infect Dis 11:671–676
Mellmann A, Harmsen D, Cummings CA, Zentz EB, Leopold SR, Rico A, Prior K, Szczepanowski R, Ji Y, Zhang W, McLaughlin SF, Henkhaus JK, Leopold B, Bielaszweska M, Prager R, Brzoska PM, Moore RL, Guenther S, Rothberg JM, Karch J (2011) Prospective genomic characterization of the German enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O104:H4 outbreak by rapid next generation sequencing technology. PLoS One 6(7):e22751
Loś JM, Loś M, Węgrzyn G (2011) Bacteriophages carrying Shiga toxin genes: genomic variations, detection and potential treatment of pathogenic bacteria. Future Microbiol 6:909–924
Mauro SA, Koudelka GB (2011) Shiga toxin: expression, distribution, and its role in the environment. Toxins 3:608–625
Richardson SE, Karmali MA, Becker LE, Smith CR (1988) The histopathology of the hemolytic uremic syndrome associated with verocytotoxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Hum Pathol 19:1102–1108
Ruggenenti P, Noris M, Remuzzi G (2001) Thrombotic microangiopathy, hemolytic uremic syndrome, and thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura. Kidney Int 60:831–846
Bielaszewska M, Karch H (2005) Consequences of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli infection for the vascular endothelium. Thromb Haemost 94:312–318
Sandvig K (2001) Shiga toxins. Toxicon 39:1629–1635
Müthing J, Schweppe CH, Karch H, Friedrich AW (2009) Shiga toxins, glycosphingolipid diversity, and endothelial cell injury. Thromb Haemost 101:252–264
Ling H, Boodhoo A, Hazes B, Cummings MD, Armstrong GD (1998) Structure of the Shiga-like toxin I B-pentamer complexed with an analogue of its receptor Gb3. Biochemistry 37:1777–1788
Jackson MP, Neill RJ, O’Brien AD, Holmes RK, Newland JW (1987) Nucleotide sequence analysis and comparison of the structural genes for Shiga-like toxin I and Shiga-like toxin II encoded by bacteriophages from Escherichia coli 933. FEMS Microbiol Lett 44:109–114
Lingwood CA, Law H, Richardson S, Petric M, Brunton JL, De Grandis S, Karmali M (1987) Glycolipid binding of purified and recombinant Escherichia coli produced verotoxin in vitro. J Biol Chem 262:8834–8839
Waddell T, Head S, Petric M, Cohen A, Lingwood C (1988) Globotriosyl ceramide is specifically recognized by the Escherichia coli verocytotoxin 2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 152:674–679
Müthing J, Meisen I, Zhang W, Bielaszewska M, Mormann M, Bauerfeind R, Schmidt MA, Friedrich AW, Karch H (2012) Promiscuous Shiga toxin 2e and its intimate relationship to Forssman. Glycobiology 22:849–862
Head SC, Karmali MA, Lingwood CA (1991) Preparation of VT1 and VT2 hybrid toxins from their purified dissociated subunits. Evidence for B subunit modulation of a subunit function. J Biol Chem 266:3617–3621
Fraser ME, Cherney MM, Marcato P, Mulvey GL, Armstrong GD, James MNG (2006) Binding of adenine to Stx2, the protein toxin from Escherichia coli O157:H7. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun 62:627–630
Obrig TG (2010) Escherichia coli Shiga toxin mechanisms of action in renal disease. Toxins 2:2769–2794
Ostroff SM, Tarr PI, Neill MA, Lewis JH, Hargrett-Bean N, Kobayashi JM (1989) Toxin genotypes and plasmid profiles as determinants of systemic sequelae in Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. J Infect Dis 160:994–998
Friedrich AW, Bielaszewska M, Zhang WL, Pulz M, Kuczius T, Ammon A, Karch H (2002) Escherichia coli harboring Shiga toxin 2 gene variants: frequency and association with clinical symptoms. J Infect Dis 185:74–84
Orth D, Würzner R (2010) Complement in typical hemolytic uremic syndrome. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:620–624
Schüller S (2011) Shiga toxin interaction with human intestinal epithelium. Toxins 3:626–639
Te Loo DMWM, Monnens LAH, van der Velden TJAM, Vermeer MA, Preyers F, Demacker PNM, van den Heuvel LPWJ, van Hinsbergh VWM (2000) Binding and transfer of verocytotoxin by polymorphonuclear leukocytes in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 95:3396–3402
Brigotti M, Carnicelli D, Ravanelli E, Barbieri S, Ricci F, Bontadini A, Tozzi AE, Scavia G, Caprioli A, Tazzari PL (2008) Interactions between Shiga toxins and human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Leukoc Biol 84:1019–1027
Arfilli V, Carnicelli D, Rocchi L, Ricci F, Pagliaro P, Tazzari PL, Brigotti M (2010) Shiga toxin 1 and ricin A chain bind to human polymorphonuclear leucocytes through a common receptor. Biochem J 432:173–180
Brigotti M, Tazzari PL, Ravanelli E, Carnicelli D, Barbieri S, Rocchi L, Arfilli V, Scavia G, Ricci F, Bontadini A, Alfieri RR, Pretonini PG, Pecoraro C, Tozzi AE, Caprioli A (2010) Endothelial damage induced by Shiga toxins delivered by neutrophils during transmigration. J Leukoc Biol 88:201–210
Brigotti M, Tazzari PL, Ravanelli E, Carnicelli D, Rocchi L, Arfilli V, Scavia G, Minelli F, Ricci F, Pagliaro P, Ferretti AV, Pecoraro C, Paglialonga F, Edefonti A, Procaccino MA, Tozzi AE, Caprioli A (2011) Clinical relevance of Shiga toxin concentrations in the blood of patients with hemolytic uremic syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis 30:486–490
Brigotti M, Carnicelli D, Arfilli V, Rocchi L, Ricci F, Pagliaro P, Tazzari PL, Vara AG, Amelia M, Manoli F, Monti S (2011) Change in conformation with reduction of α-helix content causes loss of neutrophil binding activity in fully cytotoxic Shiga toxin 1. J Biol Chem 286:34514–34521
Ramegowda B, Tesh VL (1996) Differentiation-associated toxin receptor modulation, cytokine production, and sensitivity of Shiga-like toxins in human monocytes and monocytic cell lines. Infect Immun 64:1173–1180
Geelen JM, van der Velden TJ, van den Heuvel LP, Monnens LA (2007) Interactions of Shiga-like toxin with human peripheral blood monocytes. Pediatr Nephrol 22:1181–1187
Lee SY, Lee MS, Cherla RP, Tesh VL (2008) Shiga toxin 1 induces apoptosis through the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in human monocytic cells. Cell Microbiol 10:770–780
Sandvig K, Garred O, Prydz K, Kozlov JV, Hansen SH, van Deurs B (1992) Retrograde transport of endocytosed Shiga toxin to the endoplasmic reticulum. Nature 358:510–512
Johannes L, Goud B (2000) Facing inward from compartment shores: how many pathways were we looking for? Traffic 1:119–123
Sandvig K, van Deurs B (2002) Transport of protein toxins into cells: pathways used by ricin, cholera toxin and Shiga toxin. FEBS Lett 529:49–53
Spooner RA, Smith DC, Easton AJ, Roberts LM, Lord JM (2006) Retrograde transport pathways utilised by viruses and protein toxins. Virol J 3:26
Römer W, Berland L, Chambon V, Gaus K, Windschiegl B, Tenza D, Aly MRE, Fraisier V, Florent JC, Perrais D, Lamaze C, Raposo G, Steinem C, Sens P, Bassereau P, Johannes L (2007) Shiga toxin induces tubular membrane invaginations for its uptake into cells. Nature 450:670–675
Johannes L, Römer W (2010) Shiga toxins—from cell biology to biomedical applications. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:105–116
Sandvig K, Torgersen ML, Engedal N, Skotland T, Iversen TG (2010) Protein toxins from plants and bacteria: probes for intracellular transport and tools in medicine. FEBS Lett 584:2626–2634
Sandvig K, Bergan J, Dyve AB, Skotland T, Torgersen ML (2010) Endocytosis and retrograde transport of Shiga toxin. Toxicon 56:1181–1185
Ewers H, Helenius A (2011) Lipid-mediated endocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a004721
Yu M, Haslam DB (2005) Shiga toxin is transported from the endoplasmic reticulum following interaction with the luminal chaperone HEDJ/ERdj3. Infect Immun 73:2524–2532
