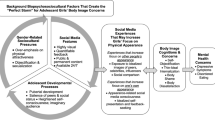
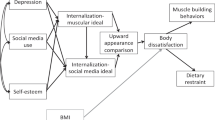
Abstract
Purpose of the Review
Children with obesity experience disordered eating attitudes and behaviors at high rates, which increases their risk for adult obesity and eating disorder development. As such, it is imperative to screen for disordered eating symptoms and identify appropriate treatments.
Recent Findings
Family-based multicomponent behavioral weight loss treatment (FBT) is effective at treating childhood obesity and demonstrates positive outcomes on psychosocial outcomes, including disordered eating. FBT utilizes a socio-ecological treatment approach that focuses on the development of individual and family healthy energy-balance behaviors as well as positive self- and body esteem, supportive family relationships, richer social networks, and the creation of a broader environment and community that facilitates overall physical and mental health.
Summary
Existing literature suggests FBT is an effective treatment option for disordered eating and obesity in children. Future work is needed to confirm this conclusion and to examine the progression and interaction of obesity and disordered eating across development to identify the optimal time for intervention.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Papers of particular interest, published recently, have been highlighted as: • Of importance •• Of major importance
• Ogden CL, Carroll MD, Lawman HG, et al. Trends in obesity prevalence among children and adolescents in the United States, 1988–1994 through 2013–2014. JAMA. 2016;315(21):2292–9. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.6361. Analysis of obesity trends from 1988–1994 to 2013–2014 showing obesity rates of 17% and extreme obesity rates of 5.8% in children aged 2–19.
Goldschmidt AB, Aspen VP, Sinton MM, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Wilfley DE. Disordered eating attitudes and behaviors in overweight youth. Obesity. 2008;16(2):257–64.
Sheehan DV, Herman BK. The psychological and medical factors associated with untreated binge eating disorder. The primary care companion for CNS disorders. 2015;17(2). https://doi.org/10.4088/PCC.14r01732.
Herpertz-Dahlmann B. Adolescent eating disorders: update on definitions, symptomatology, epidemiology, and comorbidity. Child Adolesc Psychiatr Clin N Am. 2015;24(1):177–96.
Pulgaron ER. Childhood obesity: a review of increased risk for physical and psychological comorbidities. Clin Ther. 2013;35(1):A18–32.
Cunningham SA, Kramer MR, Narayan KV. Incidence of childhood obesity in the United States. N Engl J Med. 2014;370(5):403–11.
•• He J, Cai Z, Fan X. Prevalence of binge and loss of control eating among children and adolescents with overweight and obesity: an exploratory meta-analysis. Int J Eat Disord. 2017;50(2):91–103. An exploratory meta-analysis showing more than a quarter of children and adolescents with overweight and obesity endorse binge/LOC eating.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Falkner N, Story M, Perry C, Hannan PJ, Mulert S. Weight-teasing among adolescents: correlations with weight status and disordered eating behaviors. Int J Obes. 2002;26(1):123–31.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Wall M, Story M, Sherwood NE. Five-year longitudinal predictive factors for disordered eating in a population-based sample of overweight adolescents: implications for prevention and treatment. Int J Eat Disord. 2009;42(7):664–72.
Pervanidou P, Bastaki D, Chouliaras G, Papanikolaou K, Laios E, Kanaka-Gantenbein C, et al. Circadian cortisol profiles, anxiety and depressive symptomatology, and body mass index in a clinical population of obese children. Stress. 2013;16(1):34–43.
Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Roemmich JN, Beecher MD. Family-based obesity treatment, then and now: twenty-five years of pediatric obesity treatment. Health Psychol. 2007;26(4):381–91.
Bishop-Gilyard CT, Berkowitz RI, Wadden TA, Gehrman CA, Cronquist JL, Moore RH. Weight reduction in obese adolescents with and without binge eating. Obesity. 2011;19(5):982–7.
•• Balantekin KN, Hayes JF, Sheinbein DH, Kolko RP, Stein RI, Saelens BE, et al. Patterns of eating disorder pathology are associated with weight change in family-based behavioral obesity treatment. Obesity. 2017;25(12):2115–22. An empirical study demonstrating varied patterns of eating disorder pathology in treatment-seeking children with obesity. Results also indicate family-based treatment for childhood obesity effectively reduces eating disorder pathology and weight in participating children, regardless of severity of eating disorder pathology.
Butryn ML, Wadden TA. Treatment of overweight in children and adolescents: does dieting increase the risk of eating disorders? Int J Eat Disord. 2005;37(4):285–93.
Braet C. Patient characteristics as predictors of weight loss after an obesity treatment for children. Obesity. 2006;14(1):148–55.
