Abstract
Objective and design
To investigate the role of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), carbon monoxide (CO), and biliverdin (BVD) in the zymosan-induced TMJ arthritis in rats.
Materials and Methods
Mechanical threshold was assessed before and 4 h after TMJ arthritis induction in rats. Cell influx, myeloperoxidase activity, and histological changes were measured in the TMJ lavages and tissues. Trigeminal ganglion and periarticular tissues were used for HO-1, TNF-α, and IL-1β mRNA time course expression and immunohistochemical analyses. Hemin (0.1, 0.3, or 1 mg kg−1), DMDC (0.025, 0.25, or 2.5 µmol kg−1), biliverdin (1, 3, or 10 mg kg−1), or ZnPP-IX (1, 3 or 9 mg kg−1) were injected (s.c.) 60 min before zymosan. ODQ (12.5 µmol kg−1; s.c.) or glibenclamide (10 mg kg−1; i.p.) was administered 1 h and 30 min prior to DMDC (2.5 µmol kg−1; s.c), respectively.
Results
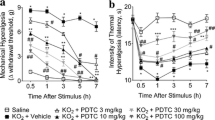
Hemin (1 mg kg−1), DMDC (2.5 µmol kg−1), and BVD (10 mg kg−1) reduced hypernociception and leukocyte migration, which ZnPP (3 mg kg−1) enhanced. The effects of DMDC were counteracted by ODQ and glibenclamide. The HO-1, TNF-α, and IL-1β mRNA expression and immunolabelling increased.
Conclusions
HO-1/BVD/CO pathway activation provides anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects on the zymosan-induced TMJ hypernociception in rats.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DMDC:
-
Dimethyl dicarbonate
- ZnPP-IX:
-
Zinc protoporphyrin IX
- ODQ:
-
1H- [1,2,4] oxadiazolo[4,3,-a]quinoxalin-1-one
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha
- IL-1β:
-
Interleukin-1beta
References
Cairns BE. Pathophysiology of TMD pain—basic mechanisms and their implications for pharmacotherapy. J Oral Rehab. 2010;37:391–410.
Greene CS, Klasser GD, Epstein JB. Revision of the American association of dental research’s science information statement about temporomandibular disorders. J Can Dent Assoc. 2010;76:a115.
Graff-Radford SB, Abbott JJ. Temporomandibular Disorders and Headache. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2016;28(3):335–49.
Gegout P, Gillet P, Chevrier D, Guinchamp C, Terlain B, Netter P. Characterization of zymosan-induced arthritis in the rat: effects on joint inflammation and cartilage metabolism. Life Sci. 1994;55:321–26.
Keystone EC, Schorlemmer HU, Pope C, Allison AC. Zymosan induced arthritis. A model of chronic proliferative arthritis following activation of the alternative pathway of complement. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;20:1396–401.
Rocha FA Jr, Aragão AG, Oliveira RC, Pompeu MM, Vale MR, Ribeiro RA. Periarthritis promotes gait disturbance in zymosan-induced arthritis in rats. Inflam Research. 1999;48:485–90.
Chaves HV, Ribeiro RA, Souza AMB, Silva AAR, Gomes AS, Val ML, Bezerra MM, Brito GAC. Experimental model of zymosan-induced arthritis in the rat temporomandibular joint: role of nitric oxide and neutrophils. J Biomed Biotech. 2011. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/707985.
Arinci A, Ademoglu E, Aslan A, Mutlu-Turkoglu U, Karabulut AB, Karan A. Molecular correlates of temporomandibular joint disease. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99:666–70.
Kaneyama K, Segami N, Sun W, Sato J, Fujimura K. Analysis of tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-6, interleukin-1beta, soluble tumor necrosis factor receptors I and II, interleukin-6 soluble receptor, interleukin-1 soluble receptor type II, interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, and protein in the synovial fluid of patients with temporomandibular joint disorders. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2005;99:276–84.
Abraham NG, Lin JH, Schwartzman ML, Levere RD, Shibahara S. The physiological significance of heme oxygenase. Int J Biochem. 1988;20:543–58.
Baranano DE, Snyder SH. Neural roles for heme oxygenase: contrasts to nitric oxide synthase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001;98:10996–1002.
Bonelli M, Savitskaya A, Steiner CW, Rath E, Bilban M, Wagner O, Bach FH, Smolen JS, Scheinecker C. Heme oxygenase-1 end-products carbon monoxide and biliverdin ameliorate murine collagen-induced arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2012;30:73–8.
Ibáñez L, Alcaraz MJ, Maicas N, Guede D, Caeiro JR, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB, Ferrándiz ML. Up-regulation of the inflammatory response by ovariectomy in collagen-induced arthritis. Effects of Tin Protoporphyrin IX. Inflammation. 2011;34:585–96.