Garred O, Dubinina E, Holm PK, Olsnes S, van Deurs B, Kozlov JV, Sandvig K (1995) Role of processing and intracellular transport for optimal toxicity of Shiga toxin and toxin mutants. Exp Cell Res 218:39–49
Endo Y, Tsurugi K, Yutsudo T, Takeda Y, Ogasawara T, Igarashi K (1988) Site of action of a Vero toxin (VT2) from Escherichia coli O157:H7 and of Shiga toxin on eukaryotic ribosomes. RNA N-glycosidase activity of the toxins. Eur J Biochem 171:45–50
O’Brien AD, Tesh VL, Donohue-Rolfe A, Jackson MP, Olsnes S, Sandvig K, Lindberg AA, Keusch GT (1992) Shiga toxin: biochemistry, genetics, mode of action, and role in pathogenesis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 180:65–94
Barbieri L, Valbonesi P, Brigotti M, Montanara L, Stirpe F, Sperti S (1998) Shiga-like toxin I is a polynucleotide:adenosine glycosidase. Mol Microbiol 29:661–662
McCluskey AJ, Bolewska-Pedyczak E, Jarvik N, Chen G, Sidhu SS, Gariépy J (2012) Charged and hydrophobic surfaces on the A chain of Shiga-like toxin 1 recognize the C-terminal domain of ribosomal stalk proteins. PLoS One 7(2):e31191
Tesh VL (2012) Activation of cell stress response pathways by Shiga toxins. Cell Microbiol 14:1–9
Brigotti M, Accorsi P, Carnicelli D, Rizzi S, González Vara A, Montanaro L, Sperti S (2001) Shiga toxin 1: damage to DNA in vitro. Toxicon 39:341–348
Brigotti M, Carnicelli D, Vara AG (2004) Shiga toxin 1 acting on DNA in vitro is a heat-stable enzyme not requiring proteolytic activation. Biochimie 86:305–309
Sestili P, Alfieri R, Carnicelli D, Martinelli C, Barbieri L, Stirpe F, Bonelli M, Petronini PG, Brigotti M (2005) Shiga toxin 1 and ricin inhibit the repair of H2O2-induced DNA single strand breaks in cultured mammalian cells. DNA Repair 4:271–277
Sandvig K, Torgersen ML, Raa HA, van Deurs B (2008) Clathrin-independent endocytosis: from nonexisting to an extreme degree of complexity. Histochem Cell Biol 129:267–276
Obrig TG, del Vecchio PJ, Brown JE, Moran TP, Rowland BM, Judge TK, Rothman SW (1988) Direct cytotoxic action of Shiga toxin on human vascular endothelial cells. Infect Immun 56:2373–2378
Louise CB, Obrig TG (1991) Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic-uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin, Interleukin-1β, and tumor necrosis factor alpha on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun 59:4173–4179
Louise CB, Obrig TG (1992) Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: combined cytotoxic effects of Shiga toxin and lipopolysaccharide (endotoxin) on human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun 60:1536–1543
van de Kar NCAJ, Monnens LAH, Karmali MA, van Hinsbergh VWM (1992) Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 induce expression of the verocytotoxin receptor globotriaosylceramide on human endothelial cells: implications for the pathogenesis of the hemolytic uremic syndrome. Blood 80:2755–2764
Kaye SA, Louise CB, Boyd B, Lingwood CA, Obrig TG (1993) Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome: interleukin-1β enhancement of Shiga toxin cytotoxicity toward human vascular endothelial cells in vitro. Infect Immun 61:3886–3891
Obrig TG, Louise CB, Lingwood CA, Boyd B, Barley-Malony L, Daniel TO (1993) Endothelial heterogeneity in Shiga toxin receptors and responses. J Biol Chem 268:15484–15488
van de Kar NCAJ, Kooistra T, Vermeer M, Lesslauer W, Monnens LAH, van Hinsbergh VWM (1995) Tumor necrosis factor α induces endothelial galactosyl transferase activity and verocytotoxin receptors. Role of specific tumor necrosis factor receptors and protein kinase C. Blood 85:734–743
Louise CB, Tran MC, Obrig TG (1997) Sensitization of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to Shiga toxin: involvement of protein kinase C and NF-κB. Infect Immun 65:3337–3344
Stone MK, Kolling GL, Lindner MH, Obrig TG (2008) p38 Mitogen-activated protein kinase mediates lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor alpha induction of Shiga toxin 2 sensitivity in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Infect Immun 76:1115–1121
Nolasco LH, Turner NA, Bernardo A, Tao Z, Cleary TG, Dong J, Moake JL (2005) Hemolytic uremic syndrome-associated Shiga toxins promote endothelial-cell secretion and impar ADAMTS13 cleavage of unusually large von Willebrand factor multimers. Blood 106:4199–4209
Huang J, Motto DG, Bundle DR, Sadler JE (2010) Shiga toxin B subunits induce vWF secretion by human endothelial cells and thrombotic microangiopathy in ADAMST13-deficient mice. Blood 116:3653–3659
Liu F, Huang J, Sadler JE (2011) Shiga toxin (Stx)1B and Stx2B induce von Willebrand factor secretion from human umbilical vein endothelial cells through different signaling pathways. Blood 118:3392–3398
Morigi M, Micheletti G, Figliuzzi M, Imberti B, Karmali MA, Remuzzi A, Remuzzi G, Zoja C (1995) Verotoxin-1 promotes leukocyte adhesion to cultured endothelial cells under physiologic flow conditions. Blood 86:4553–4558
Geelen JM, Valsecchi F, van der Velden T, van den Heuvel L, Monnens L, Morigi M (2008) Shiga-toxin-induced firm adhesion of human leukocytes to endothelium is in part mediated by heparan sulfate. Nephrol Dial Transplant 23:3091–3095
Zanchi C, Zoja C, Morigi M, Valsecchi F, Liu XY, Rottoli D, Locatelli M, Buelli S, Pezzotta A, Mapelli P, Geelen J, Remuzzi G, Hawiger J (2008) Fractalkine and CX3CR1 mediate leukocyte capture by endothelium in response to Shiga toxin. J Immunol 181:1460–1469
Brigotti M, Alfieri R, Sestili P, Bonelli M, Petronini PG, Guidarelli A, Barbieri L, Stirpe F, Sperti S (2002) Damage to nuclear DNA induced by Shiga toxin 1 and ricin in human endothelial cells. FASEB J 16:365–372
Matussek A, Lauber J, Bergau A, Hansen W, Rohde M, Dittmar KEJ, Gunzer M, Mengel M, Gatzlaff P, Hartmann M, Buer J, Gunzer F (2003) Molecular and functional analysis of Shiga toxin-induced response patterns in human vascular endothelial cells. Blood 102:1323–1332
Torgersen ML, Engedal N, Pedersen AMG, Husebye H, Espevik T, Sandvig K (2011) Toll-like receptor facilitates binding of Shiga toxin to colon carcinoma and primary endothelial cells. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol 61:63–75
Goerdt S, Sorg C (1992) Endothelial heterogeneity and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: a paradigm for the pathogenesis of vascular disorders. Clin Invest 70:89–98
Augustin HG, Kozian DH, Johnson RC (1994) Differentiation of endothelial cells: analysis of the constitutive and activated endothelial cell phenotypes. BioEssays 16:901–906
Aird WC (2003) Endothelial cell heterogeneity. Crit Care Med 31:S221–S230
Aird WC (2008) Endothelium in health and disease. Pharmacol Rep 60:139–143
Ohmi K, Kiyokawa N, Takeda T, Fujimoto J (1998) Human microvascular endothelial cells are strongly sensitive to Shiga toxins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 251:137–141
Morigi M, Galbusera M, Binda E, Imberti B, Gastoldi S, Remuzzi A, Zoja C, Remuzzi G (2001) Verotoxin-1-induced up-regulation of adhesive molecules renders microvascular endothelial cells thrombogenic at high shear stress. Blood 98:1828–1835
Obrig TG, Seaner RM, Bentz M, Lingwood CA, Boyd B, Smith A, Narrow W (2003) Induction by sphingomyelinase of Shiga toxin receptor and Shiga toxin 2 sensitivity in human microvascular endothelial cells. Infect Immun 71:845–849
Jacewicz MS, Acheson DWK, Binion DG, West GA, Lincicome LL, Fiocchi C, Keusch GT (1999) Responses of human intestinal microvascular endothelial cells to Shiga toxins 1 and 2 and pathogenesis of hemorrhagic colitis. Infect Immun 67:1439–1444
Keusch GT, Acheson DWK, Aaldering L, Erban J, Jacewicz MS (1996) Comparison of the effects of Shiga-like toxin 1 on cytokine- and butyrate-treated human umbilical and saphenous vein endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 173:1164–1170
