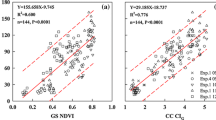
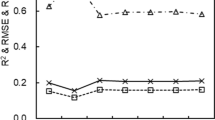
Abstract
China consumes more than 1/3 of global N fertilizers for rice with less than 1/5 of the world rice planting area. As a consequence, N efficiency is low and nitrate pollution risk is high. Developing efficient N management strategies and technologies for rice are therefore needed. Here, we developed an active canopy sensor-based precision N management strategy for rice in Northeast China. Four site-years of field N rate experiments were conducted in 2008 and 2009 in Sanjiang Plain, Heilongjiang, China. The GreenSeeker active sensor was used to collect rice canopy reflectance data at different growth stages. Three on-farm experiments were conducted in 2011 to evaluate the performance of the developed strategy. The results show that the crop sensor can be used to calculate rice yield potential without additional topdressing N application at stem elongation or booting stage. The GreenSeeker-based precision N management strategy has a regional optimum N rate of 90–110 kg N ha−1 as initial total amount and 45 and 20 % as basal and tillering N application. It uses the crop sensor to estimate the topdressing N rate at stem elongation stage. GreenSeeker-based precision management and chlorophyll meter-based site-specific N management increased the partial factor productivity of farmers by 48 and 65 %, respectively, without significant change in grain yield. The crop sensor-based N management strategy can therefore improve N use efficiency of rice. It is more suitable for practical on-farm applications, and will contribute to the sustainable development of rice farming.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bajwa S, Mishra AR, Norman RJ (2010) Canopy reflectance response to plant nitrogen accumulation in rice. Precis Agric 11:488–506. doi:10.1007/s11119-009-9142-0
Bijay-Singh SRK, Jaspreet-Kaur JML, Martin KL, Yadvinder-Singh V-S, Chandna P, Choudhary OP, Gupta RK, Thind HS, Jagmohan-Singh UHS, Khurana HS, Ajay-Kumar URK, Vashistha M, Raun WR, Gupta R (2011) Assessment of the nitrogen management strategy using an optical sensor for irrigated wheat. Agron Sustain Dev 31:589–603. doi:10.1007/s13593-011-0005-5
Cantrell RP, Teeves TG (2002) The cereal of the world’s poor takes center stage. Science 296:53. doi:10.1126/science.1070721
Cao Q, Cui Z, Chen X, Khosla R, Dao TH, Miao Y (2012) Quantifying spatial variability of indigenous nitrogen supply for precision nitrogen management in small scale farming. Precis Agric 13:45–61. doi:10.1007/s11119-011-9244-3
Dobermann A, Witt C, Dawe D, Gines HC, Nagarajan R, Satawathananont S, Son TT, Tan PS, Wang GH, Chien NV, Thoa VTK, Phung CV, Stalin P, Muthukrishnan P, Ravi V, Babu M, Chatu MAA (2002) Site-specific nutrient management for intensive rice cropping systems in Asia. Field Crops Res 74:37–66. doi:10.1016/S0378-4290(01)00197-6
FAOSTAT (2008) FAO Statistical databases. Available at http://www.fao.org. Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of the United Nations, Rome.
Hodgen PJ, Raun WR, Johnson GV, Teal RK, Freeman KW, Brixey KB, Martin KL (2005) Relationship between response indices measured in-season and at harvest in winter wheat. J Plant Nutr 28:221–235. doi:10.1081/PLN-200047605
Johnson GV, Raun WR (2003) Nitrogen response index as a guide to fertilizer management. J Plant Nutr 26:249–262. doi:10.1081/PLN-120017134
Li F, Miao Y, Zhang F, Cui Z, Li R, Chen X, Zhang H, Schroder J, Raun WR, Jia L (2009a) In-season optical sensing improves nitrogen use efficiency for winter wheat. Soil Sci Soc Am J 73:1566–1574. doi:10.2136/sssaj2008.0150
Li G, Peng X, Liu Y, Sheng D, Bao Y (2009b) Effects of applying N at later growth stage on rice yield and quality in cold area of China (in Chinese with English abstract). J Northeast Agric Univ 40(3):7–11
Li F, Miao Y, Chen X, Zhang H, Jia L, Bareth G (2010) Estimating winter wheat biomass and nitrogen status using an active crop sensor. Intell Autom Soft Co 16(6):1221–1230
Miao Y, Stewart BA, Zhang F (2011) Long-term experiments for sustainable nutrient management in China. A review Agron Sustain Dev 31:397–414. doi:10.1051/agro/2010034
Mullen RW, Freeman KW, Raun WR, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Solie JB (2003) Identifying an in-season response index and then potential to increase wheat yield with nitrogen. Agron J 95:347–351. doi:10.2134/agronj2003.0347
Nguyen HT, Kim JH, Nguyen AT, Nguyen LT, Shin JC, Lee BW (2006) Using canopy reflectance and partial least squares regression to calculate within-field statistical variation in crop growth and nitrogen status of rice. Precis Agric 7(4):249–264. doi:10.1007/s11119-006-9010-0
Ortiz-Monasterio JI, Raun WR (2007) Reduced nitrogen and improved farm income for irrigated spring wheat in the Yaqui Valley, Mexico, using sensor based nitrogen management. J Agric Sci 145:1–8. doi:10.1017/S0021859607006995
