Abstract
Objective
The status of B10 cells in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has not been consistently reported. In this study, we observed the kinetic changes of the B10 cells in collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) mice and the influence of multiple cytokines on the B10 cells to investigate the potential mechanism underlying the changes of B10 cells.
Methods
The kinetic changes of frequency and function of the CD19+CD1dhiCD5+ cells in splenic cells were observed during the complete progress of CIA mice. The kinetic changes of cytokines IL-4, IL-6, IL-17A, IL-18, TNF-α, IFN-γ and TGF-β1 were also detected. Then influence of these cytokines on the status of B10 cells was investigated both in vitro and in vivo.
Results
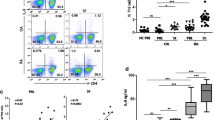
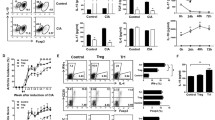
The frequency and suppressive ability of the CD19+CD1dhiCD5+ cells increased to its peak on the 14th day while gradually decreased subsequently. IFN-γ showed a similar tendency with the CD19+CD1dhiCD5+ cells, whereas IL-6, IL-17A, IL-18, TNF-α, and TGF-β1 reached its peak on the 28–35th day. In addition, IFN-γ up-regulated while TGF-β1 down-regulated the frequency and function of the CD19+CD1dhiCD5+ cells both in vitro and in vivo.
Conclusion
The B10 cells in CIA mice could be regulated by IFN-γ and TGF-β1, suggesting that the status of B10 cells in RA may be influenced by the balance of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory factors, and the impaired B10 cells could be recovered in vitro by adequate treatment before being used for a therapeutic method in clinical practice.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Klareskog L, Catrina A, Paget S. Rheumatoid Arthritis. Lancet. 2009;373:659–72.
Nakken B, Munthe LA, Konttinen YT, Sandberg AK, Szekanecz Z, Alex P, et al. B-cells and their targeting in rheumatoid arthritis—current concepts and future perspectives. Autoimmun Rev. 2011;11:28–34.
Reddy V, Croca S, Gerona D, De La Torre I, Isenberg D, McDonald V, et al. Serum rituximab levels and efficiency of B cell depletion: differences between patients with rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology. 2013;52:951–2.
Bredemeier M, Oliveira FK, Rocha CM. Low-versus high-dose Rituximab for Rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Arthritis Care Res. 2014;66:228–35.
Evans JG, Chavez-Rueda KA, Eddaoudi A, Meyer-Bahlburg A, Rawlings DJ, Ehrenstein MR, et al. Novel suppressive function of transitional 2 B cells in experimental arthritis. J Immunol. 2007;178:7868–78.
Mauri C, Gray D, Mushtaq N, Londei M. Prevention of arthritis by interleukin 10-producing B cells. J Exp Med. 2003;197:489–501.
Neta R, Salvin S. Specific suppression of delayed hypersensitivity: the possible presence of a suppressor B cell in the regulation of delayed hypersensitivity. J Immunol. 1974;113:1716–25.
Matsushita T, Horikawa M, Iwata Y, Tedder TF. Regulatory B cells (B10 cells) and regulatory T cells have independent roles in controlling experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis initiation and late-phase immunopathogenesis. J Immunol. 2010;185:2240–52.
Watanabe R, Ishiura N, Nakashima H, Kuwano Y, Okochi H, Tamaki K, et al. Regulatory B cells (B10 cells) have a suppressive role in murine lupus: CD19 and B10 cell deficiency exacerbates systemic autoimmunity. J Immunol. 2010;184:4801–9.
Yang M, Sun L, Wang S, Ko K-H, Xu H, Zheng B-J, et al. Cutting edge: novel function of B cell-activating factor in the induction of IL-10-producing regulatory B cells. J Immunol. 2010;184:3321–5.
Yang M, Deng J, Liu Y, Ko K-H, Wang X, Jiao Z, et al. IL-10–producing regulatory B10 cells ameliorate collagen-induced arthritis via suppressing Th17 cell generation. Am J Pathol. 2012;180:2375–85.
Llorente L, Richaud-Patin Y, Fior R, Alcocer-Varela J, Wijdenes J, Fourrier BM, et al. In vivo production of interleukin-10 by non-t cells in rheumatoid arthritis, Sjöugren’s syndrome, and systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 1994;37:1647–55.
Iwata Y, Matsushita T, Horikawa M, DiLillo DJ, Yanaba K, Venturi GM, et al. Characterization of a rare IL-10-competent B-cell subset in humans that parallels mouse regulatory B10 cells. Blood. 2011;117:530–41.