Yoshida T, Sugiyama T, Koide N, Mori I, Yokochi T (2003) Human microvascular endothelial cells resist Shiga toxins by IFN-γ treatment in vitro. Microbiology 149:2609–2614
Louise CB, Obrig TG (1994) Human renal microvascular endothelial cells as a potential target in the development of the hemolytic uremic syndrome as related to fibrinolysis factor expression, in vitro. Microvasc Res 47:377–387
Louise CB, Obrig TG (1995) Specific interaction of Escherichia coli O157:H7-derived Shiga-like toxin II with human renal endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 172:1397–1401
van Setten PA, van Hinsbergh VWM, van der Velden TJAN, van de Kar NCAJ, Vermeer M, Mahan JD, Assmann KJM, van den Heuvel LPWJ, Monnens LAH (1997) Effects of TNFα on verocytotoxin cytotoxicity in purified human glomerular microvascular endothelial cells. Kidney Int 51:1245–1256
Warnier M, Römer W, Geelen J, Lesieur J, Amessou M, van den Heuvel L, Monnens L, Johannes L (2006) Trafficking of Shiga toxin/Shiga-like toxin-1 in human glomerular microvascular endothelial cells and human mesangial cells. Kidney Int 70:2085–2091
Nestoridi E, Tsukurov O, Kushak RI, Ingelfinger JR, Grabowski EF (2005) Shiga toxin enhances functional tissue factor on human glomerular endothelial cells: implications for the pathophysiology of hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Thromb Haemost 3:752–762
Te Loo DM, Monnens L, van der Velden T, Karmali M, van den Heuvel L, van Hinsbergh V (2006) Shiga toxin-1 affects nitric oxide production by human glomerular endothelial and mesangial cells. Pediatr Nephrol 21:1815–1823
Herrera M, Garvin JL (2005) Recent advances in the regulation of nitric oxide in the kidney. Hypertension 45:1062–1067
Guessous F, Marcinkiewicz M, Polanowska-Grabowska R, Kongkhum S, Heatherly D, Obrig T, Gear ARL (2005) Shiga toxin 2 and lipopolysaccharide induce human microvascular endothelial cells to release chemokines and factors that stimulate platelet function. Infect Immun 73:8306–8316
Zoja C, Angioletti S, Donadelli R, Zanchi C, Tomasoni S, Binda E, Imberti B, te Loo M, Monnens L, Remuzzi G, Morigi M (2002) Shiga toxin-2 triggers endothelial leukocyte adhesion and transmigration via NF-κB dependent up-regulation of IL-8 and MCP-1. Kidney Int 62:846–856
Greinacher A, Friesecke S, Abel P, Dressel A, Stracke S, Fiene M, Ernst F, Selleng K, Weissenborn K, Schmidt BM, Schiffer M, Felix SB, Lerch MM, Kielstein JT, Mayerle J (2011) Treatment of severe neurological deficits with IgG depletion through immunoadsorption in patients with Escherichia coli O104:H4-associated haemolytic uraemic syndrome: a prospective trial. Lancet 378:1166–1173
Matano S, Inamura K, Konishi M, Okumura T, Kawai H, Okamura T, Takat Y, Yamada K, Obata M, Nagata H, Muramoto Y, Sugimoto T (2011) Encephalopathy, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and hemolytic-uremic syndrome after infection with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli O111. J Infect Chemother. doi:10.1007/s10156-011-0336-9
Ramegowda B, Samuel JE, Tesh VL (1999) Interaction of Shiga toxins with human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 180:1205–1213
Eisenhauer PB, Chaturvedi P, Fine RE, Ritchie AJ, Pober JS, Cleary TG, Newburg DS (2001) Tumor necrosis alpha increases human cerebral endothelial cell Gb3 and sensitivity to Shiga toxin. Infect Immun 69:1889–1894
Stricklett PK, Hughes AK, Ergonul Z, Kohan DE (2002) Molecular basis for up-regulation by inflammatory cytokines of Shiga toxin 1 cytotoxicity and globotriaosylceramide expression. J Infect Dis 186:976–982
Hughes AK, Ergonul Z, Stricklett PK, Kohan DE (2002) Molecular basis for high renal cell sensitivity to the cytotoxic effects of Shigatoxin-1: upregulation of globotriaosylceramide expression. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:2239–2245
Eisenhauer PB, Jacewicz MS, Conn KJ, Koul O, Wells JM, Fine RE, Newburg DS (2004) Escherichia coli Shiga toxin 1 and TNF-α induce cytokine release by human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells. Microb Pathog 36:189–196
Stricklett PK, Hughes AK, Kohan DE (2005) Inhibition of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase ameliorates cytokine up-regulated Shigatoxin-1 toxicity in human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Infect Dis 191:461–471
Pijpers AHJM, van Setten PA, van den Heuvel LPWJ, Assmann KJM, Dijkman HBPM, Pennings AHM, Monnens LAH, van Hinsbergh VWM (2001) Verocytotoxin-induced apoptosis of human microvascular endothelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol 12:767–778
Yoshida T, Fukuda M, Koide N, Ikeda H, Sugiyama T, Kato Y, Ishikawa N, Yokochi T (1999) Primary cultures of human endothelial cells are susceptible to low doses of Shiga toxins and undergo apoptosis. J Infect Dis 180:2048–2052
Molostov G, Morris A, Rose P, Basu S (2001) Interaction of cytokines and growth factor in the regulation of verotoxin-induced apoptosis in cultured human endothelial cells. Br J Haematol 113:891–897
Erwert RD, Winn RK, Harlan JM, Bannerman DD (2002) Shiga-like toxin inhibition of FLICE-like inhibitory protein expression sensitizes endothelial cells to bacterial lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 277:40567–40574
Ergonul Z, Hughes AK, Kohan DE (2003) Induction of apoptosis of human brain microvascular endothelial cells by Shiga toxin 1. J Infect Dis 187:154–158
Erwert RD, Eiting KT, Tupper JC, Winn RK, Harlan JM, Bannerman DD (2003) Shiga toxin induces decreased expression of the anti-apoptotic protein Mc1-1 concomitant with the onset of endothelial apoptosis. Microb Pathog 35:87–93
Fuji J, Wood K, Matsuda F, Carneiro-Filho BA, Schlegel KH, Yutsudo T, Binnington-Boyd B, Lingwood CA, Obata F, Kim KS, Yoshida SI, Obrig T (2008) Shiga toxin 2 causes apoptosis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells via C/EBP homologous protein. Infect Immun 76:3679–3689
Tesh VL (2010) Induction of apoptosis by Shiga toxins. Future Microbiol 5:431–453
Bauwens A, Bielaszewska M, Kemper B, Langehanenberg P, von Bally G, Reichelt R, Mulac D, Humpf HU, Friedrich AW, Kim KS, Karch H, Müthing J (2011) Differential cytotoxic actions of Shiga toxin 1 and Shiga toxin 2 on microvascular and macrovascular endothelial cells. Thromb Haemost 105:515–528
Carl D, Kemper B, Wernicke G, von Bally G (2004) Parameter-optimized digital holographic microscope for high-resolution living-cell analysis. Appl Opt 43:6536–6544
Marquet P, Rappaz B, Magistretti PJ, Cuche E, Emery Y, Colomb T, Depeursinge C (2005) Digital holographic microscopy: a noninvasive contrast imaging technique allowing quantitative visualization of living cells with subwavelength axial accuracy. Opt Lett 30:468–470
Depeursinge C, Colomb T, Emery Y, Kühn J, Charrière F, Rappaz B, Marquet P (2007) Digital holographic microscopy applied to life sciences. Conf Proc IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc 2007:6244–6247
Langehanenberg P, Ivanova L, Bernhardt I, Ketelhut S, Vollmer A, Dirksen D, Georgiev G, von Bally G, Kemper B (2009) Automated three-dimensional tracking of living cells by digital holographic microscopy. J Biomed Opt 14:014018
Kemper B, von Bally G (2008) Digital holographic microscopy for live cell applications and technical inspection. Appl Opt 47:A52–A61
Kemper B, Bauwens A, Vollmer A, Ketelhut S, Langehanenberg P, Müthing J, Karch H, von Bally G (2010) Label-free quantitative cell division monitoring of endothelial cells by digital holographic microscopy. J Biomed Opt 15:036009
Levery SB (2005) Glycosphingolipid structural analysis and glycosphingolipidomics. Methods Enzymol 405:300–369