Crow S, Eisenberg ME, Story M, Neumark-Sztainer D. Psychosocial and behavioral correlates of dieting among overweight and non-overweight adolescents. J Adolesc Health. 2006;38(5):569–74.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Story M, Hannan PJ, Perry CL, Irving LM. Weight-related concerns and behaviors among overweight and nonoverweight adolescents: implications for preventing weight-related disorders. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2002;156(2):171–8.
Tanofsky-Kraff M, Yanovski SZ, Wilfley DE, Marmarosh C, Morgan CM, Yanovski JA. Eating-disordered behaviors, body fat, and psychopathology in overweight and normal-weight children. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2004;72(1):53–61.
Loth KA, Watts AW, Van Den Berg P, Neumark-Sztainer D. Does body satisfaction help or harm overweight teens? A 10-year longitudinal study of the relationship between body satisfaction and body mass index. J Adolesc Health. 2015;57(5):559–61.
Cooper PJ, Fairburn CG. Confusion over the core psychopathology of bulimia nervosa. Int J Eat Disord. 1993;13(4):385–9.
Sonneville KR, Grilo CM, Richmond TK, Thurston IB, Jernigan M, Gianini L, et al. Prospective association between overvaluation of weight and binge eating among overweight adolescent girls. J Adolesc Health. 2015;56(1):25–9.
• Lampard AM, Maclehose RF, Eisenberg ME, Larson NI, Davison KK, Neumark-Sztainer D. Adolescents who engage exclusively in healthy weight control behaviors: who are they? Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2016;13(1):5. A study suggesting that healthy weight control strategies in adolescents are associated with lower body dissatisfaction, high self-esteem, and lower depressive symptoms.
Stephen EM, Rose JS, Kenney L, Rosselli-Navarra F, Weissman RS. Prevalence and correlates of unhealthy weight control behaviors: findings from the national longitudinal study of adolescent health. J Eat Disord. 2014;2(1):16.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Wall M, Story M, Standish AR. Dieting and unhealthy weight control behaviors during adolescence: associations with 10-year changes in body mass index. J Adolesc Health. 2012;50(1):80–6.
Stice E, Gau JM, Rohde P, Shaw H. Risk factors that predict future onset of each DSM–5 eating disorder: predictive specificity in high-risk adolescent females. J Abnorm Psychol. 2017;126(1):38–51.
Cheng HL, Amatoury M, Steinbeck K. Energy expenditure and intake during puberty in healthy nonobese adolescents: a systematic review. Am J Clin Nutr. 2016;104(4):1061–74.
Tanofsky-Kraff M, Cohen ML, Yanovski SZ, Cox C, Theim KR, Keil M, et al. A prospective study of psychological predictors of body fat gain among children at high risk for adult obesity. Pediatrics. 2006;117(4):1203–9.
Bulik CM, Sullivan PF, Kendler KS. Genetic and environmental contributions to obesity and binge eating. Int J Eat Disord. 2003;33(3):293–8.
Diamond A. Executive functions. Annu Rev Psychol. 2013;64:135–68.
Reinert KR, Po'e EK, Barkin SL. The relationship between executive function and obesity in children and adolescents: a systematic literature review. J Obes. 2013;2013:820956. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/820956.
Darcy AM, Fitzpatrick KK, Manasse SM, Datta N, Klabunde M, Colborn D, et al. Central coherence in adolescents with bulimia nervosa spectrum eating disorders. Int J Eat Disord. 2015;48(5):487–93.
Goldschmidt AB, O'Brien S, Lavender JM, Pearson CM, Le Grange D, Hunter SJ. Executive functioning in a racially diverse sample of children who are overweight and at risk for eating disorders. Appetite 2018;124:43–49.
Gowey MA, Lim CS, Dutton GR, Silverstein JH, Dumont-Driscoll MC, Janicke DM. Executive function and dysregulated eating behaviors in pediatric obesity. J Pediatr Psychol 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsx091
Goldschmidt AB, Hipwell AE, Stepp SD, McTigue KM, Keenan K. Weight gain, executive functioning, and eating behaviors among girls. Pediatrics. 2015;136(4):e856–e63.
Gowey MA, Reiter-Purtill J, Becnel J, Peugh J, Mitchell JE, Zeller MH, et al. Weight-related correlates of psychological dysregulation in adolescent and young adult (AYA) females with severe obesity. Appetite. 2016;99:211–8.
Wilfley DE, Vannucci A, White EK. Early intervention of eating-and weight-related problems. J Clin Psychol Med Settings. 2010;17(4):285–300.
