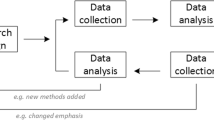
Abstract
In a blinded inference study, researchers are asked to analyze condition-blinded datasets and make inferences about various aspects of the data generation process, such as whether or not a variable that manipulates some target cognitive process varied across conditions. This procedure directly tests researchers’ ability to make valid conclusions about underlying processes based on data patterns and assesses the extent to which they accurately report the level of uncertainty associated with their research conclusions. As such, blinded inference studies are a valuable tool in the effort to improve research practices. In this comment, we review three recent studies in the cognitive modeling literature to highlight the benefits of blinded inference, and we make recommendations for future blinded inference studies. We conclude by encouraging modelers to champion the blinded inference method as a fundamental component of effective psychological research.

Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
Details of this study, including complete instructions to the contributions and their inferences about response bias, are available at https://osf.io/92ahy.
References
Boehm, U., Annis, J., Michael, J. F., Guy, E. H., Heathcote, A., Kellen, D., Krypotos, A.-M., Lerche, V., Gordon, D. L., Thomas, J. P., van Ravenzwaaij, D., Servant, M., Singmann, H., Jeffrey, J. S., Voss, A., Wiecki, T., Matzke, D., & Wagenmakers, E.-J. (2018). Estimating across-trial variability parameters of the diffusion decision model: expert advice and recommendations. Journal of Mathematical Psychology, 87, 46–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmp.2018.09.004.
Brier, G. W. (1950). Verification of forecasts expressed in terms of probability. Monthly Weather Review, 78, 1–3.
Dutilh, G., Annis, J., Brown, S. D., Cassey, P., Evans, N. J., Grasman, R. P. P. P., Hawkins, G. E., Heathcote, A., Holmes, W. R., Krypotos, A. M., Kupitz, C. N., Leite, F. P., Lerche, V., Lin, Y. S., Logan, G. D., Palmeri, T. J., Starns, J. J., Trueblood, J. S., van Maanen, L., van Ravenzwaaij, D., Vandekerckhove, J., Visser, I., Voss, A., White, C. N., Wiecki, T. V., Rieskamp, J., & Donkin, C. (2018). The quality of response time data inference: a blinded, collaborative assessment of the validity of cognitive models. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 1–19. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13423-017-1417-2.
Lee, M. D., Criss, A., Devezer, B., Donkin, C., Etz, A., Leite, F. P., Matzke, D., Rouder, J. N., Trueblood, J. S., White, C. N., Vandekerckhove, J. (in press). Robust modeling in cognitive science.
MacCoun, R., & Perlmutter, S. (2015). Blind analysis: hide results to seek the truth. Nature, 526, 187–189. https://doi.org/10.1038/526187a.
Macmillan, N. A., & Creelman, C. D. (2005). Detection theory: A user's guide (2nd ed.). Mahwah, NJ, US: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates Publishers.
Plato. (1952). Plato’s Phaedrus. Cambridge: University Press.
Rae, B., Heathcote, A., Donkin, C., Averell, L., & Brown, S. (2014). The hare and the tortoise: emphasizing speed can change the evidence used to make decisions. Journal of Experimental Psychology: Learning, Memory, and Cognition, 40, 1226–1243.
Ratcliff, R. (1978). Theory of memory retrieval. Psychological Review, 85, 59–108. https://doi.org/10.1037//0033-295X.85.2.59.
Ratcliff, R., & Tuerlinckx, F. (2002). Estimating parameters of the diffusion model: approaches to dealing with contaminant reaction times and parameter variability. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 9, 438–481. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03196302.
Rinkenauer, G., Osman, A., Ulrich, R., Müller-Gethmann, H., & Mattes, S. (2004). On the locus of speed-accuracy trade-off in reaction time: inferences from the lateralized readiness potential. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 133, 261–282.
Shiffrin, R. M., & Steyvers, M. (1997). A model for recognition memory: REM—retrieving effectively from memory. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review, 4, 145–166.
Silberzahn, R., Uhlmann, E. L., Martin, D., Anselmi, P., Aust, F., Awtrey, E. C., … Nosek, B. A. (2018). Many analysts, one dataset: making transparent how variations in analytical choices affect results. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science, 1, 337–356. https://doi.org/10.17605/OSF.IO/QKWST
Starns, J. J., Ratcliff, R., & McKoon, G. (2012). Evaluating the unequal-variance and dual-process explanations of zROC slopes with response time data and the diffusion model. Cognitive Psychology, 64, 1–34.
Starns, J. J., Cataldo, A. M., Rotello, C. M., et al. (in press). Assessing theoretical conclusions with blinded inference to investigate a potential inference crisis. Advances in Methods and Practices in Psychological Science.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Starns, J.J., Cataldo, A.M. & Rotello, C.M. Blinded Inference: an Opportunity for Mathematical Modelers to Lead the Way in Research Reform. Comput Brain Behav 2, 223–228 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42113-019-00040-3
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42113-019-00040-3