Merrill AH Jr (2011) Sphingolipid and glycosphingolipid metabolic pathways in the era of sphingolipidomics. Chem Rev 111:6387–6422
Kolter T, Proia RL, Sandhoff K (2002) Combinatorial ganglioside biosynthesis. J Biol Chem 277:25859–25862
Sandhoff K, Kolter T (2003) Biosynthesis and degradation of mammalian glycosphingolipids. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B 358:847–861
Lahiri S, Futerman AH (2007) The metabolism and function of sphingolipids and glycosphingolipids. Cell Mol Life Sci 64:2270–2284
Stults CLM, Sweeley CC, Macher BA (1989) Glycosphingolipids: structure, biological source, and properties. Methods Enzymol 179:167–214
Lochnit G, Geyer R, Heinz E, Rietschel ET, Zähringer U, Müthing J (2001) Chemical biology and biomedicine: glycolipids and glycosphingolipids. In: Fraser-Reid B, Tatsuta K, Thiem J (eds) Glycoscience: chemistry and chemical biology, vol III. Springer, Heidelberg, pp 2183–2249
Chester MA (1999) IUPAC-IUB Joint Commission on Biochemical Nomenclature (JCBN). Nomenclature of glycolipids. Recommendations 1997. Glycoconj J 16:1–6
Hakomori SI (2008) Structure and function of glycosphingolipids and sphingolipids: recollections and future trends. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:325–346
Lopez PHH, Schnaar R (2009) Gangliosides in cell recognition and membrane protein regulation. Curr Opin Struct Biol 19:549–557
Yu RK, Nakatani Y, Yanagisawa M (2009) The role of glycosphingolipid metabolism in the developing brain. J Lipid Res 50:S440–S445
Stancevic B, Kolesnick R (2010) Ceramide-rich platforms in transmembrane signaling. FEBS Lett 584:1728–1740
Hannun YA, Obeid LM (2008) Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: lessons from sphingolipids. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 9:139–150
Gault CR, Obeid LM, Hannun YA (2010) An overview of sphingolipid metabolism: from synthesis to breakdown. Adv Exp Med Biol 688:1–23
Karlsson KA (1989) Animal glycosphingolipids as membrane attachment sites for bacteria. Annu Rev Biochem 58:309–350
Smith DC, Lord JM, Roberts LM, Johannes L (2004) Glycosphingolipids as toxin receptors. Semin Cell Dev Biol 15:397–408
Lencer WI (2004) Retrograde transport of cholera toxin into the ER of host cells. Int J Med Microbiol 293:491–494
Lencer WI, Saslowsky D (2005) Raft trafficking of AB5 subunit bacterial toxins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1746:314–321
Pina DG, Johannes L (2005) Cholera and Shiga toxin B-subunits: thermodynamic and structural considerations for function and biomedical applications. Toxicon 45:389–393
Fujinaga Y (2006) Transport of bacterial toxins into target cells: pathways followed by cholera toxin and botulinum progenitor toxin. J Biochem 140:155–160
Chinnapen DJF, Chinnapen H, Saslowsky D, Lencer WI (2007) Rafting with cholera toxin: endocytosis and trafficking from plasma membrane to ER. FEMS Microbiol Lett 266:129–137
Binz T, Rummel A (2009) Cell entry strategy of clostridial neurotoxin. J Neurochem 109:1584–1595
Brunger AT, Rummel A (2009) Receptor and substrate interactions of clostridial neurotoxins. Toxicon 54:550–560
Kroken AR, Karalewitz AP, Fu Z, Baldwin MR, Kim JJ, Barbieri JT (2011) Unique ganglioside binding by botulinum neurotoxins C and D-SA. FEBS J 278:4486–4496
Engedal N, Skotland T, Torgersen ML, Sandvig K (2011) Shiga toxin and its use in targeted cancer therapy and imaging. Microb Biotechnol 4:32–46
Kovbasnjuk O, Mourtazina R, Baibakov B, Wang T, Elowsky C, Choti MA, Kane A, Donowitz M (2005) The glycosphingolipid globotriaosylceramide in the metastatic transformation of colon cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19087–19092
Falguières T, Maak M, von Weyhern C, Sarr M, Sastre X, Poupon MF, Robine S, Johannes L, Janssen KP (2008) Human colorectal tumors and metastases express Gb3 and can be targeted by an intestinal pathogen-based delivery tool. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2498–2508
Distler U, Souady J, Hülsewig M, Drmić-Hofman I, Haier J, Friedrich AW, Karch H, Senninger N, Dreisewerd K, Berkenkamp S, Schmidt MA, Peter-Katalinić J, Müthing J (2009) Shiga toxin receptor Gb3Cer/CD77: tumor association and promising therapeutic target in pancreas and colon cancer. PLoS One 4:e6813
Beddoe T, Paton AW, Le Nours J, Rossjohn J, Paton JC (2010) Structure, biological functions and applications of the AB5 toxins. Trends Biochem Sci 35:411–418
Hotz B, Backer MV, Backer JM, Buhr HJ, Hotz HG (2010) Specific targeting of tumor endothelial cells by Shiga-like toxin-vascular endothelial growth factor fusion protein as a novel treatment strategy for pancreatic cancer. Neoplasia 12:797–806
Maak M, Nitsche U, Keller L, Wolf P, Sarr M, Thiebaud M, Rosenberg R, Langer R, Kleeft J, Friess H, Johannes L, Janssen KP (2011) Tumor-specific targeting of pancreatic cancer with Shiga toxin B-subunit. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1918–1928
Lingwood CA (1999) Glycolipid receptors for verotoxin and Helicobacter pylori: role in pathology. Biochim Biophys Acta 1455:375–386
Nakajima H, Kiyokawa N, Katagiri YU, Taguchi T, Suzuki T, Sekino T, Mimori K, Ebata T, Saito M, Nakao H, Takeda T, Fujimoto J (2001) Kinetic analysis of binding between Shiga toxin and receptor glycolipid Gb3Cer by surface plasmon resonance. J Biol Chem 276:42915–42922
Meisen I, Friedrich AW, Karch H, Witting U, Peter-Katalinić J, Müthing J (2005) Application of combined high-performance thin-layer chromatography immunostaining and nanoelectrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight tandem mass spectrometry to the structural characterization of high- and low-affinity binding ligands of Shiga toxin 1. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 19:3659–3665
DeGrandis S, Law H, Brunton J, Gyles C, Lingwood CA (1989) Globotetraosylceramide is recognized by the pig edema disease toxin. J Biol Chem 264:12520–12525
Gillard BK, Jones MA, Marcus DM (1987) Glycosphingolipids of human umbilical vein endothelial cells and smooth muscle cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 256:435–445
Gillard BK, Jones MA, Turner AA, Lewis DE, Marcus DM (1990) Interferon-γ alters expression of endothelial cell-surface glycosphingolipids. Arch Biochem Biophys 279:122–129
Gillard BK, Heath JP, Thurmon LT, Marcus DM (1991) Association of glycosphingolipids with intermediate filaments of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 192:433–444
Gillard BK, Thurmon LT, Marcus DM (1993) Variable subcellular localization of glycosphingolipids. Glycobiology 3:57–67
Müthing J, Duvar S, Heitmann D, Hanisch FG, Neumann U, Lochnit G, Geyer R, Peter-Katalinić J (1999) Isolation and structural characterization of glycosphingolipids of in vitro propagated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Glycobiology 9:459–468
Okuda T, Nakakita SI, Nakayama KI (2010) Structural characterization and dynamics of globotetraosylceramide in vascular endothelial cells under TNF-α stimulation. Glycoconj J 27:287–296
Louise CB, Kaye SA, Boyd B, Lingwood CA, Obrig TG (1995) Shiga toxin-associated haemolytic uremic syndrome: effect of sodium butyrate on sensitivity of human umbilical vein endothelial cells to Shiga toxin. Infect Immun 63:2766–2769
Müthing J (2000) Analyses of glycosphingolipids by high-performance liquid chromatography. Methods Enzymol 312:45–64
Müthing J (1996) High-resolution thin-layer chromatography of gangliosides. J Chromatogr A 720:3–25
Müthing J (1998) TLC in structure and recognition studies of glycosphingolipids. In: Hounsell EF (ed) Methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totawa, pp 183–195
Kannagi R (2000) Monoclonal anti-glycosphingolipid antibodies. Methods Enzymol 312:160–179
