Abstract
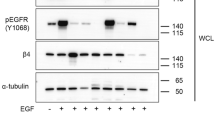
The laminin-binding integrin α6β4 plays key roles in both normal epithelial and endothelial cells and during tumor cell progression, metastasis, and angiogenesis. Previous cysteine mutagenesis studies have suggested that palmitoylation of α6β4 protein supports a few integrin-dependent functions and molecular associations. Here we took another approach and obtained strikingly different results. We used overexpression and RNAi knockdown in multiple cell types to identify protein acyl transferase DHHC3 as the enzyme responsible for integrin β4 and α6 palmitoylation. Ablation of DHHC3 markedly diminished integrin-dependent cellular cable formation on Matrigel, integrin signaling through Src, and β4 phosphorylation on key diagnostic amino acids (S1356 and 1424). However, unexpectedly, and in sharp contrast to prior α6β4 mutagenesis results, knockdown of DHHC3 accelerated the degradation of α6β4, likely due to an increase in endosomal exposure to cathepsin D. When proteolytic degradation was inhibited (by Pepstatin A), rescued α6β4 accumulated intracellularly, but was unable to reach the cell surface. DHHC3 ablation effects were strongly selective for α6β4. Cell-surface levels of ~10 other proteins (including α3β1) were not diminished, and the appearance of hundreds of other palmitoylated proteins was not altered. Results obtained here demonstrate a new substrate for the DHHC3 enzyme and provide novel opportunities for modulating α6β4 expression, distribution, and function.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rabinovitz I, Gipson IK, Mercurio AM (2001) Traction forces mediated by alpha6beta4 integrin: implications for basement membrane organization and tumor invasion. Mol Biol Cell 12:4030–4043
de Pereda JM, Ortega E, Alonso-Garcia N, Gomez-Hernandez M, Sonnenberg A (2009) Advances and perspectives of the architecture of hemidesmosomes: lessons from structural biology. Cell Adh Migr 3:361–364
Georges-Labouesse EN, Messaddeq N, Yehia G, Cadalbert L, Dierich A, Le Meur M (1996) Absence of the alpha-6 integrin leads to epidermolysis bullosa and neonatal death in mice. Nat Genet 13:370–373
Pulkkinen L, Uitto J (1999) Mutation analysis and molecular genetics of epidermolysis bullosa. Matrix Biol 18:29–42
Kasirer-Friede A, Kahn ML, Shattil SJ (2007) Platelet integrins and immunoreceptors. Immunol Rev 218:247–264
Borland G, Cushley W (2004) Positioning the immune system: unexpected roles for alpha6-integrins. Immunology 111:381–383
Haworth O, Hardie DL, Burman A, Rainger GE, Eksteen B, Adams DH, Salmon M, Nash GB, Buckley CD (2008) A role for the integrin alpha6beta1 in the differential distribution of CD4 and CD8 T-cell subsets within the rheumatoid synovium. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47:1329–1334
McMillan NA, Payne E, Frazer IH, Evander M (1999) Expression of the alpha6 integrin confers papillomavirus binding upon receptor-negative B-cells. Virology 261:271–279
Lipscomb EA, Mercurio AM (2005) Mobilization and activation of a signaling competent alpha6beta4integrin underlies its contribution to carcinoma progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24:413–423
Stipp CS (2010) Laminin-binding integrins and their tetraspanin partners as potential antimetastatic targets. Expert Rev Mol Med 12:e3
Nikolopoulos SN, Blaikie P, Yoshioka T, Guo W, Giancotti FG (2004) Integrin beta4 signaling promotes tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell 6:471–483
Yang XH, Flores LM, Li Q, Zhou P, Xu F, Krop IE, Hemler ME (2010) Disruption of laminin-integrin-CD151-focal adhesion kinase axis sensitizes breast cancer cells to ErbB2 antagonists. Cancer Res 70:2256–2263
M. Colombel, C. L. Eaton, F. Hamdy, E. Ricci, G. van der Pluijm, M. Cecchini, F. Mege-Lechevallier, P. Clezardin, G. Thalmann (2011) Increased expression of putative cancer stem cell markers in primary prostate cancer is associated with progression of bone metastases. Prostate
Honeth G, Bendahl PO, Ringner M, Saal LH, Gruvberger-Saal SK, Lovgren K, Grabau D, Ferno M, Borg A, Hegardt C (2008) The CD44+/CD24− phenotype is enriched in basal-like breast tumors. Breast Cancer Res 10:R53
