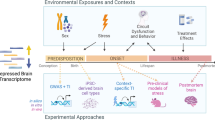
Abstract
According to the WHO approximately 350 million individuals worldwide are affected by depression, making it the global leading cause of disability. Depression also closely associates with suicide. The last three decades have seen a wealth of genetic studies aiming to identify genes associated with depression and suicidal behavior, whereas more recent advances in our understanding of how the genome is functionally regulated, coupled with developments in high-throughput sequencing methods, have led to an increased capacity and interest in the study of functional genomics. These studies provide us with a unique opportunity to understand how the brain is regulated and to more directly investigate genomic processes that may be at fault in the depressed and suicidal brain. In this review, we discuss recent advances in studies investigating transcriptomic and epigenomic studies of depression and suicide.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GWAS:
-
Genome-wide association studies
- GEWIS:
-
Genome-environment-wide interaction studies
- mCH:
-
Non-CpG methylation
- MDD:
-
Major depression
- dlPFC:
-
Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- ncRNA:
-
Non-coding RNA
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- LCM:
-
Laser capture microdissection
- FACS:
-
Fluorescence-activated cell sorting
- MBD-seq:
-
Methyl-CpG-binding domain protein sequencing
- DMRs:
-
Differentially methylated regions
References
Papers of Particular Interest, Published recently, Have Been Highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
• Turecki G, Brent DA. Suicide and suicidal behaviour. Lancet. 2016;387(10024):1227–39. A model of suicide and suicidal behaviour
Sullivan PF, Neale MC, Kendler KS. Genetic epidemiology of major depression: review and meta-analysis. American Journal of Psychiatry AJP. 2000;157(10):1552–62.
Hindorff LA, Sethupathy P, Junkins HA, Ramos EM, Mehta JP, Collins FS, Manolio TA. Potential etiologic and functional implications of genome-wide association loci for human diseases and traits. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106(23):9362–7.
Bosker FJ, Hartman CA, Nolte IM, Prins BP, Terpstra P, Posthuma D, Nolen WA. Poor replication of candidate genes for major depressive disorder using genome-wide association data. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2010;16(5):516–32.
Dunn EC, Brown RC, Dai Y, Rosand J, Nugent NR, Amstadter AB, Smoller JW. Genetic determinants of depression. Harvard Review of Psychiatry. 2015;23(1):1–18.
• Turecki G. The molecular bases of the suicidal brain. Nature Reviews Neuroscience Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014;15(12):802–16. A review on the molecular neurobiology of suicide
• Fraga MF, Ballestar E, Paz MF, Ropero S, Setien F, Ballestar ML, Esteller M. Epigenetic differences arise during the lifetime of monozygotic twins. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2005;102(30):10604–9. A study showing accumulating epigenetic differences between monozygotic twins despite shared genetic code
Thomas D. Gene–environment-wide association studies: emerging approaches. Nat Rev Genet Nature Reviews Genetics. 2010;11(4):259–72.
Thomas D. Methods for investigating gene-environment interactions in candidate pathway and genome-wide association studies. Annu Rev Public Health Annual Review of Public Health. 2010;31(1):21–36.
Dunn EC, Wiste A, Radmanesh F, Almli LM, Gogarten SM, Sofer T, Smoller JW. Genome-wide association study (Gwas) and genome-wide by environment interaction study (Gweis) of depressive symptoms in African American and Hispanic/Latina women. Depression and Anxiety Depress Anxiety. 2016;33(4):265–80.
Petronis A. Epigenetics as a unifying principle in the aetiology of complex traits and diseases. Nature. 2010;465(7299):721–7.
Waddington CH. Organisers & genes. Cambridge: University Press; 1940.
Bird A. Perceptions of epigenetics. Nature. 2007;447(7143):396–8.
Urdinguio RG, Sanchez-Mut JV, Esteller M. Epigenetic mechanisms in neurological diseases: genes, syndromes, and therapies. The Lancet Neurology. 2009;8(11):1056–72.
Portela A, Esteller M. Epigenetic modifications and human disease. Nat Biotechnol Nature Biotechnology. 2010;28(10):1057–68.
•• Lister R, Mukamel EA, Nery JR, Urich M, Puddifoot CA, Johnson ND, Ecker JR. Global epigenomic reconfiguration during mammalian brain development. Science. 2013;341(6146):1237905. An important study characterizing several epigenetic marks in neurons throughout development
Kulis M, Esteller M. DNA methylation and cancer. Adv Genet. 2010;70:27–56.