Nutikka A, Binnington-Boyd B, Lingwood CA (2003) Methods for the identification of host receptors for Shiga toxin. Methods Mol Med 73:197–208
Raa H, Grimmer S, Schwudke D, Bergan J, Wälchli S, Skotland T, Shevchenko A, Sandvig K (2009) Glycosphingolipid requirements for endosome-to-Golgi transport of Shiga toxin. Traffic 10:868–882
Lingwood CA, Manis A, Mahfoud R, Khan F, Binnington B, Mylvaganam M (2010) New aspects of the regulation of glycosphingolipid receptor function. Chem Phys Lipids 163:27–35
Lingwood CA, Binnington B, Manis A, Branch DR (2010) Globotriaosylceramide receptor function—where membrane structure and pathology intersect. FEBS Lett 584:1879–1886
Robson WLM, Leung AKC, Montgomery MD (1991) Causes of death in hemolytic uremic syndrome. Child Nephrol Urol 11:228–233
Siegler RL (1994) Spectrum of extrarenal involvement in postdiarrheal hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Pediatr 125:511–518
Stins MF, Gilles F, Kim KS (1997) Selective expression of adhesion molecules on human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Neuroimmunol 76:81–90
Schweppe CH, Bielaszewska M, Pohlentz G, Friedrich AW, Büntemeyer H, Schmidt MA, Kim KS, Peter-Katalinić J, Karch H, Müthing J (2008) Glycosphingolipids in vascular endothelial cells: relationship of heterogeneity in Gb3Cer/CD77 receptor expression with differential Shiga toxin 1 cytotoxicity. Glycoconj J 25:291–304
Pellizzari A, Pang H, Lingwood CA (1992) Binding of verocytotoxin 1 to its receptor is influenced by differences in receptor fatty acid content. Biochemistry 31:1363–1370
Arab S, Lingwood CA (1996) Influence of phospholipid chain length on verotoxin/globotriaosylceramide binding in model membranes: comparison of a supported bilayer film and liposomes. Glycoconj J 13:159–166
Satchell SC, Tasman CH, Singh A, Ni L, Geelen J, von Ruhland CJ, O’Hare MJ, Saleem MA, van den Heuvel LP, Mathieson PW (2006) Conditionally immortalized human glomerular endothelial cells expressing fenestrations in response to VEGF. Kidney Int 69:1633–1640
Betz J, Bauwens A, Kunsmann L, Bielaszewska M, Mormann M, Humpf HU, Karch H, Friedrich AW, Müthing J (2012) Uncommon membrane distribution of Shiga toxin glycosphingolipid receptors in toxin-sensitive human glomerular microvascular endothelial cells. Biol Chem 393:133–147
Kanda T, Ariga T, Kubodera H, Jin HL, Owada K, Kasama T, Yamawaki M, Mizusawa H (2004) Glycosphingolipid composition of primary cultured human brain microvascular endothelial cells. J Neurosci Res 78:141–150
Müthing J, Distler U (2010) Advances on the compositional analysis of glycosphingolipids combining thin-layer chromatography with mass spectrometry. Mass Spectrom Rev 29:425–479
Meisen I, Mormann M, Müthing J (2011) Thin-layer chromatography, overlay technique and mass spectrometry: a versatile triad advancing glycosphingolipidomics. Biochim Biophys Acta 1811:875–896
Meisen I, Peter-Katalinić J, Müthing J (2003) Discrimination of neolacto-series gangliosides with α2-3- and α2-6-linked N-acetylneuraminic acid by nanoelectrospray ionization low-energy collision-induced dissociation tandem quadrupole TOF MS. Anal Chem 75:5719–5725
Meisen I, Peter-Katalinić J, Müthing J (2004) Direct analysis of silica gel extracts from immunostained glycosphingolipids by nanoelectrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Anal Chem 76:2248–2255
Hoffmann P, Hülsewig M, Duvar S, Ziehr H, Mormann M, Peter-Katalinić J, Friedrich AW, Karch H, Müthing J (2010) On the structural diversity of Shiga toxin glycosphingolipid receptors in lymphoid and myeloid cells determined by nanoelectrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun Mass Spectrom 24:2295–2304
Schweppe CH, Hoffmann P, Nofer JR, Pohlentz G, Mormann M, Karch H, Friedrich AW, Müthing J (2010) Neutral glycosphingolipids in human blood: a precise mass spectrometry analysis with special reference to lipoprotein-associated Shiga toxin receptors. J Lipid Res 51:2282–2294
Edgell CJS, MacDonald CC, Graham JB (1983) Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridizatíon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:3734–3737
Domon B, Costello CE (1988) Structure elucidation of glycosphingolipids and gangliosides using high-performance tandem mass spectrometry. Biochemistry 27:1534–1543
Domon B, Costello CE (1988) A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentation in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj J 5:397–409
Pust S, Dyve AB, Torgersen ML, van Deurs B, Sandvig K (2010) Interplay between toxin transport and flotillin localization. PLoS One 5:e8844
Brown DA, Rose KJ (1992) Sorting of GPI-anchored proteins to glycolipid enriched membrane subdomains during transport to the apical cell surface. Cell 68:533–544
Simons K, Gerl MJ (2010) Revitalizing membrane rafts: new tools and insights. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11:688–699
Munro S (2003) Lipid rafts: elusive or illusive? Cell 115:377–388
Dietrich C, Yang B, Fujiwara T, Kusumi A, Jacobson K (2002) Relationship of lipid rafts to transient confinement zones detected by single particle tracking. Biophys J 82:274–284
Gaus K, Gratton E, Kable EPW, Jones AS, Gelissen I, Kritharides L, Jessup W (2003) Visualizing lipid raft structure and raft domains in living cells with two-photon microscopy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:15554–15559
Lagerholm BC, Weinreb GE, Jacobson K, Thompson NL (2005) Detecting microdomains in intact cell membranes. Annu Rev Phys Chem 56:309–336
Azuma R, Kitagawa T, Kobayashi H, Konogaya A (2006) Particle simulation approach for subcellular dynamics and interactions of biological molecules. BMC Bioinforma 7(Suppl 4):S20
Kahya N (2006) Targeting membrane proteins to liquid-ordered phases: molecular self-organization explored by fluorescence correlation spectroscopy. Chem Phys Lipids 141:158–168
Eggeling C, Ringemann C, Medda R, Schwarzmann G, Sandhoff K, Polyakova S, Belov VN, Hein B, von Middendorff C, Schönle A, Hell SW (2009) Direct observation of the nanoscale dynamics of membrane lipids in a living cell. Nature 457:1159–1162
Engel S, Scolari S, Thaa B, Krebs N, Korte T, Herrmann A, Veit M (2010) FLIM-FRET and FRAP reveal association of virus haemagglutinin with membrane rafts. Biochem J 425:567–573
Zhong J (2011) From simple to complex: investigating the effects of lipid composition and phase on the membrane interactions of biomolecules using in situ atomic force microscopy. Integr Biol 3:632–644
Bastos AE, Scolari S, Stöckl M, de Almeida RF (2012) Applications of fluorescence lifetime spectroscopy and imaging to lipid domains in vivo. Methods Enzymol 504:57–81
Lingwood D, Simons K (2010) Lipid rafts as a membrane-organizing principle. Science 327:46–50
Simons K, Sampaio JL (2011) Membrane organization and lipid rafts. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3:a004697
Zaas DW, Duncan M, Wright JR, Abraham SN (2005) The role of lipid rafts in the pathogenesis of bacterial infections. Biochim Biophys Acta 746:305–313
Allen JA, Halverson-Tamboli RA, Rasenick MM (2007) Lipid raft microdomains and neurotransmitter signalling. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:128–140
Hanzal-Bayer MF, Hancock JF (2007) Lipid rafts and membrane traffic. FEBS Lett 581:2098–2104
Vieira FS, Corrêa G, Einicker-Lamast M, Coutinho-Silva R (2010) Host-cell lipid rafts: a safe door for micro-organisms? Biol Cell 102:391–407
Fessler MB, Parks JS (2011) Intracellular lipid flux and membrane microdomains as organizing principles in inflammatory cell signaling. J Immunol 187:1529–1535