Kral TV, Moore RH, Chittams J, Jones E, O’Malley L, Fisher JO. Identifying behavioral phenotypes for childhood obesity. Appetite. 2018;127:87–96.
Giel KE, Teufel M, Junne F, Zipfel S, Schag K. Food-related impulsivity in obesity and binge eating disorder—a systematic update of the evidence. Nutrients. 2017;9(11):1170.
Swinburn BA, Sacks G, Hall KD, McPherson K, Finegood DT, Moodie ML, et al. The global obesity pandemic: shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet. 2011;378(9793):804–14.
Sallis JF, Glanz K. Physical activity and food environments: solutions to the obesity epidemic. Milbank Q. 2009;87(1):123–54.
Grabe S, Ward LM, Hyde JS. The role of the media in body image concerns among women: a meta-analysis of experimental and correlational studies. Psychol Bull. 2008;134(3):460–76.
Zubatsky M, Berge J, Neumark-Sztainer D. Longitudinal associations between parenting style and adolescent disordered eating behaviors. Eat Weight Disord. 2015;20(2):187–94.
Sokol RL, Qin B, Poti J. Parenting styles and body mass index: a systematic review of prospective studies among children. Obes Rev. 2017;18(3):281–92.
Loth KA, MacLehose RF, Fulkerson JA, Crow S, Neumark-Sztainer D. Are food restriction and pressure-to-eat parenting practices associated with adolescent disordered eating behaviors? Int J Eat Disord. 2014;47(3):310–4.
Rodgers RF, Paxton SJ, Massey R, Campbell KJ, Wertheim EH, Skouteris H, et al. Maternal feeding practices predict weight gain and obesogenic eating behaviors in young children: a prospective study. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act. 2013;10(1):24.
Menzel JE, Schaefer LM, Burke NL, Mayhew LL, Brannick MT, Thompson JK. Appearance-related teasing, body dissatisfaction, and disordered eating: a meta-analysis. Body Image. 2010;7(4):261–70.
Jackson TD, Grilo CM, Masheb RM. Teasing history, onset of obesity, current eating disorder psychopathology, body dissatisfaction, and psychological functioning in binge eating disorder. Obesity. 2000;8(6):451–8.
Neumark-Sztainer D. The interface between the eating disorders and obesity fields: moving toward a model of shared knowledge and collaboration. Eat Weight Disord. 2009;14(1):51–8.
Sánchez-Carracedo D, Neumark-Sztainer D, López-Guimera G. Integrated prevention of obesity and eating disorders: barriers, developments and opportunities. Public Health Nutr. 2012;15(12):2295–309.
Neumark-Sztainer DR, Friend SE, Flattum CF, Hannan PJ, Story MT, Bauer KW, et al. New moves—preventing weight-related problems in adolescent girls: a group-randomized study. Am J Prev Med. 2010;39(5):421–32.
Stock S, Miranda C, Evans S, Plessis S, Ridley J, Yeh S, et al. Healthy buddies: a novel, peer-led health promotion program for the prevention of obesity and eating disorders in children in elementary school. Pediatrics. 2007;120(4):e1059–e68.
• O’connor EA, Evans CV, Burda BU, Walsh ES, Eder M, Lozano P. Screening for obesity and intervention for weight management in children and adolescents: evidence report and systematic review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2017;317(23):2427–44. A systematic review and meta-analysis demonstrating that moderate intensity multicomponent lifestyle interventions for children are effective at reducing childhood obesity.
Whitaker KL, Jarvis MJ, Beeken RJ, Boniface D, Wardle J. Comparing maternal and paternal intergenerational transmission of obesity risk in a large population-based sample. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010;91(6):1560–7.
Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Wrotniak BH, Daniel TO, Kilanowski C, Wilfley D, et al. Cost-effectiveness of family-based group treatment for child and parental obesity. Child Obes. 2014;10(2):114–21.
Spear BA, Barlow SE, Ervin C, Ludwig DS, Saelens BE, Schetzina KE, et al. Recommendations for treatment of child and adolescent overweight and obesity. Pediatrics. 2007;120(Supplement 4):S254–S88.
• Wilfley DE, Saelens BE, Stein RI, Best JR, Kolko RP, Schechtman KB et al. Dose, content, and mediators of family-based treatment for childhood obesity: a multisite randomized clinical trial. JAMA Pediatr. 2017;171(12):1151–9 A randomized-controlled trial suggested a high-dose of social facilitation maintenance treatment (SFM), a socio-ecological approach that emphasizes parental facilitation of children’s peer networks and improvement of children’s body image, as well as their responses to teasing, is effective for maintaining weight loss in children.