Klose RJ, Bird AP. Genomic DNA methylation: the mark and its mediators. Trends Biochem Sci. 2006;31(2):89–97.
Deng G, Chen A, Pong E, Kim YS. Methylation in hMLH1 promoter interferes with its binding to transcription factor CBF and inhibits gene expression. Oncogene. 2001;20(48):7120–7.
Oda S, Fukami T, Yokoi T, Nakajima M. Epigenetic regulation is a crucial factor in the repression of UGT1A1 expression in the human kidney. Drug Metab Dispos. 2013;41(10):1738–43.
Domcke S, Bardet AF, Ginno PA, Hartl D, Burger L, Schübeler D. Competition between DNA methylation and transcription factors determines binding of NRF1. Nature. 2015;528(7583):575–9.
Maunakea AK, Nagarajan RP, Bilenky M, Ballinger TJ, D’Souza C, Fouse SD, Costello JF. Conserved role of intragenic DNA methylation in regulating alternative promoters. Nature. 2010;466(7303):253–7.
Turecki G, Ota VK, Belangero SI, Jackowski A, Kaufman J. Early life adversity, genomic plasticity, and psychopathology. The Lancet Psychiatry. 2014;1(6):461–6.
Lutz P, Almeida D, Fiori L, Turecki G. Childhood maltreatment and stress-related psychopathology: the epigenetic memory hypothesis. CPD Current Pharmaceutical Design. 2015;21(11):1413–7.
Lutz P, Turecki G. DNA methylation and childhood maltreatment: from animal models to human studies. Neuroscience. 2014;264:142–56. doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.07.069.
Talens RP, Boomsma DI, Tobi EW, Kremer D, Jukema JW, Willemsen G, Heijmans BT. Variation, patterns, and temporal stability of DNA methylation: considerations for epigenetic epidemiology. FASEB J. 2010;24(9):3135–44.
Flanagan JM, Brook MN, Orr N, Tomczyk K, Coulson P, Fletcher O, Garcia-Closas M. Temporal stability and determinants of white blood cell DNA methylation in the breakthrough generations study. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev. 2014;24(1):221–9.
• Ziller MJ, Gu H, Müller F, Donaghey J, Tsai LT, Kohlbacher O, Meissner A. Charting a dynamic DNA methylation landscape of the human genome. Nature. 2013;500(7463):477–81. A study conducting whole-genome bisulfite sequencing across 30 diverse human cell and tissue types
Ladd-Acosta C, Pevsner J, Sabunciyan S, Yolken RH, Webster MJ, Dinkins T, Feinberg AP. DNA methylation signatures within the human brain. Am J Hum Genet. 2007;81(6):1304–15.
Ghosh S, Yates AJ, Frühwald MC, Miecznikowski JC, Plass C, Smiraglia D. Tissue specific DNA methylation of CpG islands in normal human adult somatic tissues distinguishes neural from non-neural tissues. Epigenetics. 2010;5(6):527–38.
Xin Y, Chanrion B, Liu M, Galfalvy H, Costa R, Ilievski B, Haghighi F. Genome-wide divergence of DNA methylation marks in cerebral and cerebellar cortices. PLoS One. 2010;5(6) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011357.
Liang P, Song F, Ghosh S, Morien E, Qin M, Mahmood S, Held WA. Genome-wide survey reveals dynamic widespread tissue-specific changes in DNA methylation during development. BMC Genomics. 2011;12(1):231.
Davies MN, Volta M, Pidsley R, Lunnon K, Dixit A, Lovestone S, Mill J. Functional annotation of the human brain methylome identifies tissue-specific epigenetic variation across brain and blood. Genome Biol Genome Biology. 2012;13(6):R43.
Varley KE, Gertz J, Bowling KM, Parker SL, Reddy TE, Pauli-Behn F, Myers RM. Dynamic DNA methylation across diverse human cell lines and tissues. Genome Res. 2013;23(3):555–67.
Turecki G, Meaney MJ. Effects of the social environment and stress on glucocorticoid receptor gene methylation: a systematic review. Biol Psychiatry. 2016;79(2):87–96. A meta-analysis summarizing studies that show a robust effect of childhood maltreatment on glucocorticoid receptor methylation
Walton E, Hass J, Liu J, Roffman JL, Bernardoni F, Roessner V, Ehrlich S. Correspondence of DNA methylation between blood and brain tissue and its application to schizophrenia research. SCHBUL Schizophrenia Bulletin. 2015;42(2):406–14.
