Abstract
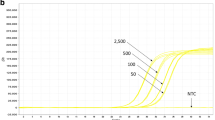
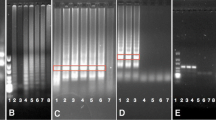
The genetically modified (GM) rice Kefeng 6 has gained resistance against several rice pests by inserting the cpti and cry1Ac genes. As this transgenic line is not approved for import, processing and cultivation in the European Union (EU), sensitive and specific detection methods need to be available to monitor any illegal presence of Kefeng 6 in food products within the EU. The aim of this study was to develop and validate an event-specific detection method by means of quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) for the detection of Kefeng 6 in foodstuff. A primer pair and hydrolysis probe were designed according to the right border junction sequence of the transgene. The qPCR assay was validated according to the ENGL/EURL-GMFF guidelines for GMO testing and is presented according to the MIQE guidelines. The in-house validation process resulted in a limit of detection of 5 DNA copies of the transgene with confidence intervals (95 %) between 0.07 and 0.52, a PCR efficiency of 105 % and a correlation coefficient (R 2) value of 0.9997. The specificity of the assay was tested by end-point PCR, gel electrophoresis and subsequent sequencing of the PCR products. By testing DNA of several GM and non-GM crops, cross reactivity of the assay was not observed. Further, 35 food products were analyzed for the presence of Kefeng 6 by means of the event-specific detection method. For 9 out of 35 samples, PCR products for Kefeng 6 DNA were observed.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Rep 9:208–218
Babekova R, Funk T, Pecoraro S, Engel K-H, Busch U (2009) Development of an event-specific real-time PCR detection method for the transgenic Bt rice line KMD1. Eur Food Res Technol 228(5):707–716
Busch U, Pecoraro S, Posthoff K, Estendorfer-Rinner S (2004) Erster Nachweis einer gentechnisch veränderten Papaya in Europa - Beanstandung eines in der EU nicht zugelassenen gentechnisch veränderten Organismus. Deut Lebensm Rundsch 100(10):377–380
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans J, Huggett J, Kubista M, Mueller R, Nolan T, Pfaffl MW, Shipley GL, Vandesompele J, Wittwer CT (2009) The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem 55(4):611–622
CERA (2010) GM Crop Database. Center for Environmental Risk Assessment (CERA), ILSI Research Foundation. http://cera-gmc.org/index.php?action=gm_crop_database
Chen M, Shelton A, Ye G-y (2011) Insect-resistant genetically modified rice in china: from research to commercialization. Annu Rev Entomol 56(1):81–101
Chen M, Zhao J-Z, Ye G-Y, Fu Q, Shelton AM (2006) Impact of insect-resistant transgenic rice on target insect pests and non-target arthropods in China. Insect Sci 13(6):409–420
Datta SK, Datta K, Soltanifar N, Donn G, Potrykus I (1992) Herbicide-resistant Indica rice plants from IRRI breeding line IR72 after PEG-mediated transformation of protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol 20(4):619–629
Dörries H–H, Remus I, Grönewald A, Grönewald C, Berghof-Jäger K (2010) Development of a qualitative, multiplex real-time PCR kit for screening of genetically modified organisms (GMOs). Anal Bioanal Chem 396(6):2043–2054
EC (2003a) Regulation (EC) No 1829/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 on genetically modified food and feed. Official Journal of the European Union L 268/1
EC (2003b) Regulation (EC) No 1830/2003 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 22 September 2003 concerning the traceability and labelling of genetically modified organisms and the traceability of food and feed products produced from genetically modified organisms and amending Directive 2001/18/EC. Official Journal of the European Union L 268/24
EC (2011) Regulation (EC) No 619/201 of 24 June 2011 laying down the methods of sampling and analysis for the official control of feed as regards presence of genetically modified material for which an authorisation procedure is pending or the authorization of which has expired. Official Journal of the European Union L166 (9)
ENGL (2009) Definition of minimum performance requirements for analytical methods for GMO testing. http://gmo-crljrceceuropaeu/doc/Min_Perf_Requirements_Analytical_methodspdf
Guertler P, Paul V, Steinke K, Wiedemann S, Preißinger W, Albrecht C, Spiekers H, Schwarz FJ, Meyer HHD (2010) Long-term feeding of genetically modified corn (MON810)—fate of cry1Ab DNA and recombinant protein during the metabolism of the dairy cow. Livest Sci 131(2–3):250–259