Sonnino S, Prinetti A, Mauri L, Chigorno V, Tettamanti G (2006) Dynamic and structural properties of sphingolipids as driving forces for the formation of membrane domains. Chem Rev 106:2111–2125
Sonnino S, Mauri L, Chigorno V, Prinetti A (2007) Gangliosides as components of lipid membrane domains. Glycobiology 17:1R–13R
Prinetti A, Loberto N, Chigorno V, Sonnino S (2009) Glycosphingolipid behaviour in complex membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:184–193
Pike LJ (2009) The challenge of lipid rafts. J Lipid Res 50:S323–S328
Gupta G, Surolia A (2010) Glycosphingolipids in microdomain formation and their spatial organization. FEBS Lett 584:1634–1641
Maeda Y, Kinoshita T (2011) Structural remodeling, trafficking and functions of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. Prog Lipid Res 50:411–424
Aicart-Ramos C, Valero RA, Rodriguez-Crespo I (2011) Protein palmitoylation and subcellular trafficking. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:2981–2994
Quinn PJ (2010) A lipid matrix model of membrane raft structure. Prog Lipid Res 49:390–406
Maggio B, Fanani ML, Rosetti CM, Wilke N (2006) Biophysics of sphingolipids II. Glycosphingolipids: an assortment of multiple structural information transducers at the membrane surface. Biochim Biophys Acta 1758:1922–1944
Westerlund B, Slotte JP (2009) How the molecular features of glycosphingolipids affect domain formation in fluid membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta 1788:194–201
Hakomori SI (2002) The glycosynapse. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:225–232
Hakomori SI (2000) Cell adhesion/recognition and signal transduction through glycosphingolipid microdomain. Glycoconj J 17:143–151
Todeschini AR, Hakomori SI (2008) Functional role of glycosphingolipids and gangliosides in control of cell adhesion, motility, and growth, through glycosynaptic microdomains. Biochim Biophys Acta 1780:421–433
Hakomori SI (2010) Glycosynaptic microdomains controlling tumor cell phenotype through alteration of cell growth, adhesion, and mortality. FEBS Lett 584:1901–1906
Fantini J, Maresca M, Hammache D, Yahi N, Delézay O (2000) Glycosphingolipid (GSL) microdomain as attachment platforms for host pathogens and their toxins on intestinal epithelial cells: activation of signal transduction pathways and perturbations of intestinal absorption and secretion. Glycoconj J 17:173–179
Kasahara K, Sanai Y (2000) Functional roles of glycosphingolipids in signal transduction via lipid rafts. Glycoconj J 17:153–162
Sorice M, Longo A, Garofalo T, Mattei V, Misasi R, Pavan A (2004) Role of GM3-enriched microdomains in signal transduction regulation in T lymphocytes. Glycoconj J 20:63–70
Sonnino S, Prinetti A, Nakayama H, Yangida M, Ogawa H, Iwabuchi K (2009) Role of very long fatty acid-containing glycosphingolipids in membrane organization and cell signaling: the model of lactosylceramide in neutrophils. Glycoconj J 26:615–621
Iwabuchi K, Nakayama H, Iwahara C, Takamori K (2010) Significance of glycosphingolipid fatty acid chain length on membrane microdomain-mediated signal transduction. FEBS Lett 584:1642–1652
Yoshizaki F, Nakayama H, Iwahara C, Takamori K, Ogawa H, Iwabuchi K (2008) Role of glycosphingolipid-enriched microdomains in innate immunity: microdomain-dependent phagocytic cell functions. Biochim Biophys Acta 170:383–392
Schengrund CL (2010) Lipid rafts: keys to neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull 82:7–17
Fantini J (2003) How sphingolipids bind and shape proteins: molecular basis of lipid–protein interactions in lipid shells, rafts and related biomembrane domains. Cell Mol Life Sci 60:1027–1032
London E, Brown DA (2000) Insolubility of lipids in Triton X-100: physical origin and relationship to sphingolipid/cholesterol membrane domains (rafts). Biochim Biophys Acta 1508:182–195
Lingwood D, Simons K (2007) Detergent resistance as a tool in membrane research. Nat Protoc 2:2159–2165
Brown DA (2006) Lipid rafts, detergent-resistant membranes, and raft targeting signals. Physiology 21:430–439
Lichtenberg D, Goni FM, Heerklotz H (2005) Detergent-resistant membranes should not be identified with membrane rafts. Trends Biochem Sci 30:430–436
Sens P, Johannes L, Bassereau P (2008) Biophysical approaches to protein-induced membrane deformations in trafficking. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20:476–482
Safouane M, Berland L, Callan-Jones A, Sorre B, Römer W, Johannes L, Toombes GES, Bassereau P (2010) Lipid cosorting mediated by Shiga toxin induced tubulation. Traffic 11:1519–1529
Kovbasnjuk O, Edidin M, Donovitz M (2001) Role of lipid rafts in Shiga toxin 1 interaction with the apical surface of Caco-2 cells. J Cell Sci 114:4025–4031
Hanashima T, Miyake M, Yahiro K, Iwamaru Y, Ando A, Morinaga N, Noda M (2008) Effect of Gb3 in lipid rafts in resistance to Shiga-like toxin of mutant Vero cells. Microb Pathog 45:124–133
Falguières T, Mallard F, Baron C, Hanau D, Lingwood C, Goud B, Salamero J, Johannes L (2001) Targeting of Shiga toxin B-subunit to retrograde transport route in association with detergent-resistant membranes. Mol Biol Cell 12:2453–2468
Falguières T, Römer W, Amessou M, Afonso C, Wolf C, Tabet JC, Lamaze C, Johannes L (2006) Functionally different pools of Shiga toxin receptor, globotriaosylceramide, in HeLa cells. FEBS J 273:5205–5218
Smith DC, Sillence DJ, Falguières T, Jarvis RM, Johannes L, Lord JM, Platt FM, Roberts LM (2006) The association of Shiga-like toxin with detergent-resistant membranes is modulated by glucosylceramide and is an essential requirement in the endoplasmic reticulum for a cytotoxic effect. Mol Biol Cell 17:1375–1387
Katagiri YU, Mori T, Nakajima H, Katagiri C, Taguchi T, Takeda T, Kiyokawa N, Fujimoto J (1999) Activation of Src family kinase Yes induced by Shiga toxin binding to globotriaosylceramide (Gb3Cer/CD77) in low density, detergent-insoluble microdomains. J Biol Chem 274:35278–35282
Takenouchi H, Kiyokawa N, Taguchi T, Matsui J, Katagiri YU, Okita H, Okuda K, Fujimoto J (2004) Shiga toxin binding to globotriaosylceramide induces intracellular signals that mediate cytoskeleton remodeling in human renal carcinoma-derived cells. J Cell Sci 117:3911–3922
Tam P, Mahfoud R, Nutikka A, Khine AA, Binnington B, Paroutis P, Lingwood C (2008) Differential intracellular transport and binding of verotoxin 1 and verotoxin 2 to globotriaosylceramide-containing lipid assemblies. J Cell Physiol 216:750–763
Mafoud R, Manis A, Lingwood CA (2009) Fatty acid-dependent globotriaosylceramide receptor function in detergent resistant membranes. J Lipid Res 50:1744–1755
Mafoud R, Manis A, Binnington B, Ackerley C, Lingwood CA (2010) A major fraction of glycosphingolipids in model and cellular cholesterol-containing membranes is undetectable by their binding proteins. J Biol Chem 285:36049–36059
Lingwood D, Binnington B, Róg T, Vattulainen I, Grzybek M, Coskun Ü, Lingwood CA, Simons K (2011) Cholesterol modulates glycolipid conformation and receptor activity. Nat Chem Biol 7:260–262
Kenworthy A (2002) Peering inside lipid rafts and caveolae. Trends Biochem Sci 27:435–438
Michel V, Bakovic M (2007) Lipid rafts in health and disease. Biol Cell 99:129–140
Lajoie P, Nabi IR (2010) Lipid rafts, caveolae, and their endocytosis. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol 282:135–163
Anderson RGW (1998) The caveolae membrane system. Annu Rev Biochem 67:199–225
Frank PG, Woodman SE, Park DS, Lisanti MP (2003) Caveolin, caveolae, and endothelial cell function. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 23:1161–1168
Cohen AW, Hnasko R, Schubert W, Lisanti MP (2004) Role of caveolae and caveolins in health and disease. Physiol Rev 84:1341–1379