Uddin M, Koenen KC, Aiello AE, Wildman DE, Santos RD, Galea S. Epigenetic and inflammatory marker profiles associated with depression in a community-based epidemiologic sample. Psychological Medicine Psychol Med. 2010;41(05):997–1007.
Davies MN, Krause L, Bell JT, Gao F, Ward KJ, Wu H, Wang J. Hypermethylation in the ZBTB20 gene is associated with major depressive disorder. Genome Biol Genome Biology. 2014;15(4):R56.
Autry AE, Monteggia LM. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neuropsychiatric disorders. Pharmacol Rev. 2012;64(2):238–58.
Januar V, Ancelin M, Ritchie K, Saffery R, Ryan J. BDNF promoter methylation and genetic variation in late-life depression. Translational Psychiatry Transl Psychiatry. 2015;5(8):e619.
Kang H, Kim J, Bae K, Kim S, Shin I, Kim H, Yoon J. Longitudinal associations between BDNF promoter methylation and late-life depression. Neurobiol Aging. 2015;36(4):1764.
Kim J, Kang H, Kim S, Kim S, Shin I, Kim H, Yoon J. BDNF promoter methylation associated with suicidal ideation in patients with breast cancer. The International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine Int J Psychiatry Med. 2015;49(1):75–94.
Kang H, Kim J, Lee J, Kim S, Bae K, Kim S, Yoon J. BDNF promoter methylation and suicidal behavior in depressive patients. J Affect Disord. 2013;151(2):679–85.
Na K, Won E, Kang J, Chang HS, Yoon H, Tae WS, Ham B. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor promoter methylation and cortical thickness in recurrent major depressive disorder. Sci Rep Scientific Reports. 2016;6:21089.
Molendijk ML, Bus BA, Spinhoven P, Penninx BW, Kenis G, Prickaerts J, Elzinga BM. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in major depressive disorder: state–trait issues, clinical features and pharmacological treatment. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2010;16(11):1088–95.
• Tsankova NM, Berton O, Renthal W, Kumar A, Neve RL, Nestler EJ. Sustained hippocampal chromatin regulation in a mouse model of depression and antidepressant action. Nature Neuroscience Nat Neurosci. 2006;9(4):519–25. A study providing evidence of an important role for histone remodeling in the pathophysiology and treatment of depression
Tadić A, Wagner S, Schlicht KF, Peetz D, Borysenko L, Dreimüller N, Lieb K. The early non-increase of serum BDNF predicts failure of antidepressant treatment in patients with major depression: a pilot study. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2011;35(2):415–20.
Tadić A, Müller-Engling L, Schlicht KF, Kotsiari A, Dreimüller N, Kleimann A, Frieling H. Methylation of the promoter of brain-derived neurotrophic factor exon IV and antidepressant response in major depression. Mol Psychiatry. 2013;19(3):281–3.
• Lopez JP, Mamdani F, Labonte B, Beaulieu M, Yang JP, Berlim MT, Turecki G. Epigenetic regulation of BDNF expression according to antidepressant response. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2012;18(4):398–9. A discovered association between H3K27me3 at the BDNF locus, expression, and response to antidepressants
Chen ES, Ernst C, Turecki G. The epigenetic effects of antidepressant treatment on human prefrontal cortex BDNF expression. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology Int J Neuropsychopharm. 2010;14(03):427–9.
Byrne EM, Carrillo-Roa T, Henders AK, Bowdler L, Mcrae AF, Heath AC, Wray NR. Monozygotic twins affected with major depressive disorder have greater variance in methylation than their unaffected co-twin. Translational Psychiatry Transl Psychiatry. 2013;3(6):e269.
Malki K, Koritskaya E, Harris F, Bryson K, Herbster M, Tosto MG. Epigenetic differences in monozygotic twins discordant for major depressive disorder. Translational Psychiatry Transl Psychiatry. 2016;6(6):e839.
Córdova-Palomera A, Fatjó-Vilas M, Gastó C, Navarro V, Krebs M, Fañanás L. Genome-wide methylation study on depression: differential methylation and variable methylation in monozygotic twins. Translational Psychiatry Transl Psychiatry. 2015;5(4):e557.