Hernández M, Esteve T, Prat S, Pla M (2004) Development of real-time PCR systems based on SYBR® Green I, Amplifluor(TM) and TaqMan® technologies for specific quantitative detection of the transgenic maize event GA21. J Cereal Sci 39(1):99–107
ISO24276:2006 (2006) Foodstuffs—methods of analysis for the detection of genetically modified organisms and derived products—general requirements and definitions. (http://wwwisoorg/iso/catalogue_detail?csnumber=37125)
James C (2010) Global status of commercialized biotech/GM crops: 2010. ISAAA Brief No. 42:ISAAA. Ithaca, NY
Paine JA, Shipton CA, Chaggar S, Howells RM, Kennedy MJ, Vernon G, Wright SY, Hinchliffe E, Adams JL, Silverstone AL, Drake R (2005) Improving the nutritional value of Golden Rice through increased pro-vitamin A content. Nat Biotechnol 23(4):482–487
Pray CE, Ramaswami B, Huang J, Hu R, Bengali P, Zhang H (2006) Costs and enforcement of biosafety regulations in India and China. Int J Technol Glob 2(1–2):137–157
Reiting R, Grohmann L, Mäde D (2010) A testing cascade for the detection of genetically modified rice by real-time PCR in food and its application for detection of an unauthorized rice line similar to KeFeng6. J Verbrauch Lebensm 5(2):185–188
Rong J, Song Z, Su J, Xia H, Lu B-R, Wang F (2005) Low frequency of transgene flow from Bt/CpTI rice to its nontransgenic counterparts planted at close spacing. New Phytol 168(3):559–566
Saha P, Majumder P, Dutta I, Ray T, Roy S, Das S (2006) Transgenic rice expressing Allium sativum leaf lectin with enhanced resistance against sap-sucking insect pests. Planta 223(6):1329–1343
Savary S, Willocquet L, Elazegui FA, Castilla NP, Teng PS (2000) Rice pest constraints in tropical Asia: quantification of yield losses due to rice pests in a range of production situations. Plant Dis 84(3):357–369. doi:10.1094/PDIS.2000.84.3.357
Su C, Xie J, Wang X, Peng Y (2011) Integrated structure and event-specific real-time detection of transgenic cry1Ac/SCK rice Kefeng 6. Eur Food Res Technol 232(2):351–359
Tu J, Zhang G, Datta K, Xu C, He Y, Zhang Q, Khush GS, Datta SK (2000) Field performance of transgenic elite commercial hybrid rice expressing Bacillus thuringiensis delta-endotoxin. Nat Biotechnol 18(10):1101–1104
Waiblinger H-U, Graf N, Broll H, Grohmann L, Pietsch K (2011) Evaluation of real-time PCR results at the limit of detection. J Verbrauch Lebensm:1–7
Wang W-X, Zhu T-H, Lai F-X, Fu Q (2011) Event-specific qualitative and quantitative detection of transgenic rice Kefeng-6 by characterization of the transgene flanking sequence. Eur Food Res Technol 232(2):237–305
Wu G, Wu Y, Nie S, Zhang L, Xiao L, Cao Y, Lu C (2010) Real-time PCR method for detection of the transgenic rice event TT51-1. Food Chem 119(1):417–422
Xiao G-y (2009) Recent advances in development of herbicide resistant transgenic hybrid rice in China. Rice Sci 16(3):235–239
Ye X, Al-Babili S, Kloti A, Zhang J, Lucca P, Beyer P, Potrykus I (2000) Engineering the provitamin A (beta-carotene) biosynthetic pathway into (carotenoid-free) rice endosperm. Science 287(5451):303–305
Ye G-Y, Shu Q-Y, Yao H-W, Cui H-R, Cheng X-Y, Hu C, Xia Y-W, Gao M-W, Altosaar I (2001) Field evaluation of resistance of transgenic rice containing a synthetic cry1Ab gene from Bacillus thuringiensis Berliner to two stem borers. J Econ Entomol 94(1):271–276
Zi X (2005) GM rice forges ahead in China amid concerns over illegal planting. Nat Biotechnol 23(6):637
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank the Bavarian State Ministry of the Environment and Public Health for funding this project. Andrea Harwardt, Krimhilde Posthoff, Ulrike Mulats, Claudia Bujotzek, Melina Mehmedovic, Daniela Sebah, and Karola Grünwald are gratefully acknowledged for their excellent technical work. We thank Dr. Ralf Reiting (Hessen State Laboratory, Kassel, Germany) and Dr. Gabriele Näumann (Authority for Social Affairs, Family, Health and Consumer Protection, Institute for Hygiene and the Environment, Hamburg, Germany) for their co-operation and for providing rice samples.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guertler, P., Huber, I., Pecoraro, S. et al. Development of an event-specific detection method for genetically modified rice Kefeng 6 by quantitative real-time PCR. J. Verbr. Lebensm. 7, 63–70 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-011-0748-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00003-011-0748-6