Abstract.
Background: Sepsis is associated with the highest risk of progression to acute lung injury or the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Ketamine has been advocated for anesthesia in endotoxemic and other severely ill patients because it is a cardiovascular stimulant. Our study was designed to investigate the effect of ketamine on the endotoxin-induced acute lung injury in vivo.
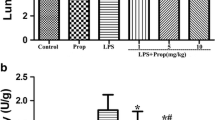
Materials and methods: Adult male Wistar rats were randomly divided into 6 groups: saline controls; rats challenged with endotoxin (5 mg/kg) and treated with saline; challenged with endotoxin (5 mg/kg) and treated with ketamine (0.5 mg/kg); challenged with endotoxin (5 mg/kg) and treated with ketamine (5 mg/kg); challenged with endotoxin (5 mg/kg) and treated with ketamine (50 mg/kg); saline injected and treated with ketamine (50 mg/kg). TNF-α, IL-6 and NF-kappa B were investigated in the tissues of the lung after 2 h. Myeloperoxidase (MPO) activity and wet/dry weight ratio were investigated 6 h later.
Results: We demonstrated that intravenous administration of endotoxin could provoke significant lung injury, which was characterized by increase of MPO activity and wet/dry weight ratio, TNF-α and IL-6 expression and NF-kappa B activation. Ketamine (5, 50 mg/kg) inhibited endotoxin-induced NF-kappa B activation. Ketamine only at a dose of 50 mg/kg inhibited TNF-α and IL-6 production, and decreased MPO activity and wet/dry weight ratio after endotoxin challenge.
Conclusions: Ketamine, only at a supra-anesthetic dosage, could inhibit endotoxin-induced pulmonary inflammation in vivo.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 27 August 2004; returned for revision 11 November 2004; accepted by A. Falus 15 November 2004
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, J., Li, W., Duan, M. et al. Large dose ketamine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in rats. Inflamm. res. 54, 133–137 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-004-1334-5
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-004-1334-5