Abstract
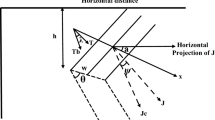
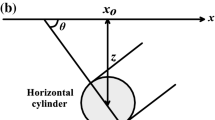
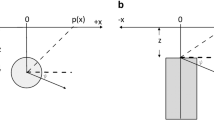
The magnetic anomaly due to a buried dike consists of the sum of two easily separated elementary functions. These functions, which have simple symmetry, are called even and odd functions. The correlation factors (r 0,1 for the even andr 0,2 for the odd function) between least-squares residual anomalies from even and odd functions are computed. Correlation values are used to determine the depth to the top and the half-width of the dike. The method also includes the determination of the index parameter and the amplitude coefficient. The validity of the method is tested against a theoretical and a field example where the parameters of the latter were determined by other investigators in comparing the results.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelrahman, E. M. (1990),Magnetic Interpretation of Long Horizontal Cylinders Using Correlation Factors Between Successive Least-squares Residual Anomaly Profiles, Pure and Appl. Geophys.132, 521–531.
Abdelrahman, E. M., andEl-Araby, H. M. (1993),Shape and Depth Solutions from Gravity Data Using Correlation Factors Between Successive Least-squares Residuals, Geophysics58, 1785–1791.
Atchuta Rao, D., andRam Babu, H. V. (1981),Nomograms for Rapid Evaluation of Magnetic Anomalies over Long Tabular Bodies, Pure and Appl. Geophys.119, 1037–1050.
Bhimasankaram, V. L. S., Mohan N. L., andSeshagiri Rao, S. V. (1978),Interpretation of Magnetic Anomalies of Dikes Using Fourier Transform, Geoexploration16, 259–266.
Hutchison, R. D. (1958),Magnetic Analysis by Logarithmic Curves, Geophysics23, 749–769.
Koulomzine, T. H., Lamontagne, Y., andNadeau, A. (1970),New Methods for the Direct Interpretation of Magnetic Anomalies Caused by Inclined Dikes of Infinite Length, Geophysics35, 812–830.
Parker Gay, S. (1963),Standard Curves for Interpretation of Magnetic Anomalies over Long Tabular Bodies, Geophysics28, 161–200.
Powell, D. W. (1967),Fitting Observed Profiles to a Magnetized Dike or Fault-step Model, Geophys. Prospect.15, 208–220.
Radhakrishna Murthy, I. V. (1985),The Midpoint Method: Magnetic Interpretation of Dikes and Faults, Geophysics50, 834–839.
Ram Babu, H. V., Subrahmanyam, A. S., andAtchuta Rao, D. (1982),A Comparative Study of The Relation Figures of Magnetic Anomalies Due to Two-dimensional Dike and Vertical Step Models, Geophysics47, 926–931.
Rao, B. S. R., Radhakrishna Murty, I. V., andVisweswara Rao, C. (1973),Two Methods for Computer Interpretation of Magnetic Anomalies of Dikes, Geophysics38, 710–718.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kara, I., Özdemir, M. & Ahmet Yüksel, F. Interpretation of magnetic anomalies of dikes using correlation factors. PAGEOPH 147, 777–788 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01089702
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01089702