Abstract
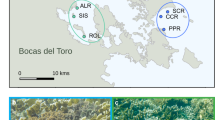
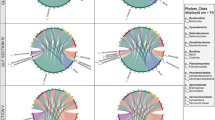
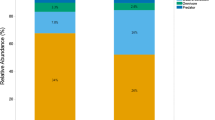
A general and practical understanding of the processes that drive microbiome assembly and structure are paramount to understanding organismal biology, health, and evolution. In this study of stream-dwelling crayfish, we conceptualized colonization of microbial symbionts as a series of ecological filters that operate at the environment, host, and host microsite levels, and identified key ecological processes at each level. A survey of Cambarus sciotensis in western Virginia, USA, showed that the local environment and host microsites interact to create complex patterns of microbial diversity and composition. An in situ experiment confirmed a prevailing effect of host microsite on microbial composition, and also showed that an ectosymbiotic worm (Annelida; Branchiobdellida) which feeds on biofilms and other symbionts had significant effects on microbial composition of the host carapace, but not gills. Bacterial communities of the carapace were taxonomically rich and even, and correlated with microbial communities of the ambient environment. Conversely, communities on gills were less diverse and dominated by two taxa with potential functional significance: Comamonadaceae and Chitinophagaceae. The bacterial communities of the gills appear to be tightly coupled to host biology, and those of the carapace are mostly determined by environmental context. Our work provides the first characterization of the crayfish microbiome and shows how multi-scale and experimental studies of symbiont community assembly provide valuable insights into how the animal microbiome is structured under conditions of natural complexity. Furthermore, this study demonstrates that metazoan symbiont taxa, i.e., the branchiobdellidans, can alter microbiome assembly and structure.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MJ (2001) A new method for non-parametric multivariate analysis of variance. Austral Ecol 26:32–46
Bäckhed F, Ley RE, Sonnenburg JL, Peterson DA, Gordon JI (2005) Host-bacterial mutualism in the human intestine. Science 307:1915–1920
Bauer RT (1998) Gill-cleaning mechanisms of the crayfish Procambarus clarkii (Astacidea: Cambaridae): experimental testing of setobranch function. Invertebr Biol 117:129–143
Bright M, Bulgheresi S (2010) A complex journey: transmission of microbial symbionts. Nat Rev Microbiol 8:218–230
Brown BL, Creed RP (2004) Host preference by an aquatic ectosymbiotic annelid on 2 sympatric species of host crayfishes. J N Am Benthol Soc 23:90–100
Brown B, Creed RP, Dobson WE (2002) Branchiobdellid annelids and their crayfish hosts: are they engaged in a cleaning symbiosis? Oecologia 132:250–255
Brown BL, Creed RP, Skelton J, Rollins MA, Farrell KJ (2012) The fine line between mutualism and parasitism: complex effects in a cleaning symbiosis demonstrated by multiple field experiments. Oecologia 170:199–207
Caporaso JG, Kuczynski J, Stombaugh J, Bittinger K, Bushman FD, Costello EK, Fierer N, Pena AG, Goodrich JK, Gordon JI, Huttley GA, Kelley ST, Knights D, Koenig JE, Ley RE, Lozupone CA, McDonald D, Muegge BD, Pirrung M, Reeder J, Sevinsky JR, Tumbaugh PJ, Walters WA, Widmann J, Yatsunenko T, Zaneveld J, Knight R (2010) QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nat Methods 7:335–336
Clay K (2014) Defensive symbiosis: a microbial perspective. Funct Ecol 28:293–298
