Abstract
The rupture of atherosclerotic plaques is the leading cause of death in developed countries. Early identification of vulnerable plaque is the essential step in preventing acute coronary events. Intravascular photoacoustic (IVPA) technology is able to visualize chemical composition of atherosclerotic plaque with high specificity and sensitivity. Integrated with intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) imaging, this multimodal intravascular IVPA/IVUS imaging technology is able to provide both structural and chemical compositions of arterial walls for detecting and characterizing atherosclerotic plaques. In this paper, we present representative multimodal IVPA/IVUS imaging systems and discuss current scientific innovations, potential limitations, and prospective improvements for characterization of coronary atherosclerosis.

Adapted from [24]

Adapted from [33]

Adapted from [24]

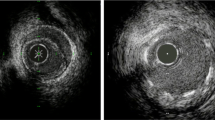
Adapted from [23]

Adapted from [21]

Adapted from [20]
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Narula J, Strauss HW. Imaging of unstable atherosclerotic lesions. Eur J Nucl Med Mol I. 2005;32:1–5.
Weber C, Noels H. Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med. 2011;17:1410–22.
Virmani R, Kolodgie FD, Burke AP, Finn AV, Gold HK, Tulenko TN, et al. Atherosclerotic plaque progression and vulnerability to rupture: angiogenesis as a source of intraplaque hemorrhage. Arterioscl Throm Vas. 2005;25:2054–61.
Narula J, Strauss HW. The popcorn plaques. Nat Med. 2007;13:532–4.
Meissner OA, Rieber J, Babaryka G, Oswald M, Reim S, Siebert U, et al. Intravascular optical coherence tomography: comparison with histopathology in atherosclerotic peripheral artery specimens. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2006;17:343–9.
Nissen SE, Gurley JC, Grines CL, Booth DC, Mcclure R, Berk M, et al. Intravascular ultrasound assessment of lumen size and wall morphology in normal subjects and patients with coronary–artery disease. Circulation. 1991;84:1087–99.
Li Y, Jing J, Heidari E, Zhu J, Qu Y, Chen Z. Intravascular optical coherence tomography for characterization of atherosclerosis with a 1.7 micron swept-source laser. Sci Rep. 2017;7:14525.
Li Y, Jing J, Qu Y, Miao Y, Zhang B, Ma T, et al. Fully integrated optical coherence tomography, ultrasound, and indocyanine green-based fluorescence tri-modality system for intravascular imaging. Biomed Opt Exp. 2017;8:1036–44.
Wang HW, Langohr IM, Sturek M, Cheng JX. Imaging and quantitative analysis of atherosclerotic lesions by CARS-based multimodal nonlinear optical microscopy. Arterioscl Throm Vas. 2009;29:1342–8.
Lilledahl MB, Haugen OA, Davies CD, Svaasand LO. Characterization of vulnerable plaques by multiphoton microscopy. J Biomed Opt. 2007;12:044005.
Marcu L. Fluorescence lifetime in cardiovascular diagnostics. J Biomed Opt. 2010;15:011106.
Marcu L, Jo JA, Fang Q, Papaioannou T, Reil T, Qiao JH, et al. Detection of rupture-prone atherosclerotic plaques by time-resolved laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy. Atherosclerosis. 2009;204:156–64.
Romer TJ, Brennan JF 3rd, Puppels GJ, Zwinderman AH, van Duinen SG, van der Laarse A, et al. Intravascular ultrasound combined with Raman spectroscopy to localize and quantify cholesterol and calcium salts in atherosclerotic coronary arteries. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2000;20:478–83.
Waxman S, Dixon SR, L’Allier P, Moses JW, Petersen JL, Cutlip D, et al. In vivo validation of a catheter-based near-infrared spectroscopy system for detection of lipid core coronary plaques initial results of the SPECTACL study. Jacc Cardiovasc Imag. 2009;2:858–68.
Wei W, Li X, Zhou QF, Shung KK, Chen ZP. Integrated ultrasound and photoacoustic probe for co-registered intravascular imaging. J Biomed Opt. 2011;16:16001.
Yuan Y, Yang S, Xing D. Preclinical photoacoustic imaging endoscope based on acousto-optic coaxial system using ring transducer array. Opt Lett. 2010;35:2266–8.
Ji XR, Xiong KD, Yang SH, Xing D. Intravascular confocal photoacoustic endoscope with dual-element ultrasonic transducer. Opt Exp. 2015;23:9130–6.
Yang JM, Maslov K, Yang HC, Zhou QF, Shung KK, Wang LHV. Photoacoustic endoscopy. Opt Lett. 2009;34:1591–3.
Hui J, Cao YC, Zhang Y, Kole A, Wang P, Yu GL, et al. Real-time intravascular photoacoustic–ultrasound imaging of lipid-laden plaque in human coronary artery at 16 frames per second. Sci Rep. 2017;7:1417.
