Abstract
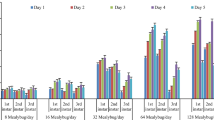
The citrus mealybugPlanococcus citri (Risso) and the vine mealybugPlanococcus ficus (Signoret) (Hemiptera: Pseudococcidae) are two worldwide polyphagous pests of citrus, vineyards and ornamental plants in greenhouses. Biological control of these pests may rely on the combined release of parasites and predators, which can be affected by intraguild predation (IGP). This study investigated the feeding behavior of different stages ofCryptolaemus montrouzieri Mulsant (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) on mealybugs parasitized byAnagyrus pseudococci (Girault) (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 days. The study was conducted in a climate-controlled room at 28±1° C, 16L:8D, and 65±10% r.h. The highest consumption values for all stages ofC. montrouzieri occurred with 2- and 4-day parasitized mealybugs, whereas the predator did not feed on either species of mealybug parasitized for longer periods, due to the onset of mummification.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acheche, H., Fattouch, S., Mhirsi, S., Marzouki, N. and Marrakchi, M. (1999) Use of optimized PCR methods for the detection of GLRaV3: a closterovirus associated with grapevine leafroll in Tunisian grapevine plants.Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 17:31–42.
Arim, M. and Marquet, P.A. (2004) Intraguild predation: a widespread interaction related to species biology.Ecol. Lett. 7:557–564.
Ben-Dov, Y. and Germain, V. (2003) Scalenet: A Database of Scale Insects of the World. http://www.Sel.Barc.Usda.Gov.ScalenetScalenet.
Bentley, W. (2002) Vine mealybug,Planococcus ficus, management for North and Central Coast vineyards. ucce.ucdavis.edu/files/filelibrary/2002/4381.pdf.
Berlinger, M.J. (1977) The Mediterranean vine mealybug and its natural enemies in southern Israel.Phytoparasitica 5:3–14.
Borer, E.T. (2002) Intraguild predation in larval parasitoids: implications for coexistence.J. Anim. Ecol. 71:957–965.
Borer, E.T., Briggs, C.J., Murdoch, W.W. and Swarbrick, S.L. (2003) Testing intraguild predation theory in a field system: does numerical dominance shift along a gradient of productivity?Ecol. Lett. 6:929–935.
Brodeur, J. and Rosenheim, J.A. (2000) Intraguild interactions in aphid parasitoids.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 97:93–108.
Cabaleiro, C. and Segura, A. (1997) Field transmission of grapevine leafroll associated virus 3 (GLRaV-3) by the mealybugPlanococcus citri.Plant Dis. 81:283–287.
Cardinale, B.J., Harvey, C.T., Gross, K. and Ives, A.R. (2003) Biodiversity and biocontrol: emergent impact of a multi-enemy assemblage on pest suppression and crop yield in an agroecosystem.Ecol. Lett. 6:857–865.
Colfer, R.G. and Rosenheim, J.A. (2001) Predation on immature parasitoids and its influence on aphid population suppression.Oecologia 126:292–304.
Duso, C. (1989) Indagini bioecogiche suPlanococcus ficus sign. nel veneto [Indigenous bioecology ofPlanococcus ficus in the Veneto region].Boll. Lab. Entomol. Agrar. ‘Filippo Silvestri’ 46:3–20.
Frazer, B.D., Gilbert, N., Ives, P.M. and Ranworth, D.A. (1981) Predator reproduction and overall predatorprey relationship.Can. Entomol. 113:1015–1024.
Fritz, R.S. (1982) Selection for host modification by insect parasitoids.Evolution 36:283–288.
Heidari, M. and Copland, M.J.W. (1992) Host finding byCryptolaemus montrouzieri (Col., Coccinellidae), a predator of mealybugs (Hom., Pseudococcidae).Entomophaga 37:621–625.
Hussey, N.W. and Scopes, N. (1985) Biological Pest Control: The Glasshouse Experience. Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY, USA.
Islam, K.S., Perera, H.A.S. and Copland, M.J.W. (1997) The effects of parasitism by an encyrtid parasitoid,Anagyrus pseudococci on the survival, reproduction and physiological changes of the mealybug,Planococcus citri.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 34:77–83.
Joyce, A.L., Hoddle, M.S., Bellows, T.S. and Gonzaléz, D. (2001) Oviposition behaviour ofCoccidoxenoides peregrinus, a parasitoid ofPlanococcus ficus.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 98:49–57.
Kaydan, M.B., Kilincer, N., Uygun, N., Japoshvilli, G. and Gaimari, S. (2006) Parasitoids and predators of Pseudococcidae (Hemiptera: Coccoidea) in Ankara, Turkey.Phytoparasitica 34:331–337.
Kester, K.M. and Jackson, D.M. (1996) When good bugs go bad: intraguild predation byJalysus wickhami on the parasitoid,Cotesia congregata.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 81:271–276.
Lucas, E., Coderre, D. and Brodeur, J. (1998) Intraguild predation among aphid predators: characterization and influence of extraguild prey density. http://www.fidaticles.com/cf_dls/n3_m2120/n3.