Fuchsova B, Juliá AA, Rizavi H, Frasch A, Pandey G. Altered expression of neuroplasticity-related genes in the brain of depressed suicides. Neuroscience. 2015;299:1–17.
Hercher C, Canetti L, Turecki G, Mechawar N. Anterior cingulate pyramidal neurons display altered dendritic branching in depressed suicides. J Psychiatr Res. 2010;44(5):286–93.
Maheu ME, Davoli MA, Turecki G, Mechawar N. Amygdalar expression of proteins associated with neuroplasticity in major depression and suicide. J Psychiatr Res. 2013;47(3):384–90.
Monsalve EM, García-Gutiérrez MS, Navarrete F, Giner S, Laborda J, Manzanares J. Abnormal expression pattern of notch receptors, ligands, and downstream effectors in the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex and amygdala of suicidal victims. Molecular Neurobiology Mol Neurobiol. 2013;49(2):957–65.
Zhurov V, Stead JD, Merali Z, Palkovits M, Faludi G, Schild-Poulter C, Poulter MO. Molecular pathway reconstruction and analysis of disturbed gene expression in depressed individuals who died by suicide. PLoS One. 2012;7(10) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0047581.
Kang HJ, Voleti B, Hajszan T, Rajkowska G, Stockmeier CA, Licznerski P, Duman RS. Decreased expression of synapse-related genes and loss of synapses in major depressive disorder. Nature Medicine Nat Med. 2012;18(9):1413–7.
Kékesi KA, Juhász G, Simor A, Gulyássy P, Szegő ÉM, Hunyadi-Gulyás É, Czurkó A. Altered functional protein networks in the prefrontal cortex and amygdala of victims of suicide. PLoS One. 2012;7(12) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0050532.
Chang L, Jamain S, Lin C, Rujescu D, Tseng GC, Sibille E. A conserved BDNF, glutamate- and GABA-enriched gene module related to human depression identified by coexpression meta-analysis and DNA variant genome-wide association studies. PLoS One. 2014;9(3) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0090980.
Fromer M, Pocklington AJ, Kavanagh DH, Williams HJ, Dwyer S, Gormley P, O’Donovan MC. De novo mutations in schizophrenia implicate synaptic networks. Nature. 2014;506(7487):179–84.
Tang A, Chen H, Li TP, Metzbower SR, Macgillavry HD, Blanpied TA. A trans-synaptic nanocolumn aligns neurotransmitter release to receptors. Nature. 2016; doi:10.1038/nature19058.
Sequeira A, Mamdani F, Ernst C, Vawter MP, Bunney WE, Lebel V, Turecki G. Global brain gene expression analysis links glutamatergic and GABAergic alterations to suicide and major depression. PLoS One. 2009;4(8) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0006585.
Klempan TA, Sequeira A, Canetti L, Lalovic A, Ernst C, Ffrench-Mullen J, Turecki G. Altered expression of genes involved in ATP biosynthesis and GABAergic neurotransmission in the ventral prefrontal cortex of suicides with and without major depression. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2007;14(2):175–89.
Yin, H., Pantazatos, S. P., Galfalvy, H., Huang, Y., Rosoklija, G. B., Dwork, A. J., Mann, J. J. (2016). A pilot integrative genomics study of GABA and glutamate neurotransmitter systems in suicide, suicidal behavior, and major depressive disorder.
Giorgetti M, Tecott LH. Contributions of 5-HT2C receptors to multiple actions of central serotonin systems. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;488(1–3):1–9.
Werry TD, Loiacono R, Sexton PM, Christopoulos A. RNA editing of the serotonin 5HT2C receptor and its effects on cell signalling, pharmacology and brain function. Pharmacol Ther. 2008;119(1):7–23.
Dracheva S, Patel N, Woo DA, Marcus SM, Siever LJ, Haroutunian V. Increased serotonin 2C receptor mRNA editing: a possible risk factor for suicide. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2007;13(11):1001–10.
Dracheva S, Chin B, Haroutunian V. Altered serotonin 2C receptor RNA splicing in suicide: association with editing. Neuroreport. 2008;19(3):379–82.
Lyddon R, Dwork AJ, Keddache M, Siever LJ, Dracheva S. Serotonin 2c receptor RNA editing in major depression and suicide. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry. 2012;14(8):590–601.