Li XA, Everson WV, Smart EJ (2005) Caveolae, lipid rafts, and vascular disease. Trends Cardiovasc Med 15:92–96
Mineo C, Shaul PW (2006) Circulating cardiovascular disease risk factors and signaling in endothelial cell caveolae. Cardiovasc Res 70:31–41
Parton RG, Simons K (2007) The multiple faces of caveolae. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:185–194
Hansen CG, Nichols BJ (2009) Molecular mechanisms of clathrin-independent endocytosis. J Cell Sci 122:1713–1721
Hansen CG, Nichols BJ (2010) Exploring the caves: cavins, caveolins and caveolae. Trends Cell Biol 20:177–186
Chidlow JH Jr, Sessa WC (2010) Caveolae, caveolins, and cavins: complex control of cellular signalling and inflammation. Cardiovasc Res 86:219–225
Sprenger RR, Fontijn RD, van Marl J, Pannekoek H, Horrevoets AJG (2006) Spatial segregation of transport and signalling functions between human endothelial caveolae and lipid raft proteomes. Biochem J 400:401–410
Anderson RGW, Jacobson K (2002) A role for lipid shells in targeting proteins to caveolae, rafts, and other lipid domains. Science 296:1821–1825
Stan RV (2002) Structure and function of endothelial caveolae. Microsc Res Tech 57:350–364
Nabi IR, Le PU (2003) Caveolae/raft-dependent endocytosis. J Cell Biol 161:673–677
Parton RG, Richards AA (2003) Lipid rafts and caveolae as portals for endocytosis: new insights and common mechanisms. Traffic 4:724–738
van Deurs B, Roepstorff K, Hommelgaard AM, Sandvig K (2003) Caveolae: anchored, multifunctional platforms in the lipid ocean. Trends Cell Biol 13:92–100
Hommelgaard AM, Roepstorff K, Vilhardt F, Torgersen ML, Sandvig K, van Deurs B (2005) Caveolae: stable membrane domains with a potential for internalization. Traffic 6:720–724
Lakhan SE, Sabharanjak S, De A (2009) Endocytosis of glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored proteins. J Biomed Sci 16:93
Cheng ZJ, Singh RD, Marks DL, Pagano RE (2006) Membrane microdomains, caveolae, and caveolar endocytosis of sphingolipids. Mol Membr Biol 23:101–110
Sonnino S, Prinetti A (2009) Sphingolipids and membrane environments for caveolin. FEBS Lett 583:597–606
Yu RK, Suzuki Y, Yanagisawa M (2010) Membrane glycolipids in stem cells. FEBS Lett 584:1694–1699
Higashi N, Matsumura Y, Mizuno F, Kasahara K, Sugiura S, Mikasa K, Kita E (2010) Enhanced expression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1 in non-rafts decreases the sensitivity of vascular endothelial cells to Shiga toxin. Microb Pathog 49:141–152
Paton JC, Paton AW (2006) Shiga toxin ‘goes retro’ in human primary kidney cells. Kidney Int 70:2049–2051
Khan F, Proulx F, Lingwood CA (2009) Detergent-resistant globotriaosylceramide may define verotoxin/glomeruli-restricted haemolytic uremic syndrome pathology. Kidney Int 75:1209–1216
Betz J, Bielaszewska M, Thies A, Humpf HU, Dreisewerd K, Karch H, Kim KS, Friedrich AW, Müthing J (2011) Shiga toxin glycosphingolipid receptors in microvascular and macrovascular endothelial cells: differential association with membrane lipid raft microdomains. J Lipid Res 52:618–634
Scheiring J, Andreoli SP, Zimmerhackl LB (2008) Treatment and outcome of Shiga toxin-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS). Pediatr Nephrol 23:1749–1760
Wong CS, Jelacic S, Habeeb RL, Watkins SL, Tarr PI (2000) The risk of the hemolytic-uremic syndrome after antibiotic treatment of Escherichia coli O157:H7 infections. N Eng J Med 342:1930–1936
Serna A 4th, Boedeker EC (2008) Pathogenesis and treatment of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 24:38–47
Mukhopadhyay S, Linstedt AD (2012) Manganese blocks intracellular trafficking of Shiga toxin and protects against Shiga toxicosis. Science 335:332–335
Bitzan M (2009) Treatment options for HUS secondary to Escherichia coli O157:H7. Kidney Int 75:S62–S66
Bitzan M, Schaefer F, Reymond D (2010) Treatment of typical (enteropathic) hemolytic uremic syndrome. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:594–610
Paton AW, Morona R, Paton JC (2000) A new biological agent for treatment of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli infections and dysentery in humans. Nat Med 6:265–270
Paton AW, Morona R, Paton JC (2001) Neutralization of Shiga toxins Stx1, Stx2c, and Stx2e by recombinant bacteria expressing mimics of globotriose and globotetraose. Infect Immun 69:1967–1970
Jeong KI, Tzipori S, Sheoran AS (2010) Shiga toxin 2-specific but not Shiga toxin 1-specific human monoclonal antibody protects piglets challenged with enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli producing Shiga toxin 1 and Shiga toxin 2. J Infect Dis 201:1081–1083
Dowling TC, Chavaillaz PA, Young DG, Melton-Celsa A, O’Brien A, Thuning-Roberson C, Edelman R, Tacket CO (2005) Phase 1 safety and pharmacokinetic study of chimeric murine-human monoclonal antibody cαStx2 administered intravenously to healthy adult volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 49:1808–1812
Bitzan M, Poole R, Mehran M, Sicard E, Brockus C, Thuning-Roberson C, Rivière M (2009) Safety and pharmacokinetics of chimeric anti-Shiga toxin 1 and anti-Shiga toxin 2 monoclonal antibodies in healthy volunteers. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 53:3081–3087
Kitov PI, Sadowska JM, Mulvey G, Armstrong GD, Ling H, Pannu NS, Read RJ, Bundle DR (2000) Shiga-like toxins are neutralized by tailored multivalent carbohydrate ligands. Nature 403:669–672
Williams SJ, Davies GJ (2001) Protein–carbohydrate interactions: learning lessons from nature. Trends Biotechnol 19:356–362
Mulvey GL, Marcato P, Kitov PI, Sadowska J, Bundle DR, Armstrong GD (2003) Assessment in mice of therapeutic potential of tailored, multivalent Shiga toxin carbohydrate ligands. J Infect Dis 187:640–649
Nishikawa K, Matsuoka K, Kita E, Okabe N, Mizuguchi M, Hino K, Miyazawa S, Yamasaki C, Aoki J, Takashima S, Yamakawa Y, Nishijima M, Terunuma D, Kuzuhara H, Natori Y (2002) A therapeutic agent with oriented carbohydrates for treatment of infections by Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157:H7. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:7669–7674
Karmali MA (2004) Prospects for preventing serious systemic toxemic complications of Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli infections using Shiga toxin receptor analogues. J Infect Dis 189:355–359
Watanabe M, Matsuoka K, Kita E, Igai K, Higashi N, Miyagawa A, Watanabe T, Yanoshita R, Samejima Y, Terunuma D, Natori Y, Nishikawa K (2004) Oral therapeutic agents with highly clustered globotriose for treatment of Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli infections. J Infect Dis 189:360–368
Nishikawa K, Matsuoka K, Watanabe M, Igai K, Hino K, Hatano K, Yamada A, Abe N, Terunuma D, Kuzuhara H, Natori Y (2005) Identification of the optimal structure required for a Shiga toxin neutralizer with oriented carbohydrates to function in the circulation. J Infect Dis 191:2097–2105
Clark GC, Basak AK, Titball RW (2007) The rational design of bacterial toxin inhibitors. Curr Comput Aided Drug Des 3:1–12
Trachtman H, Cnaan A, Christen E, Gibbs K, Zhao S, Acheson DWK, Weiss R, Kaskel FJ, Spitzer A, Hirschman GH (2003) Effect of an oral Shiga toxin-binding agent on diarrhea-associated hemolytic uremic syndrome in children. JAMA 290:1337–1344
MacConnachie AA, Todd WT (2004) Potential therapeutic agents for the prevention and treatment of haemolytic uraemic syndrome in Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli infection. Curr Opin Infect Dis 17:479–482
Sharon N (2006) Carbohydrates as future anti-adhesion drugs for infectious diseases. Biochim Biophys Acta 1760:527–537
Thomas RJ (2010) Receptor mimicry as novel therapeutic treatment for biothreat agents. Bioeng Bugs 1:17–30