Wilfley DE, Stein RI, Saelens BE, Mockus DS, Matt GE, Hayden-Wade HA, et al. Efficacy of maintenance treatment approaches for childhood overweight: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA. 2007;298(14):1661–73.
Giel KE, Zipfel S, Schweizer R, Braun R, Ranke MB, Binder G, et al. Eating disorder pathology in adolescents participating in a lifestyle intervention for obesity: associations with weight change, general psychopathology and health-related quality of life. Obes Facts. 2013;6(4):307–16.
Goldschmidt AB, Best JR, Stein RI, Saelens BE, Epstein LH, Wilfley DE. Predictors of child weight loss and maintenance among family-based treatment completers. 2014;82(6):1140–1150
Sotos-Prieto M, Bhupathiraju SN, Mattei J, Fung TT, Li Y, Pan A, et al. Association of changes in diet quality with total and cause-specific mortality. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(2):143–53.
Cooper JO, Heron TE, Heward WL. Applied behavior analysis. 2nd ed. London: Pearson. 2007.
•• Haynos AF, Field AE, Wilfley DE, Tanofsky-Kraff M. A novel classification paradigm for understanding the positive and negative outcomes associated with dieting. Int J Eat Disord. 2015;48(4):362–6. A paper proposing a novel classification scheme for dieting that includes positive and negative psychological dimensions as well as high and low behavioral dimensions.
Reiner M, Niermann C, Jekauc D, Woll A. Long-term health benefits of physical activity—a systematic review of longitudinal studies. BMC Public Health. 2013;13(1):813.
Tammelin R, Yang X, Leskinen E, Kankaanpaa A, Hirvensalo M, Tammelin T, et al. Tracking of physical activity from early childhood through youth into adulthood. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2014;46:955–62.
Hayes JF, Eichen DM, Barch DM, Wilfley DE. Executive function in childhood obesity: promising intervention strategies to optimize treatment outcomes. Appetite 2018;124:10–23
Harris JL, Bargh JA. Television viewing and unhealthy diet: implications for children and media interventions. Health Commun. 2009;24(7):660–73.
Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Gordy CC, Dorn J. Decreasing sedentary behaviors in treating pediatric obesity. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2000;154(3):220–6.
Tiggemann M, Slater A. NetTweens: the Internet and body image concerns in preteenage girls. J Early Adolesc. 2014;34(5):606–20.
Haines J, McDonald J, O’Brien A, Sherry B, Bottino CJ, Schmidt ME, et al. Healthy habits, happy homes: randomized trial to improve household routines for obesity prevention among preschool-aged children. JAMA Pediatr. 2013;167(11):1072–9.
Murphy R, Straebler S, Cooper Z, Fairburn CG. Cognitive behavioral therapy for eating disorders. Psychiatr Clin North Am. 2010;33(3):611–27.
Gollwitzer PM. Weakness of the will: is a quick fix possible? Motiv Emot. 2014;38(3):305–22.
Steinberg DM, Bennett GG, Askew S, Tate DF. Weighing every day matters: daily weighing improves weight loss and adoption of weight control behaviors. J Acad Nutr Diet. 2015;115(4):511–8.
Levy RL, Finch EA, Crowell MD, Talley NJ, Jeffery RW. Behavioral intervention for the treatment of obesity: strategies and effectiveness data. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;102(10):2314–21.
Mockus DS, Macera CA, Wingard DL, Peddecord M, Thomas RG, Wilfley DE. Dietary self-monitoring and its impact on weight loss in overweight children. Int J Pediatr Obes. 2011;6(3–4):197–205.
Stice E, Rohde P, Shaw H. The body project: a dissonance-based eating disorder prevention intervention. 2nd ed. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2012.
Hawes DJ, Allen J. Evidence-based parenting interventions: current perspectives and clinical strategies. In Matthew Hodes, Susan Gau (Eds.), Positive mental health, fighting stigma and promoting resiliency for children and adolescents. London: Elsevier; 2016. p. 185–204.
Carr KA, Daniel TO, Lin H, Epstein LH. Reinforcement pathology and obesity. Curr Drug Abuse Rev. 2011;4(3):190–6.
Neumark-Sztainer D, Bauer KW, Friend S, Hannan PJ, Story M, Berge JM. Family weight talk and dieting: how much do they matter for body dissatisfaction and disordered eating behaviors in adolescent girls? J Adolesc Health. 2010;47(3):270–6.
Shomaker LB, Tanofsky-Kraff M, Matherne CE, Mehari RD, Olsen CH, Marwitz SE, et al. A randomized, comparative pilot trial of family-based interpersonal psychotherapy for reducing psychosocial symptoms, disordered-eating, and excess weight gain in at-risk preadolescents with loss-of-control-eating. Int J Eat Disord. 2017;50(9):1084–94.
