Abstract
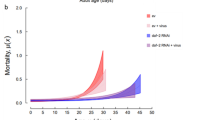
Melanization is an innate immune response in arthropods that encapsulates and kills invading pathogens. One of its rate-limiting steps is the activation of prophenoloxidase (PPO), which is controlled by an extracellular proteinase cascade and serpin inhibitors. The molecular composition of this system is largely unknown in mosquitoes with the exception of serpin-2 (SRPN2), which was previously identified as a key negative regulator of melanization. Using reverse genetic and biochemical techniques, we identified the Anopheles gambiae clip-serine proteinase CLIPB9 as a PPO-activating proteinase, which is inhibited by SRPN2. Double knockdown of SRPN2 and CLIPB9 reversed the pleiotrophic phenotype induced by SRPN2 silencing. This study identifies the first inhibitory serpin-serine proteinase pair in mosquitoes and defines a regulatory unit of melanization. Additionally, the interaction of CLIPB9 and SRPN2 affects the life span of adult female mosquitoes and therefore constitutes a well-defined potential molecular target for novel late-life acting insecticides.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- dKD:
-
Double knockdown
- IEARpNA:
-
Acetyl-Ile-Glu-Ala-Arg-p-nitroanilide
- KD:
-
Knockdown
- KS:
-
Kolmogorov–Smirnov
- LLA:
-
Late-life acting
- MS:
-
Mass spectrometry
- PPO:
-
Prophenoloxidase
References
Enayati A, Hemingway J (2010) Malaria management: past, present, and future. Annu Rev Entomol 55:569–591
Kelly-Hope L, Ranson H, Hemingway J (2008) Lessons from the past: managing insecticide resistance in malaria control and eradication programmes. Lancet Infect Dis 8:387–389
Hemingway J, Ranson H (2000) Insecticide resistance in insect vectors of human disease. Annu Rev Entomol 45:371–391
Read AF, Lynch PA, Thomas MB (2009) How to make evolution-proof insecticides for malaria control. PLoS Biol 7:e1000058
Blanford S, Chan BH, Jenkins N, Sim D, Turner RJ, Read AF, Thomas MB (2005) Fungal pathogen reduces potential for malaria transmission. Science 308:1638–1641
Michel K, Budd A, Pinto S, Gibson TJ, Kafatos FC (2005) Anopheles gambiae SRPN2 facilitates midgut invasion by the malaria parasite Plasmodium berghei. EMBO Rep 6:891–897
Kanost M, Gorman MJ (2008) In: Beckage NE (ed.) Insect immunology. Academic Press/Elsevier, San Diego, pp 69–96
Satoh D, Horii A, Ochiai M, Ashida M (1999) Prophenoloxidase-activating enzyme of the silkworm, Bombyx mori. Purification, characterization, and cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem 274:7441–7453
Kan H, Kim CH, Kwon HM, Park JW, Roh KB, Lee H, Park BJ, Zhang R, Zhang J, Soderhall K, Ha NC, Lee BL (2008) Molecular control of phenoloxidase-induced melanin synthesis in an insect. J Biol Chem 283:25316
Tang H, Kambris Z, Lemaitre B, Hashimoto C (2006) Two proteases defining a melanization cascade in the immune system of Drosophila. J Biol Chem 281:28097
Nappi A, Poirie M, Carton Y (2009) The role of melanization and cytotoxic by-products in the cellular immune responses of Drosophila against parasitic wasps. Adv Parasitol 70:99–121
Zhu Y, Wang Y, Gorman MJ, Jiang H, Kanost MR (2003) Manduca sexta serpin-3 regulates prophenoloxidase activation in response to infection by inhibiting prophenoloxidase-activating proteinases. J Biol Chem 278:46556–46564
De Gregorio E, Han SJ, Lee WJ, Baek MJ, Osaki T, Kawabata S, Lee BL, Iwanaga S, Lemaitre B, Brey PT (2002) An immune-responsive serpin regulates the melanization cascade in Drosophila. Dev Cell 3:581–592
Ligoxygakis P, Pelte N, Ji C, Leclerc V, Duvic B, Belvin M, Jiang H, Hoffmann JA, Reichhart JM (2002) A serpin mutant links Toll activation to melanization in the host defence of Drosophila. EMBO J 21:6330–6337
Zou Z, Shin SW, Alvarez KS, Kokoza V, Raikhel AS (2010) Distinct melanization pathways in the mosquito Aedes aegypti. Immunity 32:41–53
Gettins PG (2002) Serpin structure, mechanism, and function. Chem Rev 102:4751–4804
Michel K, Suwanchaichinda C, Morlais I, Lambrechts L, Cohuet A, Awono-Ambene PH, Simard F, Fontenille D, Kanost MR, Kafatos FC (2006) Increased melanizing activity in Anopheles gambiae does not affect development of Plasmodium falciparum. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:16858–16863
Christophides GK, Zdobnov E, Barillas-Mury C, Birney E, Blandin S, Blass C, Brey PT, Collins FH, Danielli A, Dimopoulos G, Hetru C, Hoa NT, Hoffmann JA, Kanzok SM, Letunic I, Levashina EA, Loukeris TG, Lycett G, Meister S, Michel K, Moita LF, Muller HM, Osta MA, Paskewitz SM, Reichhart JM, Rzhetsky A, Troxler L, Vernick KD, Vlachou D, Volz J, von Mering C, Xu J, Zheng L, Bork P, Kafatos FC (2002) Immunity-related genes and gene families in Anopheles gambiae. Science 298:159–165
Volz J, Muller HM, Zdanowicz A, Kafatos FC, Osta MA (2006) A genetic module regulates the melanization response of Anopheles to Plasmodium. Cellular microbiology 8:1392
Volz J, Osta MA, Kafatos FC, Muller HM (2005) The roles of two clip domain serine proteases in innate immune responses of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. J Biol Chem 280:40161–40168
Paskewitz SM, Andreev O, Shi L (2006) Gene silencing of serine proteases affects melanization of Sephadex beads in Anopheles gambiae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 36:701–711