Berditchevski F (2001) Complexes of tetraspanins with integrins: more than meets the eye. J Cell Sci 114:4143–4151
Sterk LM, Geuijen CA, van Den Berg JG, Claessen N, Weening JJ, Sonnenberg A (2002) Association of the tetraspanin CD151 with the laminin-binding integrins alpha3beta1, alpha6beta1, alpha6beta4 and alpha7beta1 in cells in culture and in vivo. J Cell Sci 115:1161–1173
Hemler ME (2003) Tetraspanin proteins mediate cellular penetration, invasion and fusion events, and define a novel type of membrane microdomain. Ann Rev Cell Dev Biol 19:397–422
Yang X, Kovalenko OV, Tang W, Claas C, Stipp CS, Hemler ME (2004) Palmitoylation supports assembly and function of integrin-tetraspanin complexes. J Cell Biol 167:1231–1240
Gagnoux-Palacios L, Dans M, Van’t Hof W, Mariotti A, Pepe A, Meneguzzi G, Resh MD, Giancotti FG (2003) Compartmentalization of integrin {alpha}6{beta}4 signaling in lipid rafts. J Cell Biol 162:1189–1196
Mitchell DA, Vasudevan A, Linder ME, Deschenes RJ (2006) Protein palmitoylation by a family of DHHC protein S-acyltransferases. J Lipid Res 47:1118–1127
Tsutsumi R, Fukata Y, Fukata M (2008) Discovery of protein-palmitoylating enzymes. Pflugers Arch 456:1199–1206
Ohno Y, Kihara A, Sano T, Igarashi Y (2006) Intracellular localization and tissue-specific distribution of human and yeast DHHC cysteine-rich domain-containing proteins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1761:474–483
Fang C, Deng L, Keller CA, Fukata M, Fukata Y, Chen G, Luscher B (2006) GODZ-mediated palmitoylation of GABA(A) receptors is required for normal assembly and function of GABAergic inhibitory synapses. J Neurosci 26:12758–12768
Sharma C, Yang XH, Hemler ME (2008) DHHC2 affects palmitoylation and stability of tetraspanins CD9 and CD151. Mol Biol Cell 19:3415–3425
Abrami L, Kunz B, Iacovache I, van der Goot FG (2008) Palmitoylation and ubiquitination regulate exit of the Wnt signaling protein LRP6 from the endoplasmic reticulum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:5384–5389
Alvarez E, Girones N, Davis RJ (1990) Inhibition of the receptor-mediated endocytosis of diferric transferrin is associated with the covalent modification of the transferrin receptor with palmitic acid. J Biol Chem 265:16644–16655
Percherancier Y, Planchenault T, Valenzuela-Fernandez A, Virelizier JL, Arenzana-Seisdedos F, Bachelerie F (2001) Palmitoylation-dependent control of degradation, life span, and membrane expression of the CCR5 receptor. J Biol Chem 276:31936–31944
Yanez-Mo M, Barreiro O, Gordon-Alonso M, Sala-Valdes M, Sanchez-Madrid F (2009) Tetraspanin-enriched microdomains: a functional unit in cell plasma membranes. Trends Cell Biol 19:434–446
Seehafer JG, Slupsky JR, Tang SC, Masellis-Smith A, Shaw AR (1990) Myristic acid is incorporated into the two acylatable domains of the functional glycoprotein CD9 in ester, but not in amide bonds. Biochim Biophys Acta 1039:218–226
Yang X, Claas C, Kraeft SK, Chen LB, Wang Z, Kreidberg JA, Hemler ME (2002) Palmitoylation of tetraspanin proteins: modulation of CD151 lateral interactions, subcellular distribution, and integrin-dependent cell morphology. Mol Biol Cell 13:767–781
Berditchevski F, Odintsova E, Sawada S, Gilbert E (2002) Expression of the palmitoylation-deficient CD151 weakens the association of alpha 3beta 1 integrin with the tetraspanin-enriched microdomains and affects integrin-dependent signalling. J Biol Chem 277:36991–37000
Charrin S, Manie S, Oualid M, Billard M, Boucheix C, Rubinstein E (2002) Differential stability of tetraspanin/tetraspanin interactions: role of palmitoylation. FEBS Lett 516:139–144
Keller CA, Yuan X, Panzanelli P, Martin ML, Alldred M, Sassoe-Pognetto M, Luscher B (2004) The gamma2 subunit of GABA(A) receptors is a substrate for palmitoylation by GODZ. J Neurosci 24:5881–5891
Tsutsumi R, Fukata Y, Noritake J, Iwanaga T, Perez F, Fukata M (2009) Identification of G protein alpha subunit-palmitoylating enzyme. Mol Cell Biol 29:435–447
Wang J, Xie Y, Wolff DW, Abel PW, Tu Y (2010) DHHC protein-dependent palmitoylation protects regulator of G-protein signaling 4 from proteasome degradation. FEBS Lett 584:4570–4574