Kulkarni AA, Weiss AA, Iyer SS (2010) Glycan-based high-affinity ligands for toxins and pathogen receptors. Med Res Rev 30:327–393
Orth D, Khan AB, Naim A, Grif K, Brockmeyer J, Karch H, Joannidis M, Clark SJ, Day AJ, Fidanzi S, Stoiber H, Dierich MP, Zimmerhackl LB, Würzner R (2009) Shiga toxin activates complement and binds factor H: evidence for an active role of complement in hemolytic uremic syndrome. J Immunol 182:6349–6400
Lapeyraque AL, Malina M, Fremeaux-Bacchi V, Boppel T, Kirschfink M, Oualha M, Proulx F, Clermont MJ, Le Deist F, Niaudet P, Schaefer F (2011) Eculizumab in severe Shiga-toxin-associated HUS. N Engl J Med 364:2561–2563
Orth-Höller D, Riedl M, Würzner R (2011) Inhibition of terminal complement activation in severe Shiga toxin-associated HUS—perfect example for a fast track from bench to bedside. EMBO Mol Med 3:617–619
Lingwood CA (1994) Verotoxin-binding in human renal sections. Nephron 66:21–28
Kaneko K, Kiyokawa N, Ohtomo Y, Nagaoka R, Yamashiro Y, Taguchi T, Mori T, Fujimoto J, Takeda T (2001) Apoptosis of renal tubular cells in Shiga-toxin-mediated haemolytic uremic syndrome. Nephron 87:182–185
Creydt VP, Silberstein C, Zotta E, Ibarra C (2006) Cytotoxic effect of Shiga toxin-2 holotoxin and ist B subunit on human renal tubular epithelial cells. Microbes Infect 8:410–419
Silberstein C, Creydt VP, Gerhardt E, Núñez P, Ibarra C (2008) Inhibition of water absorption in human proximal tubular epithelial cells in response to Shiga toxin-2. Pediatr Nephrol 23:1981–1990
Lentz EK, Leyva-Illades D, Lee MS, Cherla RP, Tesh VL (2011) Differential response of the human renal proximal tubular epithelial cell line HK-2 to Shiga toxin types 1 and 2. Infect Immun 79:3527–3540
van Setten PA, van Hinsbergh VWM, van den Heuvel LPWJ, van der Velden TJAN, van de Kar NCAJ, Krebbers RJM, Karmali MA, Monnens LAH (1997) Verocytotoxin inhibits mitogenesis and protein synthesis in purified human glomerular mesangial cells without affecting cell viability: evidence for two distinct mechanisms. J Am Soc Nephrol 8:1877–1888
Simon M, Cleary TG, Hernandez JD, Abboud HE (1998) Shiga toxin 1 elicits diverse biologic responses in mesangial cells. Kidney Int 54:1117–1127
Ren J, Utsunomiya I, Taguchi K, Ariga T, Tai T, Ihara Y, Miyatake T (1999) Localization of verotoxin receptors in nervous system. Brain Res 825:183–188
Obata F, Tohyama K, Bonev AD, Kolling GL, Keepers TR, Gross LK, Nelson MT, Sato S, Obrig TG (2008) Shiga toxin 2 affects the central nervous system through receptor globotriaosylceramide localized to neurons. J Infect Dis 198:1398–1406
Arab S, Murakami M, Dirks P, Boyd B, Hubbard SL, Lingwood CA, Rutka JT (1998) Verotoxins inhibit the growth of and induce apoptosis in human astrocytoma cells. J Neurooncol 40:137–150
Arab S, Rutka J, Lingwood C (1999) Verotoxin induces apoptosis and the complete, rapid, long-term elimination of human astrocytoma xenografts in nude mice. Oncol Res 11:33–39
Salhia B, Rutka JT, Lingwood C, Nutikka A, van Furth WR (2002) The treatment of malignant meningioma with verotoxin. Neoplasia 4:304–311
Johansson D, Johansson A, Grankvist K, Andersson U, Henriksson R, Bergström P, Brännström T, Behnam-Motlagh P (2006) Verotoxin-1 induction of apoptosis in Gb3-expressing human glioma cell lines. Cancer Biol Ther 5:1211–1217
Jinadasa RN, Bloom SE, Weiss RS, Duhamel GE (2011) Cytolethal distending toxin: a conserved bacetrial genotoxin that blocks cell cycle progression, leading to apoptosis of a broad range of mammalian cell lineages. Microbiology 157:1851–1875
Schmidt H, Benz R (2003) Detection and characterization of EHEC-hemolysin. Methods Mol Med 73:151–163
Paton AW, And Paton JC (2010) Escherichia coli subtilase cytotoxin. Toxins 2:215–228
Bielaszewska M, Sinha B, Kuczius T, Karch H (2005) Cytolethal distending toxin from Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O157 causes irreversible G2/M arrest, inhibition of proliferation, and death of human endothelial cells. Infect Immun 73:552–562
Friedrich AW, Lu S, Bielaszewska M, Prager R, Bruns P, Xu JG, Tschäpe H, Karch H (2006) Cytolethal distending toxin in Escherichia coli O157:H7: spectrum of conservation, structure, and endothelial toxicity. J Clin Microbiol 44:1844–1846
Bielaszewska M, Stoewe F, Fruth A, Zhang W, Prager R, Brockmeyer J, Mellmann A, Karch H, Friedrich AW (2009) Shiga toxin, cytolethal distending toxin, and hemolysin repertoires in clinical Escherichia coli O91 isolates. J Clin Microbiol 47:2061–2066
Aldick T, Bielaszewska M, Zhang W, Brockmeyer J, Schmidt H, Friedrich AW, Kim KS, Schmidt MA, Karch H (2007) Hemolysin from Shiga toxin-negative Escherichia coli O26 strains injures microvascular endothelium. Microbes Infect 9:282–290
Aldick T, Bielaszewska M, Uhlin BE, Humpf HU, Wai SN, Karch H (2009) Vesicular stabilization and activity augmentation of enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli haemolyisn. Mol Microbiol 71:1496–1508
Brockmeyer J, Aldick T, Soltwisch J, Zhang W, Tarr PI, Weiss A, Dreisewerd K, Müthing J, Bielaszewska M, Karch H (2011) Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli haemolysin is cleaved and inactivated by serine protease EspPα. Environ Microbiol 13:1327–1341
Furukawa T, Yahiro K, Tsuji AB, Terasaki Y, Morinaga N, Miyazaki M, Fukuda Y, Saga T, Moss J, Noda M (2011) Fatal hemorrhage induced by subtilase cytotoxin from Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli. Microb Pathog 50:159–167
Varki A (2001) Loss of N-glycolylneuraminic acid in humans: mechanisms, consequences, and implications for hominid evolution. Am J Phys Anthropol (Suppl 33):54–69
Wang H, Paton JC, Thorpe CM, Bonder CS, Sun WY, Paton AW (2010) Tissue factor-dependent procoagulant activity of subtilase cytotoxin, a potent AB5 toxin produced by Shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli. J Infect Dis 202:1415–1423
Byres E, Paton AW, Paton JC, Löfling JC, Smith DF, Wilce MCJ, Talbot UM, Chong DC, Yu H, Huang S, Chen X, Varki NM, Varki A (2008) Incorporation of a non-human glycan mediates human susceptibility to a bacterial toxin. Nature 456:648–652
Löfling JC, Paton AW, Varki NM, Paton JC, Varki A (2009) A dietary non-human sialic acid may facilitate hemolytic-uremic syndrome. Kidney Int 76:140–144
Varki A (2007) Glycan-based interactions involving vertebrate sialic-acid-recognizing proteins. Nature 446:1023–1029
Raman R, Venkataraman M, Ramakrishnan S, Lang W, Raguram S, Sasisekharan R (2006) Advancing glycomics: implementation strategies at the consortium for functional glycomics. Glycobiology 16:82R–90R
Acknowledgments
J.M. is grateful for continuous support of his work by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG), MU845/4-1 and MU845/4-2, the GRK 1409/1 and 1409/2 and grants from the Interdisciplinary Center of Clinical Research (IZKF) Münster, project no. Müth2/028/10 as well as the National Research Platform for Zoonoses funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF, project 01KI1106). H.K. gratefully acknowledges financial support of the DFG, KA 717/5-1, grants from the IZKF Münster, project no. Me2/021/12, and the National Research Platform for Zoonoses funded by the BMBF (project 01KI1012B). B.K. acknowledges financial support by the BMBF within the reserach focus program “Biophotonics” (FKZ 13N9270, FKZ 13N10937).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauwens, A., Betz, J., Meisen, I. et al. Facing glycosphingolipid–Shiga toxin interaction: dire straits for endothelial cells of the human vasculature. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 70, 425–457 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1060-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-1060-z