Peng X, Liu Y, Luo S, Fan L, Sheng D (2007) Nitrogen application situation and effects of nitrogen management on cost and output of paddy field in cold area of northeast China (in Chinese with English abstract). J Northeast Agric Univ 38(4):467–472
Peng S, Tang Q, Zou Y (2009) Current status and challenges of rice production in China. Plant Prod Sci 12(1):3–8. doi:10.1626/pps.12.3
Peng S, Buresh RJ, Huang J, Zhong X, Zou Y, Yang J, Wang G, Liu Y, Hu R, Tang Q, Cui K, Zhang F, Dobermann A (2010) Improving nitrogen fertilization in rice by site-specific N management—a review. Agron Sustain Dev 30:649–656. doi:10.1051/agro/2010002
Raun WR, Solie JB, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Lukina EV, Thomason WE et al (2001) In-season prediction of potential grain yield in winter wheat using canopy reflectance. Agron J 93:131–138. doi:10.2134/agronj2001.931131x
Raun WR, Solie JB, Johnson GV, Stone ML, Mullen RW, Freeman KW et al (2002) Improving nitrogen use efficiency in cereal grain production with optical sensing and variable rate application. Agron J 94:815–820. doi:10.2134/agronj2002.0815
Raun WR, Solie JB, Stone ML, Martin KL, Freeman KW, Mullen RW et al (2005) Optical sensor-based algorithm for crop nitrogen fertilization. Commun Soil Sci Plan 36:2759–2781. doi:10.1017/S0021859607006995
Schlegel AJ (2005) Challenging approaches to nitrogen fertilizer recommendations in continuous cropping systems in the Great Plains. Agron J 97:391–398. doi:10.2134/agronj2005.0391
Shanahan JF, Kitchen NR, Raun WR, Schepers JS (2008) Responsive in-season nitrogen management for cereals. Comput Electron Agr 61:51–62. doi:10.1016/j.compag.2007.06.006
Stroppiana D, Boschetti M, Brivio PA, Bocchi S (2009) Plant nitrogen concentration in paddy rice from field canopy hyperspectral radiometry. Field Crops Res 111:119–129. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2008.11.004
Teal RK, Tubana B, Girma K, Freeman KW, Arnall DB, Walsh O et al (2006) In-season prediction of corn grain yield potential using normalized difference vegetation index. Agron J 98:1488–1494. doi:10.2134/agronj2006.0103
Thomason WE, Phillips SB, Davis PH, Warren JG, Alley MM, Reiter MS (2011) Variable nitrogen rate determination from plant spectral reflectance in soft red winter wheat. Precis Agric 12:666–681. doi:10.1007/s11119-010-9210-5
Wang Y, Yang Y (2001) Effects of agriculture reclamation on hydrologic characteristics in the Sanjiang Plain, China. Chinese Geogr Sci 11(2):163–167. doi:10.1007/s11769-001-0037-x
Wanjura DF, Hatfield JL (1987) Sensitivity of spectral vegetation indices to crop biomass. Trans ASABE 30(3):810–816
Xue LH, Yang LZ (2008) Recommendations for nitrogen fertiliser topdressing rates in rice using canopy reflectance spectra. Biosyst Eng 100(4):524–534. doi:10.1016/j.biosystemseng.2008.05.005
Yan M, Deng W, Chen P (2002) Climate change in the Sanjiang plain distributed by large-scale reclamation. J Geogr Sci 12(4):405–412. doi:10.1007/BF02844597
Zhang F, Cui Z, Wang J, Li C, Chen X (2007) Current status of soil and plant nutrient management in China and improvement strategies (in Chinese with English abstract). Chinese Bull Bot 24:687–694
Zhang S, Na X, Kong B, Wang Z, Jiang H, Yu H et al (2009) Identifying wetland change in China’s Sanjiang Plain using remote sensing. Wetlands 29(1):302–313. doi:10.1672/08-04.1
Zhao G (2008) Effect of different N application ratio and rate on population quality, yield, and quality of rice in cold region (in Chinese with English abstract). M.S. Thesis. China Agricultural University, Beijing, China
Zhou Z, Liu T (2005) The current status, threats and protection way of Sanjiang Plain wetland, northeast China. J Forest Res 16(2):148–152. doi:10.1007/BF02857910
Zhu ZL (2006) On the methodology of recommendation for application rate of chemical fertilizer nitrogen to crops (in Chinese with English abstract). Plant Nutrition and Fertilizer Science 12(1):1–4
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Natural Science Foundation of China (31071859), National Basic Research Program (973-2009CB118606), The Innovative Group Grant of Natural Science Foundation of China (31121062) and Chinese Universities Scientific Fund (2012QJ162). The supports from Qixing Modern Agriculture Development Center and Jiansanjiang Institute of Agricultural Science are highly appreciated. We also would like to thank Mr. Chuanxiang Tan, Miss Quanying Zhao, Miss Minmin Su for their assistance in the field experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, Y., Miao, Y., Huang, S. et al. Active canopy sensor-based precision N management strategy for rice. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 32, 925–933 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-012-0094-9
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-012-0094-9