Abstract
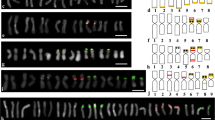
Pulsed field gel electrophoresis experiments show that chromosomal length polymorphisms are produced during meiosis in the ascomycetous plant pathogen Leptosphaeria maculans. Homologues in tetrads of L. maculans were identified on the basis of their binding to chromosome-specific probes that included β-tubulin, nitrate reductase, 18S ribosomal DNA and two Random Amplified Polymorphic DNA (RAPD) markers. Changes in size of homologues were followed during meiosis. Significant karyotype variation was evident due to the random assortment of parental homologues of different sizes. In most cases, the progeny had the same-sized homologues as the parents; however, in some instances novel-sized homologues were detected that varied in size from those of the parents by up to 50 kb. Our results are consistent with the hypothesis that these novel chromosomal length polymorphisms are produced by reciprocal recombination between parental homologous chromosomes of unequal sizes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Howlett BJ, Brownlee AG, Guest DI, Adcock G, McFadden GI (1992) The 5S ribosomal RNA gene is linked to large and small subunit ribosomal RNA genes in several oomycetes. Curr Genet 22:455–461
Kinscherf TG, Leong SA (1988) Molecular analysis of the karyotype of Ustilago maydis. Chromosoma 96:427–433
Koenraadt H, Somerville SC, Jones AL (1992) Characterisation of mutations in the β-tubulin gene of benomyl-resistant field strains of Venturia inaequalis and other plant pathogenic fungi. Phytopathology 82:1348–1354
Mengistu A, Rimmer RS, Williams PH (1993) Protocols for in vitro sporulation, ascospore release, sexual mating and fertility in crosses of Leptosphaeria maculans. Plant Dis 77:538–540
Mengistu A, Hill CB, Williams PH (1995) An improved method for mating and fertility in crosses of Leptosphaeria maculans, the causal agent of blackleg of crucifers. Plant Dis, in press
Morales VM, Seguin-Swartz G, Taylor JL (1993) Chromosome length polymorphism in Leptosphaeria maculans. Phytopathology 83:503–509
Ono B, Ishino-Aran Y (1988) Inheritance of chromosomal length polymorphisms in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr Genet 14:413–418
Orbach MJ, Porro EB, Yanofsky C (1986) Cloning and characterization of the gene for β tubulin from a benomyl resistant mutant of Neurospora crassa and its use as a dominant selectable marker. Mol Cell Biol 6:2452–2461
Plummer KM, Howlett BJ (1993) Major chromosomal length polymorphisms are evident after meiosis in the blackleg fungus, Leptosphaeria maculans. Curr Genet 24:107–113
Powell WA, Kistler HC (1990) In vivo rearrangement of foreign DNA by Fusarium oxysporum produces linear self-replicating plasmids. J Bacteriol 172:3163–3171
Russell BW, Mills D (1992) Electrophoretic karyotypes of Tilletia caries, T. controversa, and their F1 progeny: further evidence for conspecific status. Mol Plant Microbe Int 6:66–74
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York
Schechtman MG (1990) Characterisation of telomere DNA from Neurospora crassa. Gene 88:159–165
Shampay J, Szostak JW, Blackburn EH (1984) DNA sequences of telomeres maintained in yeast. Nature 310:154–157
Skinner DZ, Budde AD, Farman ML, Smith JR, Leong H, Leong SA (1993) Genome organization of Magnaporthe grisea: genetic map, electrophoretic karyotype, and occurrence of repeated DNAs. Theor Appl Genet 87:454–457
Taylor JL, Borgmann IE (1994) Characterisation of an unusual sequence from the highly virulent strain of Leptosphaeria maculans and evidence of transfer of it to the weakly virulent strain. Mol Plant Microbe Int 7:181–188
Taylor JL, Borgmann IE, Seguin-Swartz G (1991) Electrophoretic karyotyping of Leptosphaeria maculans differentiates highly virulent from weakly virulent isolates. Curr Genet 19:273–277
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucleic Acids Res 18:6531–6535
Williams RSB, Davis MA, Howlett BJ (1994) Nitrate reductase of Leptosphaeria maculans: gene sequence, chromosomal location, mutant isolation and complementation. Mol Gen Genet 244:1–8
Zolan ME (1995) Chromosome-length polymorphisms in fungi. Microbiol Rev, in press
Zolan ME, Heyler NK, Ramesh MA (1993) Gene mapping using marker chromosomes in Coprinus cinereus. In: Baltz RH, Hegeman GD, Skatrud PL (eds) Industrial organisms: basic and applied molecular genetics. American Society for Microbiology, Washington DC, pp 31–35
Zolan ME, Heyler NK, Stassen NY (1994) Inheritance of chromosome-length polymorphisms in Coprinus cinereus. Genetics 137:87–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. van den Hondel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Plummer, K.M., Howlett, B.J. Inheritance of chromosomal length polymorphisms in the ascomycete Leptosphaeria maculans . Molec. Gen. Genet. 247, 416–422 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293142
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293142