Abstract
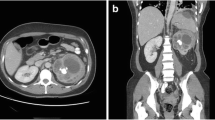
Replacement lipomatosis (RPL) is seen in patients in whom renal parenchyma is destroyed due to chronic calculous disease and inflammation. The triggering mechanism for xanthogranulomatous pyclonephritis (XCP) is also the same. We report a case in which RPL and XGP coexist in the same kidney. To our knowledge, this coexistence has not been previously reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kutzman A: Replacement lipomatosis of the kidney.Surg Gynecol Obstet 52:690–701, 1931
Calver H: Replacement lipomatosis of the kidney.Surg Clin North Am 14:813–819, 1934
Ambos MA, Bosniak MA, Gordon R, Madayag MA: Replacement lipomatosis of the kidney.AJR 130:1087–1091, 1978
Subramanyam BR, Bosniak MA, Horii SC, Megibow AJ, Balthazar EJ: Replacement lipomatosis of the kidney: Diagnosis by computer tomography and sonography.Radiology 148:791–792, 1983
Goldman SM, Hartman DS, Fishman EK, Finizio JP, Gatewood OMB, Siegelman SS: CT of xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis: Radiologic-pathologic correlation.AJR 141:963–969, 1984
Hartman DS, Davis CJ, Goldman SM, Isbister SS, Sanders RC: XGP: Sonographic-pathologic correlation of 16 cases.J Ultrasound Med 3:481–488, 1984
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Acunas, B., Acunaş, G., Rozanes, Í. et al. Coexistent xanthogranulomatous pyelonephritis and massive replacement lipomatosis of the kidney: CT diagnosis. Urol Radiol 12, 88–90 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02923975
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02923975