Lucas, E., Labrecque, C. and Coderre, D. (2004)Delphastus catalinae andColeomegilla maculata lengi (Coleoptera: Coccinellidae) as biological control agents of the greenhouse whitefly,Trialeurodes vaporariorum (Homoptera: Aleyrodidae).Pest Manag. Sci. 60:1073–1078.
Malakar-Kuenen, R., Daane, K., Bentley, W., Yokota, G. and Martin, L. (2001) Population dynamics of vine mealybug and its natural enemies in the Coachella and San Joaquin valleys.UC Plant Prot. Q. 11:1–4.
Meyhöfer, R. (2001) Intraguild predation by aphidophagous predators on parasitized aphids: the use of multiple video cameras.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 100:77–87.
Meyhöfer, R. and Hindayana, D. (2000) Effects of intraguild predation on aphid parasitoid survival.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 97:115–122.
Murdoch, W.W. (1990) The relevance of pest-enemy models to biological control.in: Mackauer, M., Ehler, L.E. and Roland, J. [Eds.] Critical Issues in Biological Control. Intercept Ltd., Andover, UK. pp. 1–24.
New, T.R. (1991) Insects as Predators. New South Wales University Press, Kensington, Australia.
Niyazau, O.P. (1967)Anagyrus pseudococci (Gir.) (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) parasitoid of the mealybugPlanococcus citri (Risso).Rev. Appl. Entomol. Ser. 61:4.
Noyes, J.S. and Hayat, M. (1994) Mealybug Parasitoids of the Anagyrini (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) with a World Review of Use in Classical Biological Control and an Index of Parasitoids of Mealybugs (Homoptera: Pseudocccidae). CAB International, Wallingford, UK.
Phoofolo, M.W. and Obrycki, J.J. (1998) Potential for intraguild predation and competition among predatory Coccinellidae and Chrysopidae.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 89:47–55.
Polis, G.A., Myers, C.A. and Holt, R.D. (1989) The ecology and evolution of intraguild predation: potential competitors that eat each other.Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 20:297–330.
Rosenheim, J.A., Kaya, H.K., Ehler, L.E., Marois, J.J. and Jaffee, B.A. (1995) Intraguild predation among biological-control agents: Theory and evidence.Biol. Control 5:303–335.
Sengonca, Ç. and Yanuwiadi, B. (1994) Frassverhalten des schmierlausraubersCryptolaemus montrouzieri Mulsant Bei durchLeptomastix dactylopii Howard parasitiertenPlanococcus citri (Risso).Mitt. Dtsch. Ges. Allg. Angew. Entomol. 9:121–124.
Telli, S.Ö. and Yiğit, A. (2000) Consumption capacity and duration of larval development of some natural enemies of citrus mealybug,Planococcus citri Risso (Hom.:Pseudococcidae).Turkish Fourth Entomological Congress (Aydın, Turkey) (Turkish, with English abstract), pp. 401–407.
Tingle, C.C.D. and Copland, M.J.W. (1988) Predicting development of the mealybug parasitoidsAnagyrus pseudococci, Leptomastix dactylopii andLeptomastidea abnormis under glasshouse conditions.Entomol. Exp. Appl. 46:19–28.
Tingle, C.C.D. and Copland, M.J.W. (1989) Progeny production and adult longevity of the mealybug parasitoidsAnagyrus pseudococci, Leptomastix dactylopii andLeptomastidea abnormis (Hym.: Encyrtidac) in relation to temperature.Entomophaga 34:111–120.
Trjapitzin, V.A. and Triapitzin, S.V. (2002) A new species ofNeoplatycerus (Hymenoptera: Encyrtidae) from Egypt, parasitoid of the vine mealybug,Planococcus ficus (Homoptera: Pseudococcidae).Entomol. News 113:203–210.
Ülgentürk, S., Noyes, J., Zeki, C. and Kaydan, M.B. (2004) Natural enemies of Coccoidea (Hemiptera) on orchard trees and neighbouring areas plants in Afyon, Ankara, Burdur, Isparta provinces, Turkey.Proc. X International Symposium on Scale Insect Studies (Adana, Turkey), pp. 361–372.
Uygun, N. (2001) Integrated pest management in Turkish citrus orchard. Agricultural Research Project Publications, Adana, Turkey (Turkish, with English abstract).
Yiğit, A. and Canhilal, R. (1998) Introduction into East Mediterranean region of cold-tolerant ecotypes of the Citrus mealybug’s predatorCryptolaemus montrouzieri Muls. (Col.:Coccinellidae), some biological properties and their adaptation to the region.Bull. Plant Prot. 38(1–2):23–41 (Turkish, with English abstract).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
http://www.phytoparasitica.org posting August 4, 2008.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muştu, M., Kilinçer, N., Ülgentürk, S. et al. Feeding behavior ofCryptolaemus montrouzieri on mealybugs parasitized byAnagyrus pseudococci . Phytoparasitica 36, 360–367 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980815
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02980815