Costello EK, Lauber CL, Hamady M, Fierer N, Gordon JI, Knight R (2009) Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time. Science 326:1694–1697
Creed RP (1994) Direct and indirect effects of crayfish grazing in a stream community. Ecology 75:2091–2103
Creed RP, Reed JM (2004) Ecosystem engineering by crayfish in a headwater stream community. J N Am Benthol Soc 23:224–236
DeSantis TZ, Hugenholtz P, Larsen N, Rojas M, Brodie EL, Keller K, Huber T, Dalevi D, Hu P, Andersen GL (2006) Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Appl Environ Microbiol 72(7):5069–5072
Dethlefsen L, Eckburg PB, Bik EM, Relman DA (2006) Assembly of the human intestinal microbiota. Trends Ecol Evol 21:517–523
Dethlefsen L, McFall-Ngai M, Relman DA (2007) An ecological and evolutionary perspective on human–microbe mutualism and disease. Nature 449:811–818
Dominguez-Bello MG, Costello EK, Contreras M, Magris M, Hidalgo G, Fierer N, Knight R (2010) Delivery mode shapes the acquisition and structure of the initial microbiota across multiple body habitats in newborns. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:11971–11975
Edgar RC (2010) Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics 26:2460–2461
Edgar RC (2013) UPARSE: highly accurate OTU sequences from microbial amplicon reads. Nat Methods 10:996
Farrell KJ, Creed RP, Brown BL (2014) Preventing overexploitation in a mutualism: partner regulation in the crayfish–branchiobdellid symbiosis. Oecologia 174:501–510
Fierer N, Morse JL, Berthrong ST, Bernhardt ES, Jackson RB (2007) Environmental controls on the landscape-scale biogeography of stream bacterial communities. Ecology 88:2162–2173
Freese HM, Schink B (2011) Composition and stability of the microbial community inside the digestive tract of the aquatic crustacean Daphnia magna. Microb Ecol 62:882–894
Geyer KM, Altrichter AE, Van Horn DJ, Takacs-Vesbach CD, Gooseff MN, Barrett JE (2013) Environmental controls over bacterial communities in polar desert soils. Ecosphere 4:art127
Gilbert SF, Sapp J, Tauber AI (2012) A symbiotic view of life: We have never been individuals. Q Rev Biol 87:325–341
Graham AL (2008) Ecological rules governing helminth–microparasite coinfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:566–570
Grice EA, Segre JA (2011) The skin microbiome. Nat Rev Microbiol 9:244–253
Harris RN, Brucker RM, Walke JB, Becker MH, Schwantes CR, Flaherty DC, Lam BA, Woodhams DC, Briggs CJ, Vredenburg VT, Minbiole KPC (2009) Skin microbes on frogs prevent morbidity and mortality caused by a lethal skin fungus. ISME J 3:818–824
Helms B, Loughman ZJ, Brown BL, Stoeckel J (2013) Recent advances in crayfish biology, ecology, and conservation. Freshwat Sci 32:1273–1275
Hobbs HHJ, Holt PC, Walton M (1967) The crayfishes and their epizootic ostracod and branchiobdellid associates of the mountain Lake, Virginia, region. Proc U S Natl Mus 123:1–84
Hoffman RL (1963) A revision of the North American annelid worms of the genus cambarincola (Oligochaeta: Branchiobdellidae). Proc US Natl Mus 114(3470):271–371
Holdich DM, Crandall K (2002) Biology of freshwater crayfish. Blackwell Science, Oxford