Narzo AF, Kozlenkov A, Roussos P, Hao K, Hurd Y, Lewis DA, Dracheva S. A unique gene expression signature associated with serotonin 2C receptor RNA editing in the prefrontal cortex and altered in suicide. Hum Mol Genet. 2014;23(18):4801–13.
Sequeira A, Gwadry FG, Ffrench-Mullen JM, Canetti L, Gingras Y, Casero RA, Turecki G. Implication of SSAT by gene expression and genetic variation in suicide and major depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry Archives of General Psychiatry. 2006;63(1):35. doi:10.1001/archpsyc.63.1.35.
Sequeira A, Klempan T, Canetti L, Ffrench-Mullen J, Benkelfat C, Rouleau GA, Turecki G. Patterns of gene expression in the limbic system of suicides with and without major depression. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2007;12(7):640–55.
Fiori LM, Mechawar N, Turecki G. Identification and characterization of spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase promoter variants in suicide completers. Biol Psychiatry. 2009;66(5):460–7.
Klempan TA, Rujescu D, Mérette C, Himmelman C, Sequeira A, Canetti L, Turecki G. Profiling brain expression of the spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1) gene in suicide. Am J Med Genet American Journal of Medical Genetics Part B: Neuropsychiatric Genetics. 2009;150B(7):934–43.
Fiori LM, Turecki G. Genetic and epigenetic influences on expression of spermine synthase and spermine oxidase in suicide completers. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology Int J Neuropsychopharm. 2010;13(06):725–36.
Lopez JP, Fiori LM, Gross JA, Labonte B, Yerko V, Mechawar N, Turecki G. Regulatory role of miRNAs in polyamine gene expression in the prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide completers. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology Int. J. Neuropsychopharm. 2013;17(01):23–32.
Pantazatos SP, Andrews SJ, Dunning-Broadbent J, Pang J, Huang Y, Arango V, Mann JJ. Isoform-level brain expression profiling of the spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase1 (SAT1) gene in major depression and suicide. Neurobiol Dis. 2015;79:123–34.
Smalheiser NR, Lugli G, Rizavi HS, Torvik VI, Turecki G, Dwivedi Y. MicroRNA expression is down-regulated and reorganized in prefrontal cortex of depressed suicide subjects. PLoS One. 2012;7(3) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0033201.
Smalheiser NR, Lugli G, Zhang H, Rizavi H, Cook EH, Dwivedi Y. Expression of microRNAs and other small RNAs in prefrontal cortex in schizophrenia, bipolar disorder and depressed subjects. PLoS One. 2014;9(1) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0086469.
Maussion G, Yang J, Yerko V, Barker P, Mechawar N, Ernst C, Turecki G. Regulation of a truncated form of tropomyosin-related kinase B (TrkB) by Hsa-miR-185* in frontal cortex of suicide completers. PLoS One. 2012;7(6) doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0039301.
Takizawa T, Nakashima K, Namihira M, Ochiai W, Uemura A, Yanagisawa M, Taga T. DNA methylation is a critical cell-intrinsic determinant of astrocyte differentiation in the fetal brain. Dev Cell. 2001;1(6):749–58.
Turner CA, Thompson RC, Bunney WE, Schatzberg AF, Barchas JD, Myers RM, Watson SJ. Altered choroid plexus gene expression in major depressive disorder. Frontiers in Human Neuroscience Front Hum Neurosci. 2014;8:238.
Kerman IA, Bernard R, Bunney WE, Jones EG, Schatzberg AF, Myers RM, Thompson RC. Evidence for transcriptional factor dysregulation in the dorsal raphe nucleus of patients with major depressive disorder. Front Neurosci Frontiers in Neuroscience. 2012;6:135.
Medina A, Watson SJ, Bunney W, Myers RM, Schatzberg A, Barchas J, Thompson RC. Evidence for alterations of the glial syncytial function in major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2016;72:15–21.
Bernard R, Kerman IA, Thompson RC, Jones EG, Bunney WE, Barchas JD, Watson SJ. Altered expression of glutamate signaling, growth factor, and glia genes in the locus coeruleus of patients with major depression. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2010;16(6):634–46.
Chandley M, Szebeni K, Szebeni A, Crawford J, Stockmeier A, Turecki G, Ordway G. Gene expression deficits in pontine locus coeruleus astrocytes in men with major depressive disorder. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2013;38(4):276–84.