Germain EC, Santos TM, Rabinovitz I (2009) Phosphorylation of a novel site on the {beta}4 integrin at the trailing edge of migrating cells promotes hemidesmosome disassembly. Mol Biol Cell 20:56–67
Kashyap T, Germain E, Roche M, Lyle S, Rabinovitz I (2011) Role of β4 integrin phosphorylation in human invasive squamous cell carcinoma: regulation of hemidesmosome stability modulates cell migration. Lab Invest 91:1414–1426
Fernandez-Hernando C, Fukata M, Bernatchez PN, Fukata Y, Lin MI, Bredt DS, Sessa WC (2006) Identification of Golgi-localized acyl transferases that palmitoylate and regulate endothelial nitric oxide synthase. J Cell Biol 174:369–377
Zhang XA, Kazarov AR, Yang X, Bontrager AL, Stipp CS, Hemler ME (2002) Function of the tetraspanin CD151-alpha6beta1 integrin complex during cellular morphogenesis. Mol Biol Cell 13:1–11
Wilhelmsen K, Litjens SH, Kuikman I, Margadant C, van Rheenen J, Sonnenberg A (2007) Serine phosphorylation of the integrin beta4 subunit is necessary for epidermal growth factor receptor induced hemidesmosome disruption. Mol Biol Cell 18:3512–3522
Greaves J, Salaun C, Fukata Y, Fukata M, Chamberlain LH (2008) Palmitoylation and membrane interactions of the neuroprotective chaperone cysteine-string protein. J Biol Chem 283:25014–25026
Greaves J, Chamberlain LH (2011) DHHC palmitoyl transferases: substrate interactions and (patho)physiology. Trends Biochem Sci 36:245–253
Vernon RB, Sage EH (1995) Between molecules and morphology. Extracellular matrix and creation of vascular form. Am J Pathol 147:873–883
Davis GE, Camarillo CW (1995) Regulation of endothelial cell morphogenesis by integrins, mechanical forces, and matrix guidance pathways. Exp Cell Res 216:113–123
Kim TH, Kim HI, Soung YH, Shaw LA, Chung J (2009) Integrin (alpha6beta4) signals through Src to increase expression of S100A4, a metastasis-promoting factor: implications for cancer cell invasion. Mol Cancer Res 7:1605–1612
Takkunen M, Grenman R, Hukkanen M, Korhonen M, de Garcia HA, Virtanen I (2006) Snail-dependent and -independent epithelial–mesenchymal transition in oral squamous carcinoma cells. J Histochem Cytochem 54:1263–1275
Greaves J, Prescott GR, Fukata Y, Fukata M, Salaun C, Chamberlain LH (2009) The hydrophobic cysteine-rich domain of SNAP25 couples with downstream residues to mediate membrane interactions and recognition by DHHC palmitoyl transferases. Mol Biol Cell 20:1845–1854
Barrett AJ (1979) Cathepsin D: the lysosomal aspartic proteinase. Ciba Found Symp, pp 37–50
Diment S, Leech MS, Stahl PD (1988) Cathepsin D is membrane-associated in macrophage endosomes. J Biol Chem 263:6901–6907
van Weert AW, Dunn KW, Gueze HJ, Maxfield FR, Stoorvogel W (1995) Transport from late endosomes to lysosomes, but not sorting of integral membrane proteins in endosomes, depends on the vacuolar proton pump. J Cell Biol 130:821–834
Lafleur MA, Xu D, Hemler ME (2009) Tetraspanin proteins regulate membrane type-1 matrix metalloproteinase-dependent pericellular proteolysis. Mol Biol Cell 20:2030–2040
Linder ME, Deschenes RJ (2007) Palmitoylation: policing protein stability and traffic. Natl Rev Mol Cell Biol 8:74–84
J. Korycka, A. Lach, E. Heger, D. M. Boguslawska, M. Wolny, M. Toporkiewicz, K. Augoff, J. Korzeniewski, A. F. Sikorski (2011) Human DHHC proteins: a spotlight on the hidden player of palmitoylation. Eur J Cell Biol
Aicart-Ramos C, Valero RA, Rodriguez-Crespo I (2011) Protein palmitoylation and subcellular trafficking. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808:2981–2994
Lukk M, Kapushesky M, Nikkila J, Parkinson H, Goncalves A, Huber W, Ukkonen E, Brazma A (2010) A global map of human gene expression. Nat Biotechnol 28:322–324
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Hong-Xing Wang for assistance with confocal microscopy and for providing a control vector. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health Grant GM38903 (to MEH).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sharma, C., Rabinovitz, I. & Hemler, M.E. Palmitoylation by DHHC3 is critical for the function, expression, and stability of integrin α6β4. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 2233–2244 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0924-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-012-0924-6