Ma L, Liu B, Jiang Z, Jiang Y. Reduced numbers of regulatory B cells are negatively correlated with disease activity in patients with new-onset rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol. 2014;33:187–95.
Flores-Borja F, Bosma A, Ng D, Reddy V, Ehrenstein MR, Isenberg DA, et al. CD19+CD24hiCD38hi B cells maintain regulatory T cells while limiting TH1 and TH17 differentiation. Sci Transl Med. 2013;5:173ra23–173ra23.
Krausz S, Garcia S, Ambarus CA, de Launay D, Foster M, Naiman B, et al. Angiopoietin-2 promotes inflammatory activation of human macrophages and is essential for murine experimental arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2012;71:1402–17.
Garcia G, Komagata Y, Slavin AJ, Maron R, Weiner HL. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis by oral or nasal administration of type II collagen. J Autoimmun. 1999;13:315–24.
Sims NA, Green JR, Glatt M, Schlict S, Martin TJ, Gillespie MT, et al. Targeting osteoclasts with zoledronic acid prevents bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50:2338–46.
Joosten LA, Lubberts E, Durez P, Helsen M, Jacobs MJ, Goldman M, et al. Role of interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Protective effect of interleukin-4 and interleukin-10 treatment on cartilage destruction. Arthritis Rheum. 1997;40:249–60.
DiLillo DJ, Griffiths R, Seshan SV, Magro CM, Ruiz P, Coffman TM, et al. B lymphocytes differentially influence acute and chronic allograft rejection in mice. J Immunol. 2011;186:2643–54.
Smith SH, Tedder TF. Targeting B-cells mitigates autoimmune diabetes in NOD mice: what is plan b? Diabetes. 2009;58:1479–81.
Cantaert T, Doorenspleet ME, FrancoSalinas G, Paramarta JE, Klarenbeek PL, Tiersma Y, et al. Increased numbers of CD5+ B lymphocytes with a regulatory phenotype in spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64:1859–68.
Blair PA, Noreña LY, Flores-Borja F, Rawlings DJ, Isenberg DA, Ehrenstein MR, et al. CD19(+) CD24 (hi) CD38 (hi) B cells exhibit regulatory capacity in healthy individuals but are functionally impaired in systemic Lupus Erythematosus patients. Immunity. 2010;32:129–40.
Zha B, Wang L, Liu X, Liu J, Chen Z, Xu J, et al. Decrease in proportion of CD19+ CD24hiCD27+ B cells and impairment of their suppressive function in Graves Disease. PLoS One. 2012;7:e49835.
Li X, Zhong H, Bao W, Boulad N, Evangelista J, Haider MA, et al. Defective regulatory B-cell compartment in patients with immune thrombocytopenia. Blood. 2012;120:3318–25.
Alex P, Szodoray P, Knowlton N, Dozmorov I, Turner M, Frank M, et al. Multiplex serum cytokine monitoring as a prognostic tool in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2007;25:584.
Gaffen SL. Recent advances in the IL-17 cytokine family. Curr Opin Immunol. 2011;23:613–9.
Oranskii S, Eliseeva L, Khanfetian R. Body structure and serum concentration of adiponectin and cytokines (IL-6, -10 and TNF-alpha) in rheumatoid arthritis combined with obesity. Voprosy Pitaniia. 2013;82:10–4.
Zhang W, Cong X-L, Qin Y-H, He Z-W, He D-Y, Dai S-M. IL-18 upregulates the production of key regulators of osteoclastogenesis from fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. 2013;36:103–9.
Kelchtermans H, Schurgers E, Geboes L, Mitera T, Van Damme J, Van Snick J, et al. Effector mechanisms of interleukin-17 in collagen-induced arthritis in the absence of interferon-gamma and counteraction by interferon-gamma. Arthritis Res Ther. 2009;11:R122.
Thornton S, Duwel LE, Boivin GP, Ma Y, Hirsch R. Association of the course of collagen-induced arthritis with distinct patterns of cytokine and chemokine messenger RNA expression. Arthritis Rheum. 1999;42:1109–18.
Acknowledgments
We thank Yanhong Wang and Chunmei Fan for their excellent technical assistance. This work was funded by a grant from National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81001335).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Responsible Editor: Liwu Li.
Z. Zheng, T. Liu and X. Li contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Liu, T., Li, X. et al. Kinetic changes of regulatory B10 cells in collagen-induced arthritis could be regulated by cytokines IFN-γ and TGF-β1. Inflamm. Res. 64, 637–645 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0846-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-015-0846-5