Chandley MJ, Szebeni A, Szebeni K, Crawford JD, Stockmeier CA, Turecki G, Ordway GA. Elevated gene expression of glutamate receptors in noradrenergic neurons from the locus coeruleus in major depression. The International Journal of Neuropsychopharmacology Int. J. Neuropsychopharm. 2014;17(10):1569–78.
Sequeira A, Morgan L, Walsh DM, Cartagena PM, Choudary P, Li J, Vawter MP. Gene expression changes in the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex and nucleus Accumbens of mood disorders subjects that committed suicide. PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35367.
Medina A, Seasholtz AF, Sharma V, Burke S, Bunney W, Myers RM, Watson SJ. Glucocorticoid and mineralocorticoid receptor expression in the human hippocampus in major depressive disorder. J Psychiatr Res. 2013;47(3):307–14.
Pandey GN, Rizavi HS, Ren X, Dwivedi Y, Palkovits M. Region-specific alterations in glucocorticoid receptor expression in the postmortem brain of teenage suicide victims. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013;38(11):2628–39.
Pérez-Ortiz JM, García-Gutiérrez MS, Navarrete F, Giner S, Manzanares J. Gene and protein alterations of FKBP5 and glucocorticoid receptor in the amygdala of suicide victims. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2013;38(8):1251–8.
Zhao J, Qi X, Gao S, Lu J, Wamelen DV, Kamphuis W, Swaab D. Different stress-related gene expression in depression and suicide. J Psychiatr Res. 2015;68:176–85.
Yin H, Galfalvy H, Pantazatos SP, Huang Y, Rosoklija GB, Dwork AJ, Mann JJ. Glucocorticoid receptor-related genes: genotype and brain gene expression relationships to suicide and major depressive disorder. Depression and Anxiety Depress Anxiety. 2016;33(6):531–40.
Herman J, Mcklveen J, Solomon M, Carvalho-Netto E, Myers B. Neural regulation of the stress response: glucocorticoid feedback mechanisms. Braz J Med Biol Res Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research. 2012;45(4):292–8.
• McGowan PO, Sasaki A, D’alessio AC, Dymov S, Labonté B, Szyf M, Meaney MJ. Epigenetic regulation of the glucocorticoid receptor in human brain associates with childhood abuse. Nature Neuroscience Nat Neurosci. 2009;12(3):342–8. The first study pointing towards a long lasting epigenetic effect of childhood abuse in the suicidal brain
Labonte B, Yerko V, Gross J, Mechawar N, Meaney MJ, Szyf M, Turecki G. Differential glucocorticoid receptor exon 1B, 1C, and 1H expression and methylation in suicide completers with a history of childhood abuse. Biol Psychiatry. 2012;72(1):41–8.
Ernst C, Nagy C, Kim S, Yang JP, Deng X, Hellstrom IC, Turecki G. Dysfunction of astrocyte connexins 30 and 43 in dorsal lateral prefrontal cortex of suicide completers. Biol Psychiatry. 2011;70(4):312–9.
Ernst C, Deleva V, Deng X, Sequeira A, Pomarenski A, Klempan T, Turecki G. Alternative splicing, methylation state, and expression profile of Tropomyosin-related kinase B in the frontal cortex of suicide completers. Arch Gen Psychiatry Archives of General Psychiatry. 2009;66(1):22.
• Nagy C, Suderman M, Yang J, Szyf M, Mechawar N, Ernst C, Turecki G. Astrocytic abnormalities and global DNA methylation patterns in depression and suicide. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2014;20(3):320–8. A characterization of suicide completers as low or high astrocytic gene expressers followed by subsequent analysis of global DNA methylation patterns in these subjects
• Labonté B, Suderman M, Maussion G, Lopez JP, Navarro-Sánchez L, Yerko V, Turecki G. Genome-wide methylation changes in the brains of suicide completers. American Journal of Psychiatry AJP. 2013;170(5):511–20. Genome-wide changes in methylation in the suicide brain
Haghighi F, Xin Y, Chanrion B, O’Donnell AH, Ge Y, Dwork AJ, et al. Increased DNA methylation in the suicide brain. Dialogues Clin Neurosci. 2014;16(3):430–8.
Schneider E, Hajj NE, Müller F, Navarro B, Haaf T. Epigenetic dysregulation in the prefrontal cortex of suicide completers. Cytogenetic and Genome Research Cytogenet Genome Res. 2015;146(1):19–27.