Huttenhower C, Gevers D, Knight R, Abubucker S, Badger JH, Chinwalla AT, Creasy HH, Earl AM, FitzGerald MG, Fulton RS, Giglio MG, Hallsworth-Pepin K, Lobos EA, Madupu R, Magrini V, Martin JC, Mitreva M, Muzny DM, Sodergren EJ, Versalovic J, Wollam AM, Worley KC, Wortman JR, Young SK, Zeng QD, Aagaard KM, Abolude OO, Allen-Vercoe E, Alm EJ, Alvarado L, Andersen GL, Anderson S, Appelbaum E, Arachchi HM, Armitage G, Arze CA, Ayvaz T, Baker CC, Begg L, Belachew T, Bhonagiri V, Bihan M, Blaser MJ, Bloom T, Bonazzi V, Brooks JP, Buck GA, Buhay CJ, Busam DA, Campbell JL, Canon SR, Cantarel BL, Chain PSG, Chen IMA, Chen L, Chhibba S, Chu K, Ciulla DM, Clemente JC, Clifton SW, Conlan S, Crabtree J, Cutting MA, Davidovics NJ, Davis CC, DeSantis TZ, Deal C, Delehaunty KD, Dewhirst FE, Deych E, Ding Y, Dooling DJ, Dugan SP, Dunne WM, Durkin AS, Edgar RC, Erlich RL, Farmer CN, Farrell RM, Faust K, Feldgarden M, Felix VM, Fisher S, Fodor AA, Forney LJ, Foster L, Di Francesco V, Friedman J, Friedrich DC, Fronick CC, Fulton LL, Gao HY, Garcia N, Giannoukos G, Giblin C, Giovanni MY, Goldberg JM, Goll J, Gonzalez A, Griggs A, Gujja S, Haake SK, Haas BJ, Hamilton HA, Harris EL, Hepburn TA, Herter B, Hoffmann DE, Holder ME, Howarth C, Huang KH, Huse SM, Izard J, Jansson JK, Jiang HY, Jordan C, Joshi V, Katancik JA, Keitel WA, Kelley ST, Kells C, King NB, Knights D, Kong HDH, Koren O, Koren S, Kota KC, Kovar CL, Kyrpides NC, La Rosa PS, Lee SL, Lemon KP, Lennon N, Lewis CM, Lewis L, Ley RE, Li K, Liolios K, Liu B, Liu Y, Lo CC, Lozupone CA, Lunsford RD, Madden T, Mahurkar AA, Mannon PJ, Mardis ER, Markowitz VM, Mavromatis K, McCorrison JM, McDonald D, McEwen J, McGuire AL, McInnes P, Mehta T, Mihindukulasuriya KA, Miller JR, Minx PJ, Newsham I, Nusbaum C, O’Laughlin M, Orvis J, Pagani I, Palaniappan K, Patel SM, Pearson M, Peterson J, Podar M, Pohl C, Pollard KS, Pop M, Priest ME, Proctor LM, Qin X, Raes J, Ravel J, Reid JG, Rho M, Rhodes R, Riehle KP, Rivera MC, Rodriguez-Mueller B, Rogers YH, Ross MC, Russ C, Sanka RK, Sankar P, Sathirapongsasuti JF, Schloss JA, Schloss PD, Schmidt TM, Scholz M, Schriml L, Schubert AM, Segata N, Segre JA, Shannon WD, Sharp RR, Sharpton TJ, Shenoy N, Sheth NU, Simone GA, Singh I, Smillie CS, Sobel JD, Sommer DD, Spicer P, Sutton GG, Sykes SM, Tabbaa DG, Thiagarajan M, Tomlinson CM, Torralba M, Treangen TJ, Truty RM, Vishnivetskaya TA, Walker J, Wang L, Wang ZY, Ward DV, Warren W, Watson MA, Wellington C, Wetterstrand KA, White JR, Wilczek-Boney K, Wu YQ, Wylie KM, Wylie T, Yandava C, Ye L, Ye YZ, Yooseph S, Youmans BP, Zhang L, Zhou YJ, Zhu YM, Zoloth L, Zucker JD, Birren BW, Gibbs RA, Highlander SK, Methe BA, Nelson KE, Petrosino JF, Weinstock GM, Wilson RK, White O, Human Microbiome Project C (2012) Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome. Nature 486:207–214
Jost L (2006) Entropy and diversity. Oikos 113:363–375
Kuczynski J, Costello EK, Nemergut DR, Zaneveld J, Lauber CL, Knights D, Koren O, Fierer N, Kelley ST, Ley RE (2010) Direct sequencing of the human microbiome readily reveals community differences. Genome Biol 11:210
Kueneman JG, Parfrey LW, Woodhams DC, Archer HM, Knight R, McKenzie VJ (2014) The amphibian skin-associated microbiome across species, space and life history stages. Mol Ecol 23:1238–1250
Lauber CL, Hamady M, Knight R, Fierer N (2009) Pyrosequencing-based assessment of soil pH as a predictor of soil bacterial community structure at the continental scale. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:5111–5120
Lee JH, Kim TW, Choe JC (2009) Commensalism or mutualism: conditional outcomes in a Branchiobdellidae crayfish symbiosis. Oecologia 159:217–224
