Abstract
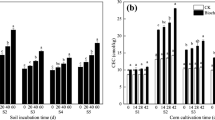
The effects of cropping corn on the decrease in the extractability of Zn added to a calcareous soil were studied by a pot experiment and chemical extractions. The results show that the concentrations of Zn exchangeable with MgCl2 (EXC-Zn) and extractable with DTPA (DTPA-Zn) in the soils with added Zn decreased with time. The processes associated with the decrease in extractability in DTPA of Zn added to soil can be described aptly by a diffusion equation which gives the proportion of added Zn in the non-DTPA fraction as a function of the square root of incubation time. This result suggests that the diffusion of Zn cations into microporous solids is a rate-limiting reaction. The relative diffusion rate coefficients (D/r2) were found to be 1.95×10-10 and 3.34×10-10 sec-1 in the soils with added Zn of 20 and 60 mg kg-1, respectively. Compared with uncropped soil, the concentrations of DTPA-Zn in the soils with added Zn were decreased by cropping. The decrease of DTPA-Zn in the soils in the presence of corn can be attributed to both its acquisition by corn and other processes associated with the growing of corn. The activity of plant roots would appear to enhance the process of decrease in the extractability in DTPA of Zn added to the soil. The source of Zn uptake by corn was affected by the loading or activity of Zn in soil. In the soil with low available Zn, the DTPA non-extractable Zn (non-DTPA-Zn) was mobilized and taken up by corn. In the soils with high available Zn, e.g. the recently added Zn, only EXC-Zn and a part of the DTPA-Zn were taken up by corn.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armour J D, Ritchie G S P and Robson A D 1989 Changes with time in the availability of soil applied zinc to navy beans and in the chemical extraction of zinc from soils. Aust. J. Soil Res. 27, 699–710.
Barrow N J 1986 Testing a mechanistic model. II. The effects of time and temperature on the reaction of zinc with a soil. J. Soil Sci. 37, 277–286.
Boawn L C 1974 Residual availability of fertilizer zinc. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 38, 800–803.
Bruemmer G M, Gerth J and Tiller K G 1988 Reaction kinetics of the adsorption and desorption of nickel, zinc and cadmium by goethite. I. Adsorption and diffusion of metals. J. Soil Sci. 39, 37–52.
Crank J 1975 The Mathematics of Diffusion. Oxford Univ. Press, London, UK.
Follett R H and Lindsay W L 1971 Changes in DTPA-extractable zinc, iron, manganese, and copper in soils following fertilization. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 35, 600–602.
Jackson B L J 1985 A modified sodium tetraphenylboron method for the routine determination of reserve potassium status of soil. J. Exp. Agric. 13, 253–262.
Kärger J and Ruthven D M 1992 Diffusion in Zeolites and Other Microporous Solids. John Wiley and Sons, New York, USA.
Lindsay W L and Norvell W A 1978 Development of a DTPA soil test for zinc, iron, manganese and copper. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 42, 421–428.
Linehan D J, Sinclair A H and Mitchell M C 1985 Mobilisation of Cu, Mn and Zn in the soil solution of barley rhizospheres. Plant and Soil 86, 147–149.
Liu X B, Yang Q, Chu T D, Wang S H, Li S R and Wu X F 1993 Effect of zinc application on corn. Acta Pedol. Sin. 30, 153–162.
Martens D C and Westermann D T 1991 Fertiliser applications for correcting micronutrient deficiencies. In Micronutrients in Agriculture. Eds. J J Mortvedt, F R Cox, L M Shuman and R M Welch. pp 549–592. Soil Sci. Soc. Am., Inc., Madison, WI, USA.
McLaren R G, McLenaghen R D and Swift R S 1991 Zinc application to pastures: effect on herbage and soil zinc concentrations. N. Z. J. Agric. Res. 34, 113–118.
Norrish K and Pickering J G 1983 Clay minerals. In Soils: an Australian Viewpoint. Ed. Division of Soils, CSIRO. pp 281–308. CSIRO, Melbourne, Australia.
Scott A D and Reed M G 1962 Chemical extraction of potassium from soils and micaceous minerals with solutions containing sodium tetraphenylboron: III. Illite. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 26, 45–48.
Shuman L M 1991 Chemical forms of micronutrients in soils. In Micronutrients in Agriculture. Eds. J J Mortvedt, F R Cox, L M Shuman and R M Welch. pp 113–144. Soil Sci. Soc. Am., Inc., Madison, WI, USA.
Soon Y K 1994 Effect of long term cropping on availability of Cu, Mn and Zn in soil following clearing of a boreal forest. Plant and Soil 160, 157–160.
Treeby M, Marschner H and Römheld V 1989 Mobilisation of iron and other micronutrients cation from a calcareus soil by plantborne, microbial, and synthetic metal chelators. Plant and Soil 114, 217–226.
US Department of Agriculture 1988 Soil Taxonomy:A Basic System of Soil Classification for Making and Interpreting Soil Surveys. Robert E. Krieger Publishing Company, Florida, USA.
Xi C F and Gong Z T 1990 Classification of soils. In Soils of China (the English edition) Ed. Institute of Soil Science, Academia Sinica. pp 11–19. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Xu J Q 1990 Clay minerals in soils. In Soils of China (the English edition). Ed. Institute of Soil Science, Academia Sinica. pp 434–459. Science Press, Beijing, China.
Zhang F S, Römheld V and Marschner H 1989 Effect of zinc deficiency in wheat on the release of zinc and iron mobilising root exudates. Z. Pflanzenernähr. Bodenkd. 152, 205–210.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, Y.B., Uren, N.C. The effects of cropping corn on the extractability of zinc added to a calcareous soil. Plant Soil 181, 221–226 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012056
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00012056