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: a multiple sequence alignment method with reduced time and space complexity. BMC Bioinformatics 5:113
Edgar RC (2004) MUSCLE: multiple sequence alignment with high accuracy and high throughput. Nucleic Acids Res 32:1792–1797
Clamp M, Cuff J, Searle SM, Barton GJ (2004) The Jalview Java alignment editor. Bioinformatics 20:426–427
Waterhouse AM, Procter JB, Martin DM, Clamp M, Barton GJ (2009) Jalview Version 2—a multiple sequence alignment editor and analysis workbench. Bioinformatics 25:1189–1191
Abascal F, Zardoya R, Posada D (2005) ProtTest: selection of best-fit models of protein evolution. Bioinformatics 21:2104–2105
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Jiang H, Mulnix AB, Kanost MR (1995) Expression and characterization of recombinant Manduca sexta serpin-1B and site-directed mutants that change its inhibitory selectivity. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 25:1093–1100
Jiang H, Wang Y, Korochkina SE, Benes H, Kanost MR (1997) Molecular cloning of cDNAs for two pro-phenol oxidase subunits from the malaria vector, Anopheles gambiae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 27:693–699
An C, Jiang H, Kanost MR (2010) Proteolytic activation and function of the cytokine Spatzle in the innate immune response of a lepidopteran insect, Manduca sexta. FEBS J 277:148
Schick C, Kamachi Y, Bartuski AJ, Cataltepe S, Schechter NM, Pemberton PA, Silverman GA (1997) Squamous cell carcinoma antigen 2 is a novel serpin that inhibits the chymotrypsin-like proteinases cathepsin G and mast cell chymase. J Biol Chem 272:1849
Blandin S, Moita LF, Kocher T, Wilm M, Kafatos FC, Levashina EA (2002) Reverse genetics in the mosquito Anopheles gambiae: targeted disruption of the Defensin gene. EMBO Rep 3:852–856
Wilkinson M, McInerney JO, Hirt RP, Foster PG, Embley TM (2007) Of clades and clans: terms for phylogenetic relationships in unrooted trees. Trends Ecol Evol 22:114–115
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast, and accurate algorithm to estimate large phylogenies by maximum likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP (2003) MrBayes 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics 19:1572–1574
Li JS, Ruyl Kim S, Christensen BM, Li J (2005) Purification and primary structural characterization of prophenoloxidases from Aedes aegypti larvae. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 35:1269–1283
Jiang H, Wang Y, Ma C, Kanost MR (1997) Subunit composition of pro-phenol oxidase from Manduca sexta: molecular cloning of subunit ProPO-P1. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 27:835–850
Huang L, Sternberg PW. In: Community TCeR (ed.) WormBook
Collins FH, Sakai RK, Vernick KD, Paskewitz S, Seeley DC, Miller LH, Collins WE, Campbell CC, Gwadz RW (1986) Genetic selection of a Plasmodium-refractory strain of the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae. Science 234:607–610
Lambrechts L, Morlais I, Awono-Ambene PH, Cohuet A, Simard F, Jacques JC, Bourgouin C, Koella JC (2007) Effect of infection by Plasmodium falciparum on the melanization immune response of Anopheles gambiae. Am J Trop Med Hyg 76:475–480
Riehle MM, Markianos K, Niare O, Xu J, Li J, Toure AM, Podiougou B, Oduol F, Diawara S, Diallo M, Coulibaly B, Ouatara A, Kruglyak L, Traore SF, Vernick KD (2006) Natural malaria infection in Anopheles gambiae is regulated by a single genomic control region. Science 312:577–579
Muller HM, Dimopoulos G, Blass C, Kafatos FC (1999) A hemocyte-like cell line established from the malaria vector Anopheles gambiae expresses six prophenoloxidase genes. J Biol Chem 274:11727–11735
Pinto SB, Lombardo F, Koutsos AC, Waterhouse RM, McKay K, An C, Ramakrishnan C, Kafatos FC, Michel K (2009) Discovery of Plasmodium modulators by genome-wide analysis of circulating hemocytes in Anopheles gambiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21270–21275
Jiang H, Wang Y, Yu XQ, Zhu Y, Kanost M (2003) Prophenoloxidase-activating proteinase-3 (PAP-3) from Manduca sexta hemolymph: a clip-domain serine proteinase regulated by serpin-1 J and serine proteinase homologs. Insect Biochem Mol Biol 33:1049–1060
Pike RN, Buckle AM, le Bonniec BF, Church FC (2005) Control of the coagulation system by serpins. Getting by with a little help from glycosaminoglycans. FEBS J 272:4842–4851
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. M. Gorman for purified M. sexta PPO and T. Graves, K. Kjos, R. Woolsey, and G. Hammon for mosquito rearing. Thanks go to Drs. J. Tomich and Y. Hiromasa at the KSU Proteomics Core Laboratory for protein digestion and mass spectrometry. Real-time PCR analyses were performed at the COBRE Core I, KSU. This work was supported by NIH grants 3P20RR017708-07S1 and P20RR017686 subawards to K.M. and GM41247 to M.K. This is contribution 10-368-J from the Kansas Agricultural Experiment Station.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, C., Budd, A., Kanost, M.R. et al. Characterization of a regulatory unit that controls melanization and affects longevity of mosquitoes. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 68, 1929–1939 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0543-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-010-0543-z