Loudon AH, Woodhams DC, Parfrey LW, Archer H, Knight R, McKenzie V, Harris RN (2014) Microbial community dynamics and effect of environmental microbial reservoirs on red-backed salamanders (Plethodon cinereus). ISME J 8:830–840
Masella AP, Bartram AK, Truszkowski JM, Brown DG, Neufeld JD (2012) PANDAseq: PAired-eND assembler for Illumina sequences. Bmc Bioinforma 13:7
McKenzie VJ, Bowers RM, Fierer N, Knight R, Lauber CL (2012) Co-habiting amphibian species harbor unique skin bacterial communities in wild populations. ISME J 6:588–596
Mihaljevic JR (2012) Linking metacommunity theory and symbiont evolutionary ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 27:323–329
Mitchell KR, Takacs-Vesbach CD (2008) A comparison of methods for total community DNA preservation and extraction from various thermal environments. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 35:1139–1147
Oksanen J, Blanchet JG, Kindt R, Legendre P, Minchin PR, O’Hara PB, Simpson GL, Solymos P, Stevens MHH, Wagner H (2016) Vegan: Community Ecology Package. R package version 2.3-5. http://CRAN.R-project.org/package=vegan
Owen CL, Bracken-Grissom H, Stern D, Crandall KA (2015) A synthetic phylogeny of freshwater crayfish: insights for conservation. Philos Trans Roy Soc London B: Biol Sci 370:20140009
Palmer TM, Doak DF, Stanton ML, Bronstein JL, Kiers ET, Young TP, Goheen JR, Pringle RM (2010) Synergy of multiple partners, including freeloaders, increases host fitness in a multispecies mutualism. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107(40):17234–17239
Pedersen AB, Fenton A (2007) Emphasizing the ecology in parasite community ecology. Trends Ecol Evol 22:133–139
Peerakietkhajorn S, Tsukada K, Kato Y, Matsuura T, Watanabe H (2015) Symbiotic bacteria contribute to increasing the population size of a freshwater crustacean, Daphnia magna. Environ Microbiol Rep 7:364–372
Pequeux A (1995) Osmotic regulation in crustaceans. J Crustac Biol 15:1–60
Qi W, Nong G, Preston JF, Ben-Ami F, Ebert D (2009) Comparative metagenomics of daphnia symbionts. BMC Genomics 10:1
Rosenberg E (2014) The family Chitinophagaceae. In: Rosenberg E, DeLong EF, Lory S, Stackebrandt E, Thompson F (eds) The prokaryotes: other major lineages of bacteria and the archaea. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin, Heidelberg, pp. 493–495
Rosewarne P, Svendsen J, Mortimer RG, Dunn A (2014) Muddied waters: suspended sediment impacts on gill structure and aerobic scope in an endangered native and an invasive freshwater crayfish. Hydrobiologia 722:61–74
Rousk J, Baath E, Brookes PC, Lauber CL, Lozupone C, Caporaso JG, Knight R, Fierer N (2010) Soil bacterial and fungal communities across a pH gradient in an arable soil. ISME J 4:1340–1351
Scheuring I, Yu DW (2012) How to assemble a beneficial microbiome in three easy steps. Ecol Lett 15:1300–1307
Schütte UME, Abdo Z, Bent SJ, Shyu C, Williams CJ, Pierson JD, Forney LJ (2008) Advances in the use of terminal restriction fragment length polymorphism (T-RFLP) analysis of 16S rRNA genes to characterize microbial communities. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 80(3):365–380
Shafquat A, Joice R, Simmons SL, Huttenhower C (2014) Functional and phylogenetic assembly of microbial communities in the human microbiome. Trends Microbiol 22:261–266
Skelton J, Farrell KJ, Creed RP, Williams BW, Ames C, Helms BS, Stoekel J, Brown BL (2013) Servants, scoundrels, and hitchhikers: current understanding of the complex interactions between crayfish and their ectosymbiotic worms (Branchiobdellida). Freshwat Sci 32:1345–1357