Guintivano J, Brown T, Jones M, Maher BS, Eaton WW, Payne JL, Kaminsky ZA. Identification and replication of a combined epigenetic and genetic biomarker predicting suicide and suicidal behaviors. Compr Psychiatry. 2014;171(12):1287–96.
• Kozlenkov A, Roussos P, Timashpolsky A, Barbu M, Rudchenko S, Bibikova M, Dracheva S. Differences in DNA methylation between human neuronal and glial cells are concentrated in enhancers and non-CpG sites. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;42(1):109–27. Work advancing the use of FACS sorting in post-mortem brain for studying epigenetic differences between neurons and glia
Kessler NJ, Baak TE, Baker MS, Laritsky E, Coarfa C, Waterland RA. CpG methylation differences between neurons and glia are highly conserved from mouse to human. Hum Mol Genet Human Molecular Genetics. 2015;25(2):223–32.
Iwamoto K, Bundo M, Ueda J, Oldham MC, Ukai W, Hashimoto E, Kato T. Neurons show distinctive DNA methylation profile and higher interindividual variations compared with non-neurons. Genome Res. 2011;21(5):688–96.
Guintivano J, Aryee MJ, Kaminsky ZA. A cell epigenotype specific model for the correction of brain cellular heterogeneity bias and its application to age, brain region and major depression. Epigenetics. 2013;8(3):290–302.
Sabunciyan, S., Aryee, M. J., Irizarry, R. A., Rongione, M., Webster, M. J., Kaufman, W. E., Consortium, G. (2012). Genome-wide DNA methylation scan in major depressive disorder. PLoS ONE, 7(4).
Arion D, Corradi JP, Tang S, Datta D, Boothe F, He A, Lewis DA. Distinctive transcriptome alterations of prefrontal pyramidal neurons in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Molecular Psychiatry Mol Psychiatry. 2015;20(11):1397–405.
• Macosko E, Basu A, Satija R, Nemesh J, Shekhar K, Goldman M, Mccarroll S. Highly parallel genome-wide expression profiling of individual cells using nanoliter droplets. Cell. 2015;161(5):1202–14. Single cell transcriptomic sequencing of 44,808 mouse retinal cells
Usoskin D, Furlan A, Islam S, Abdo H, Lönnerberg P, Lou D, Ernfors P. Unbiased classification of sensory neuron types by large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing. Nature Neuroscience Nat Neurosci. 2014;18(1):145–53.
• Zeisel A, Munoz-Manchado AB, Codeluppi S, Lonnerberg P, Manno GL, Jureus A, Linnarsson S. Cell types in the mouse cortex and hippocampus revealed by single-cell RNA-seq. Science. 2015;347(6226):1138–42. An interesting study using large-scale single-cell RNA sequencing to classify mouse somatosensory cortex and hippocampal CA1 cells into 47 molecularly distinct subclasses
• Krishnaswami SR, Grindberg RV, Novotny M, Venepally P, Lacar B, Bhutani K, Lasken RS. Using single nuclei for RNA-seq to capture the transcriptome of postmortem neurons. Nat Protoc Nature Protocols. 2016;11(3):499–524. Methods aimed at sorting and sequencing single nuclei from post-mortem brain
Nichterwitz S, Chen G, Benitez JA, Yilmaz M, Storvall H, Cao M, Hedlund E. Laser capture microscopy coupled with smart-seq2 for precise spatial transcriptomic profiling. Nature Communications Nat Comms. 2016;7:12139.
Tang F, Barbacioru C, Nordman E, Li B, Xu N, Bashkirov VI, Surani MA. RNA-seq analysis to capture the transcriptome landscape of a single cell. Nat Protoc Nature Protocols. 2010;5(3):516–35.
•• Lake BB, Ai R, Kaeser GE, Salathia NS, Yung YC, Liu R, Zhang K. Neuronal subtypes and diversity revealed by single-nucleus RNA sequencing of the human brain. Science. 2016;352(6293):1586–90. A recent study where the authors sequenced expression from 3227 nuclei derived from six regions of the post-mortem human cortex
Armañanzas R, Ascoli GA. Towards the automatic classification of neurons. Trends Neurosci. 2015;38(5):307–18.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Daniel Almeida and Gustavo Turecki declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Epigenetics
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Almeida, D., Turecki, G. Recent Progress in Functional Genomic Studies of Depression and Suicide. Curr Genet Med Rep 5, 22–34 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40142-017-0112-y
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40142-017-0112-y