Abstract
Objective and design
The aim of this study was to investigate the contribution of IL-33/ST2 axis in the onset and progression of acute liver injury using a mice model of drug-induced liver injury (DILI).
Material and treatments
DILI was induced by overdose administration of acetaminophen (APAP) by oral gavage in wild-type BALB/c, ST2-deficient mice and in different bone marrow chimeras. Neutrophils were depleted by anti-Ly6G and macrophages with clodronate liposomes (CLL).
Methods
Blood and liver were collected for biochemical, immunologic and genetic analyses. Mice were imaged by confocal intravital microscopy and liver non-parenchymal cells and hepatocytes were isolated for flow cytometry, genetic and immunofluorescence studies.
Results
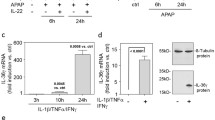
Acetaminophen overdose caused a massive necrosis and accumulation of immune cells within the liver, concomitantly with IL-33 and chemokine release. Liver non-parenchymal cells were the major sensors for IL-33, and amongst them, neutrophils were the major players in amplification of the inflammatory response triggered by IL-33/ST2 signalling pathway.
Conclusion
Blockage of IL-33/ST2 axis reduces APAP-mediated organ injury by dampening liver chemokine release and activation of resident and infiltrating liver non-parenchymal cells.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bell LN, Chalasani N. Epidemiology of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis 2009; 29:337–47.
Bjornsson ES. Epidemiology and risk factors for idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Semin Liver Dis 2014; 34:115–22.
Bernal W, Auzinger G, Dhawan A, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. Lancet. 2010;376:190–201.
Bernal W, Wendon J. Acute liver failure. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:2525–34.
Jaeschke H, Bajt ML. Intracellular signaling mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver cell death. Toxicol Sci. 2006;89:31–41.
Ni HM, Jaeschke H, Ding WX. Targeting autophagy for drug-induced hepatotoxicity. Autophagy 2012;8:709–10.
Rock KL, Latz E, Ontiveros F, Kono H. The sterile inflammatory response. Annu Rev Immunol 2010;28:321–42.
Marques PE, Oliveira AG, Pereira RV, David BA, Gomides LF, Saraiva AM, et al. Hepatic DNA deposition drives drug-induced liver injury and inflammation in mice. Hepatology. 2015;61:348–60.
Martin-Murphy BV, Holt MP, Ju C. The role of damage associated molecular pattern molecules in acetaminophen-induced liver injury in mice. Toxicol Lett 2010;192:387–94.
Baekkevold ES, Roussigne M, Yamanaka T, Johansen FE, Jahnsen FL, Amalric F, et al. Molecular characterization of NF-HEV, a nuclear factor preferentially expressed in human high endothelial venules. Am J Pathol. 2003;163:69–79.
Schmitz J, Owyang A, Oldham E, Song Y, Murphy E, McClanahan TK, et al. IL-33, an interleukin-1-like cytokine that signals via the IL-1 receptor-related protein ST2 and induces T helper type 2-associated cytokines. Immunity. 2005;23:479–90.
Carriere V, Roussel L, Ortega N, Lacorre DA, Americh L, Aguilar L, et al. IL-33, the IL-1-like cytokine ligand for ST2 receptor, is a chromatin-associated nuclear factor in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2007;104:282–7.
Lefrancais E, Cayrol C. Mechanisms of IL-33 processing and secretion: differences and similarities between IL-1 family members. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2012;23:120–7.
Pichery M, Mirey E, Mercier P, Lefrancais E, Dujardin A, Ortega N, et al. Endogenous IL-33 is highly expressed in mouse epithelial barrier tissues, lymphoid organs, brain, embryos, and inflamed tissues: in situ analysis using a novel Il-33-LacZ gene trap reporter strain. J Immunol. 2012;188:3488–95.
Lefrancais E, Roga S, Gautier V, Gonzalez-de-Peredo A, Monsarrat B, Girard JP, et al. IL-33 is processed into mature bioactive forms by neutrophil elastase and cathepsin G. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2012;109:1673–8.
Miller AM. Role of IL-33 in inflammation and disease. J Inflamm. 2011;8:22.
Hueber AJ, Alves-Filho JC, Asquith DL, Michels C, Millar NL, Reilly JH, et al. IL-33 induces skin inflammation with mast cell and neutrophil activation. Eur J Immunol. 2011;41:2229–37.