Maines MD. Carbon monoxide: an emerging regulatory of cGMP in the brain. Mol Cell Neurosci. 1993;4:389–97.
Morita T, Perrella MA, Lee ME, Kourembanas S. Smooth muscle cell-derived carbon monoxide is a regulator of vascular cGMP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1995;92:1475–79.
Otterbein LE, Bach FH, Alam J, Soares M, Tao Lu H, Wysk M, Davis RJ, Flavell RA, Choi AM. Carbon monoxide has anti-inflammatory effects involving the mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway. Nat Med. 2000;6:422–8.
Petrache I, Otterbein LE, Alam J, Wiegand GW, Choi AM. Heme oxygenase-1 inhibits TNF-alpha-induced apoptosis in cultured fibroblasts. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:312–9.
Alcaraz MJ, Fernández P, Guillén MI. Anti-inflammatory actions of the heme oxygenase-1 pathway. Curr Pharm Des. 2003;9:2541–51.
McCoubrey WK, Huang TJ, Maines MD. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA from the rat brain that encodes hemoprotein heme oxygenase-3. Eur J Biochem. 1997;247:725–32.
Vicente AM, Guillen MI, Habib A, Alcaraz MJ. Beneficial effects of heme oxygenase-1 up-regulation in the development of experimental inflammation induced by zymosan. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;307:1030–7.
Pae HO, Choi BM, Oh GS, Lee MS, Ryu DG, Rhew HY, Kim YM, Chung HT. Roles of heme oxygenase-1 in the antiproliferative and antiapoptotic effects of nitric oxide on Jurkat T cells. Mol Pharmacol. 2004;66:122–8.
Bradley PP, Christense RD, Rothstein G. Cellular and extracellular myeloperoxidase in pyogenic inflammation. Blood. 1982;60:618–22.
Chi PL, Chen YW, Hsiao LD, Chen YL, Yang CM. Heme oxygenase 1 attenuates interleukin-1β-induced cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression via a decrease in NADPH oxidase/reactive oxygen species/activator protein 1 activation in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(7):2114–25.
Clérigues V, Guillén MI, Castejón MA, Gomar F, Alcaraz MJ. Haem oxygenase-1 counteracts the effects of interleukin-1β on inflammatory and senescence markers in cartilage-subchondral bone explants from osteoarthritic patients. Clin Sci. 2012;122:239–50.
Clérigues V, Guillén MI, Castejón MA, Gomar F, Mirabet V, Alcaraz MJ. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates protective effects on inflammatory, catabolic and senescence responses induced by interleukin-1β in osteoarthritic osteoblasts. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012;83:395–405.
Grangeiro NMG, Aguiar JA, Chaves HV, Silva AAR, Lima V, Benevides NMB, Graça JR, Bezerra MM. Heme oxygenase/carbon monoxide-biliverdin pathway may be involved in the antinociceptive activity of etoricoxib, a selective COX-2 inhibitor. Pharmacol Rep. 2011;63:112–19.
Megías J, Guillén MI, Clérigues V, Rojo AI, Cuadrado A, Castejón MA. Heme oxygenase-1 induction modulates microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 expression and prostaglandin E(2) production in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2009;77:1806–13.
Park SY, Lee SW, Shin HK, Chung WT, Lee WS, Rhim BY, Hong KW, Kim CD. Cilostazol enhances apoptosis of synovial cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients with inhibition of cytokine formation via nrf2-linked heme oxygenase 1 induction. Arthritis Rheum. 2010;62:732–41.
Hayashi S, Takamiya R, Yamaguchi T, Matsumoto K, Tojo SJ, Tamatani T, Kitajima M, Makino N, Ishimura Y, Suematsu M. Induction of heme oxygenase-1 suppresses venular leukocyte adhesion elicited by oxidative stress: role of bilirrubin generated by the enzyme. Circ Res. 1999;85:663–71.
Vachharajani TJ, Work J, Issekutz AC, Granger DN. Heme oxygenase modulates selectin expression in different regional vascular beds. Am J Physiol. 2000;278:1613–7.
Benallaoua M, Francois M, Batteux F, Thelier N, Shyy JY, Fitting C. Pharmacologic induction of heme oxygenase 1 reduces acute inflammatory arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56:2585–94.
Devesa I, Ferrandiz ML, Guillen I, Cerda JM, Alcaraz MJA. Potential role of heme oxygenase-1 in the progression of rat adjuvant arthritis. Lab Invest. 2005;85:34–44.
Devesa I, Ferrándiz ML, Terencio MC, Joosten LAB, Van den Berg WB, Alcaraz MJB. Influence of heme oxygenase 1 modulation on the progression of murine collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52:3230–38.
Bussolati B, Ahmed A, Pemberton H, Landis RC, di Carlo F, Haskard DO, Manson JC. Bifunctional role for VEGF-induced heme oxygenase-1 in vivo: induction of angiogenesis and inhibition of leukocytic infiltration. Blood. 2004;103:761–66.