Cao YC, Hui J, Kole A, Wang P, Yu QH, Chen WB, et al. High-sensitivity intravascular photoacoustic imaging of lipid-laden plaque with a collinear catheter design. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25236.
Wang P, Ma T, Slipchenko MN, Liang S, Hui J, Shung KK, et al. High-speed intravascular photoacoustic imaging of lipid-laden atherosclerotic plaque enabled by a 2-kHz barium nitrite raman laser. Sci Rep. 2014;4:6889.
Jansen K, van der Steen AF, Wu M, van Beusekom HM, Springeling G, Li X, et al. Spectroscopic intravascular photoacoustic imaging of lipids in atherosclerosis. J Biomed Opt. 2014;19:026006.
Li Y, Gong X, Liu C, Lin R, Hau W, Bai X, et al. High-speed intravascular spectroscopic photoacoustic imaging at 1000 A-lines per second with a 0.9-mm diameter catheter. J Biomed Opt. 2015;20:065006.
Piao Z, Ma T, Li J, Wiedmann MT, Huang S, Yu M, et al. High speed intravascular photoacoustic imaging with fast optical parametric oscillator laser at 1.7 mum. Appl Phys Lett. 2015;107:083701.
Wu M, Springeling G, Lovrak M, Mastik F, Iskander-Rizk S, Wang T, et al. Real-time volumetric lipid imaging in vivo by intravascular photoacoustics at 20 frames per second. Biomed Opt Exp. 2017;8:943–53.
Beard PC, Mills TN. Characterization of post mortem arterial tissue using time-resolved photoacoustic spectroscopy at 436, 461 and 532 nm. Phys Med Biol. 1997;42:177–98.
Li X, Wei W, Zhou QF, Shung KK, Chen ZP. Intravascular photoacoustic imaging at 35 and 80 MHz. J Biomed Opt. 2012;17:106005.
Crazzolara H, Vonmuench W, Rose C, Thiemann U, Haase KK, Ritter M, et al. Analysis of the acoustic response of vascular tissue irradiated by an ultraviolet-laser pulse. J Appl Phys. 1991;70:1847–9.
Jansen K, van der Steen AF, van Beusekom HM, Oosterhuis JW, van Soest G. Intravascular photoacoustic imaging of human coronary atherosclerosis. Opt Lett. 2011;36:597–9.
Wang B, Karpiouk A, Yeager D, Amirian J, Litovsky S, Smalling R, et al. In vivo intravascular ultrasound-guided photoacoustic imaging of lipid in plaques using an animal model of atherosclerosis. Ultrasound Med Biol. 2012;38:2098–103.
Wang B, Karpiouk A, Yeager D, Amirian J, Litovsky S, Smalling R, et al. Intravascular photoacoustic imaging of lipid in atherosclerotic plaques in the presence of luminal blood. Opt Lett. 2012;37:1244–6.
Hui J, Yu Q, Ma T, Wang P, Cao Y, Bruning RS, et al. High-speed intravascular photoacoustic imaging at 1.7 mum with a KTP-based OPO. Biomedical. Opt Exp. 2015;6:4557–66.
Anderson RR, Farinelli W, Laubach H, Manstein D, Yaroslavsky AN, Gubeli J, et al. Selective photothermolysis of lipid-rich tissues: a free electron laser study. Laser Surg Med. 2006;38:913–9.
Dai XJ, Yang H, Shan TQ, Xie HK, Berceli SA, Jiang HB. Miniature endoscope for multimodal imaging. ACS Photon. 2017;4:174–80.
Wang P, Rajian JR, Cheng JX. Spectroscopic imaging of deep tissue through photoacoustic detection of molecular vibration. J Phys Chem Lett. 2013;4:2177–85.
American National Standard for Safe Use of Lasers, ANSI Z136.1. 2014.
Tran PH, Mukai DS, Brenner M, Chen Z. In vivo endoscopic optical coherence tomography by use of a rotational microelectromechanical system probe. Opt Lett. 2004;29:1236–8.
Li X, Ma T, Tian J, Han P, Zhou Q, Shung KK. Micromachined PIN–PMN–PT crystal composite transducer for high-frequency intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) imaging. IEEE Trans Ultrason Ferroelectr Freq Control. 2014;61:1171–8.
Park J, Li X, Zhou QF, Shung KK. Combined chirp coded tissue harmonic and fundamental ultrasound imaging for intravascular ultrasound: 20–60 MHz phantom and ex vivo results. Ultrasonics. 2013;53:369–76.
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to Dr. Qifa Zhou’s group for contributing experts in ultrasound transducer and ultrasound imaging.
Funding
National Institutes of Health (R01HL-125084, R01HL-127271, R01EY-026091, R01EY-021529, and P41EB-015890); Air Force Office of Scientific Research (FA9550-17-1-0193).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Dr. Zhongping Chen has a financial interest in OCT Medical Imaging, Inc., which, however, did not support this work.
Ethical approval
All methods were carried out in accordance with the Guide for Care and Use of Laboratory Animals.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Chen, Z. Multimodal intravascular photoacoustic and ultrasound imaging. Biomed. Eng. Lett. 8, 193–201 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-018-0061-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13534-018-0061-8