Skelton J, Creed RP, Brown BL (2014) Ontogenetic shift in host tolerance controls initiation of a cleaning symbiosis. Oikos 123:677–686
Skelton J, Creed RP, Brown BL (2015) A symbiont’s dispersal strategy: condition-dependent dispersal underlies predictable variation in direct transmission among hosts. Proc R Soc B Biol Sci 282(1819):20152081
Skelton J, Doak S, Leonard M, Creed RP, Brown BL (2016) The rules for symbiont community assembly change along a mutualism-parasitism continuum. J Anim Ecol 85:843–853
Statzner B, Fievet E, Champagne JY, Morel R, Herouin E (2000) Crayfish as geomorphic agents and ecosystem engineers: biological behavior affects sand and gravel erosion in experimental streams. Limnol Oceanogr 40:1030–1040
Statzner B, Peltret O, Tomanova S (2003) Crayfish as geomorphic agents and ecosystem engineers: effect of a biomass gradient on baseflow and flood-induced transport of gravel and sand in experimental streams. Freshw Biol 48:147–163
Taylor CA, Schuster GA, Cooper JE, DiStefano RJ, Eversole AG, Hamr P, Hobbs HH III, Robison HW, Skelton CE, Thoma RF (2007) A reassessment of the conservation status of crayfishes of the United States and Canada after 10+ years of increased awareness. Fisheries 32:372–389
Thies JE (2007) Soil microbial community analysis using terminal restriction fragment length polymorphisms. Soil Sci Soc Am J 71(2):579
Thomas MJ, Creed RP, Brown BL (2013) The effects of environmental context and initial density on symbiont populations in a freshwater cleaning symbiosis. Freshwat Sci 32:1358–1366
Thomas MJ, Creed RP, Skelton J, Brown BL (2016) Ontogenetic shifts in a freshwater cleaning symbiosis: consequences for hosts and their symbionts. Ecology 97:1507–1517
Usio N, Townsend CR (2002) Functional significance of crayfish in stream food webs: roles of omnivory, substrate heterogeneity and sex. Oikos 98:512–522
Usio N, Townsend CR (2004) Roles of crayfish: consequences of predation and bioturbation for stream invertebrates. Ecology 85:807–822
Walke JB, Becker MH, Loftus SC, House LL, Cormier G, Jensen RV, Belden LK (2014) Amphibian skin may select for rare environmental microbes. ISME J 8(11):2207–2217
Walke JB, Becker MH, Loftus SC, House LL, Teotonio TL, Minbiole KP, Belden LK (2015) Community structure and function of amphibian skin microbes: an experiment with bullfrogs exposed to a Chytrid fungus. PLoS One 10:e0139848
Acknowledgments
We sincerely thank Michael J. Thomas and Mathew Hedin for their help in the field and laboratory. Allan Dickerman and the staff of the Virginia Tech Bioinformatics Institute were critical partners for high-throughput amplicon sequencing and analysis. This manuscript benefited greatly from thoughtful comments from Michelle A. Jusino and two anonymous reviewers. Funding was provided by the National Science Foundation (DEB-0949780 to BLB and DEB-0949823 to RPC), Virginia Tech Organismal Biology and Ecology Interdisciplinary Grants (to JS and KMG), and the Virginia Bioinformatics Institute and Fralin Life Science Institute Small Grants Program (to JS, KMG, JTL and BLB).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skelton, J., Geyer, K.M., Lennon, J.T. et al. Multi-scale ecological filters shape the crayfish microbiome. Symbiosis 72, 159–170 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0469-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13199-016-0469-9