Kobayashi H, Takeno M, Saito T, Takeda Y, Kirino Y, Noyori K, Hayashi T, Ueda A, Ishigatsubo Y. Regulatory role of heme oxygenase 1 in inflammation of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2006;54:1132–42.
Steiner AA, Branco LGS, Cunha GQ, Ferreira SH. Role of the haeme oxygenase/carbon monoxide pathway in mechanical nociceptor hypersensitivity. Brit J Pharmacol. 2001;132:1673–82.
Maines MD. The heme oxygenase system: a regulator of second messenger gases. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1997;37:517–54.
Guillén MI, Megías J, Gomar F, Alcaraz MJ. Haem oxygenase-1 regulates catabolic and anabolic processes in osteoarthritic chondrocytes. J Pathol. 2008;214:515–22.
Nascimento CGO, Branco LGS. Role of the peripheral heme oxygenase–carbon monoxide pathway on the nociceptive response of rats to the formalin test: evidence for a cGMP signaling pathway. Eur J Pharmacol. 2007;556:55–61.
Nascimento CGO, Branco LGS. Role of the spinal cord heme oxygenase–carbon monoxide–cGMP pathway in the nociceptive response of rats. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008;581:71–6.
Carvalho PG, Branco LGS, Leite- Panissi CRA. Involvement of the heme oxygenase–carbon monoxide–cGMP pathway in the nociception induced by acute painful stimulus in rats. Brain Res. 2011;1385:107–13.
Cunha FQ, Teixeira MM, Ferreira SH. Pharmacological modulation of secondary mediator systems-cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP on inflammatory hyperalgesia. Br J Pharmacol. 1999;127:671–78.
Bezerra MM, Lima V, Girão VCC, Teixeira RC, Graça JRV. Antinociceptive activity of sildenafil and adrenergic agents in the writhing test in mice. Pharmacol Rep. 2008;60:339–44.
Sachs D, Cunha FQ, Ferreira SH. Peripheral analgesic blockade of hypernociception: activation of arginine/NO/cGMP/protein kinase G/ATP-sensitive K + channel pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2004;101:3680–5.
Fernandez P, Guillen MI, Gomar F, Alcaraz MJ. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 and regulation by cytokines in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;66:2049–52.
Kitamura A, Nishida K, Komiyama T, Doi H, Kadota Y, Yoshida A, Ozaki T. Increased level of heme oxygenase-1 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fluid. Mod Rheumatol. 2011;21:150–57.
Valvason C, Musacchio E, Pozzuoli A, Ramonda R, Aldegheri R, Punzi L. Influence of glucosamine sulphate on oxidative stress in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: effects on HO-1, p22Phox and iNOS expression. Rheumatol. 2008;47:31–5.
Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Silva JS, Poole S, Cunha FQ, Ferreira SH. A cascade of cytokines mediates mechanical inflammatory hypernociception in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(5):1755–60.
Verri WA Jr, Cunha TM, Parada CA, Poole S, Cunha FQ, Ferreira SH. Hypernociceptive role of cytokines and chemokines: targets for analgesic drug development? Pharmacol Ther. 2006;112(1):116–38.
Arend WP, Dayer JM. Inhibition of the production and effects of interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780380202.
Brennan FM, McInnes IB. Evidence that cytokines play a role in rheumatoid arthritis. J Clin Invest. 2008;118:3537–45.
Durham ZL, Hawkins JL, Durham PL. Tumor necrosis factor-alpha stimulates cytokine expression and transient sensitization of trigeminal nociceptive neurons. Arc Oral Biol. 2017;75:100–6.
Fernández P, Guillén MI, Gomar F, Alcaraz MJ. Expression of heme oxygenase-1 and regulation by cytokines in human osteoarthritic chondrocytes. Biochem Pharmacol. 2003;15:66:2049–52.
Lee TS, Chau LY. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates the anti-inflammatory effect of interleukin-10 in mice. Nat Med. 2002;8:240–6.
Paine A, Eiz-Vesper B, Blasczyk R, Immenschuh S. Signaling to heme oxygenase-1 and its anti-inflammatory therapeutic potential. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;80:1895–903.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Brazilian grants from Fundação Cearense de Apoio ao Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (FUNCAP), Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and Instituto de Biomedicina do Semi-Árido Brasileiro (INCT-IBISAB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interests regarding the publication of this article.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mauro Teixeira.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chaves, H.V., do Val, D.R., Ribeiro, K.A. et al. Heme oxygenase-1/biliverdin/carbon monoxide pathway downregulates hypernociception in rats by a mechanism dependent on cGMP/ATP-sensitive K+ channels. Inflamm. Res. 67, 407–422 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-018-1133-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-018-1133-z