Blissett J, Fogel A. Intrinsic and extrinsic influences on children’s acceptance of new foods. Physiol Behav. 2013;121:89–95.
Wrotniak BH, Epstein LH, Paluch RA, Roemmich JN. Parent weight change as a predictor of child weight change in family-based behavioral obesity treatment. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2004;158(4):342–7.
Wilfley DE, Tibbs TL, Van Buren D, Reach KP, Walker MS, Epstein LH. Lifestyle interventions in the treatment of childhood overweight: a meta-analytic review of randomized controlled trials. Health Psychol. 2007;26(5):521–32.
Ely AV, Cusack A. The binge and the brain. Cerebrum: the Dana forum on brain science. 2015: cer-12–15.
Strauss RS, Pollack HA. Social marginalization of overweight children. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2003;157(8):746–52.
Levine MP. Loneliness and eating disorders. J Psychol. 2012;146(1–2):243–57.
Valente TW, Fujimoto K, Chou C-P, Spruijt-Metz D. Adolescent affiliations and adiposity: a social network analysis of friendships and obesity. J Adolesc Health. 2009;45(2):202–4.
Eisenberg ME, Neumark-Sztainer D. Friends' dieting and disordered eating behaviors among adolescents five years later: findings from project EAT. J Adolesc Health. 2010;47(1):67–73.
Salvy S-J, Roemmich JN, Bowker JC, Romero ND, Stadler PJ, Epstein LH. Effect of peers and friends on youth physical activity and motivation to be physically active. J Pediatr Psychol. 2008;34(2):217–25.
Tanofsky-Kraff M, Shomaker LB, Wilfley DE, Young JF, Sbrocco T, Stephens M, et al. Excess weight gain prevention in adolescents: three-year outcome following a randomized controlled trial. J Consult Clin Psychol. 2017;85(3):218–27.
Jackson SL, Cunningham SA. Social competence and obesity in elementary school. Am J Public Health. 2015;105(1):153–8.
Shank LM, Crosby RD, Grammer AC, Shomaker LB, Vannucci A, Burke NL, et al. Examination of the interpersonal model of loss of control eating in the laboratory. Compr Psychiatry. 2017;76:36–44.
Tanofsky-Kraff M, Shomaker LB, Wilfley DE, Young JF, Sbrocco T, Stephens M, et al. Targeted prevention of excess weight gain and eating disorders in high-risk adolescent girls: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014;100(4):1010–8.
Freedman JS. Easing the teasing: helping your child cope with name-calling, ridicule, and verbal bullying. Chicago, IL: Contemporary Books. 2002.
Bouton ME, Winterbauer NE, Todd TP. Relapse processes after the extinction of instrumental learning: renewal, resurgence, and reacquisition. Behav Process. 2012;90(1):130–41.
Forman EM, Butryn ML, Manasse SM, Crosby RD, Goldstein SP, Wyckoff EP, et al. Acceptance-based versus standard behavioral treatment for obesity: results from the mind your health randomized controlled trial. Obesity. 2016;24(10):2050–6.
Harvey AG, Lee J, Williams J, Hollon SD, Walker MP, Thompson MA, et al. Improving outcome of psychosocial treatments by enhancing memory and learning. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2014;9(2):161–79.
Rodgers RF, Damiano SR, Wertheim EH, Paxton SJ. Media exposure in very young girls: prospective and cross-sectional relationships with BMIz, self-esteem and body size stereotypes. Dev Psychol. 2017;53(12):2356–63.
Pont SJ, Puhl R, Cook SR, Slusser W. Stigma experienced by children and adolescents with obesity. Pediatrics 2017:140(6):30–34.
Latner JD, Rosewall JK, Simmonds MB. Childhood obesity stigma: association with television, videogame, and magazine exposure. Body Image. 2007;4(2):147–55.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Jacqueline F. Hayes declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ellen E. Fitzsimmons-Craft declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Anna M. Karam declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Jessica Jakubiak declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Mackenzie L. Brown declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Denise E. Wilfley has received research funding through grants from the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (Grant #R01HD036904), the National Institute of Mental Health (Grant #K24MH070446), and the St. Louis Children’s Hospital Foundation.
Human and Animal Rights and Informed Consent
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Psychological Issues
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hayes, J.F., Fitzsimmons-Craft, E.E., Karam, A.M. et al. Disordered Eating Attitudes and Behaviors in Youth with Overweight and Obesity: Implications for Treatment. Curr Obes Rep 7, 235–246 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-018-0316-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13679-018-0316-9