Chackerian AA, Oldham ER, Murphy EE, Schmitz J, Pflanz S, Kastelein RA. IL-1 receptor accessory protein and ST2 comprise the IL-33 receptor complex. J Immunol. 2007;179:2551–5.
Marques PE, Oliveira AG, Pereira RV, David BA, Gomides LF, Saraiva AM, et al. Hepatic DNA deposition drives drug-induced liver injury and inflammation in mice. Hepatology. 2015;61(1):348–60.
Amaral SS, Oliveira AG, Marques PE, Quintao JL, Pires DA, Resende RR, et al. Altered responsiveness to extracellular ATP enhances acetaminophen hepatotoxicity. CCS. 2013;11:10.
Marques PE, Amaral SS, Pires DA, Nogueira LL, Soriani FM, Lima BH, et al. Chemokines and mitochondrial products activate neutrophils to amplify organ injury during mouse acute liver failure. Hepatology. 2012;56:1971–82.
Pires DA, Marques PE, Pereira RV, David BA, Gomides LF, Dias AC, et al. Interleukin-4 deficiency protects mice from acetaminophen-induced liver injury and inflammation by prevention of glutathione depletion. Inflamm Res. 2014;63:61–9.
David BA, Rubino S, Moreira TG, Freitas-Lopes MA, Araujo AM, Paul NE, et al. Isolation and high-dimensional phenotyping of gastrointestinal immune cells. Immunology. 2017;151:56–70.
Marques PE, Antunes MM, David BA, Pereira RV, Teixeira MM, Menezes GB. Imaging liver biology in vivo using conventional confocal microscopy. Nat Protoc 2015;10:258–68.
McDonald B, Pittman K, Menezes GB, Hirota SA, Slaba I, Waterhouse CC, et al. Intravascular danger signals guide neutrophils to sites of sterile inflammation. Science. 2010;330:362–6.
Cruz LN, Guerra MT, Kruglov E, Mennone A, Garcia CR, Chen J, et al. Regulation of multidrug resistance-associated protein 2 by calcium signaling in mouse liver. Hepatology 2010;52:327–37.
Martin NT, Martin MU. Interleukin 33 is a guardian of barriers and a local alarmin. Nat Immunol. 2016;17:122–31.
Marvie P, Lisbonne M, L’Helgoualc’h A, Rauch M, Turlin B, Preisser L, et al. Interleukin-33 overexpression is associated with liver fibrosis in mice and humans. J Cell Mol Med. 2010;14:1726–39.
Sakai N, Van Sweringen HL, Quillin RC, Schuster R, Blanchard J, Burns JM, et al. Interleukin-33 is hepatoprotective during liver ischemia/reperfusion in mice. Hepatology. 2012;56:1468–78.
Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, L’Helgoualc’h A, Rauch M, Patrat-Delon S, Ezan F, et al. TRAIL but not FasL and TNFalpha, regulates IL-33 expression in murine hepatocytes during acute hepatitis. Hepatology. 2012;56:2353–62.
Arshad MI, Piquet-Pellorce C, Samson M. IL-33 and HMGB1 alarmins: sensors of cellular death and their involvement in liver pathology. Liver Int. 2012;32:1200–10.
Alves-Filho JC, Sonego F, Souto FO, Freitas A, Verri WA Jr, Auxiliadora-Martins M, et al. Interleukin-33 attenuates sepsis by enhancing neutrophil influx to the site of infection. Nat Med 2010;16:708–12.
Verri WA Jr, Souto FO, Vieira SM, Almeida SC, Fukada SY, Xu D, et al. IL-33 induces neutrophil migration in rheumatoid arthritis and is a target of anti-TNF therapy. Ann Rheum Dis 2010;69:1697–703.
David BA, Rezende RM, Antunes MM, Santos MM, Freitas Lopes MA, Diniz AB, et al. Combination of mass cytometry and imaging analysis reveals origin, location, and functional repopulation of liver myeloid cells in mice. Gastroenterology. 2016;151:1176–91.
Hinson JA, Roberts DW, James LP. Mechanisms of acetaminophen-induced liver necrosis. Handb Exp Pharmacol 2010:369–405.
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank CNPq, CAPES and FAPEMIG for financial support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have nothing to disclosure.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Mauro Teixeira.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Antunes, M.M., Araújo, A.M., Diniz, A.B. et al. IL-33 signalling in liver immune cells enhances drug-induced liver injury and inflammation. Inflamm. Res. 67, 77–88 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1098-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-017-1098-3