Abstract
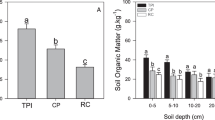
Land cover conversion intensively occurred in the Tibetan Plateau of China during the past decades. However, responses of soil properties and soil microbial activities to land cover conversion under different land cover types have not been fully understood. The objective was to assess the effects of land cover conversion on soil C and N stocks and soil microbial properties of topsoil of an alpine meadow in the Tibetan Plateau. Soil cores of surface soil (0–20 cm) were collected from three adjacent land cover types: native alpine meadow, artificial grassland and mound-shaped denuded land. Soil microbial metabolic diversity was measured using Biolog EcoPlates. Significant losses of SOC and TN storages were subject to land cover conversion in topsoil, decreasing 14.5 and 10.9 % of alpine meadow to artificial grassland and 52.9 and 51.7 % to denuded land. Alpine meadow soils had the highest soil microbial biomass and microbial metabolic activity of three land cover types. Microbial biomass and microbial metabolic activity decreased markedly after alpine meadow conversion to denuded land. Land use conversion from original alpine meadow to artificial grassland and denuded land caused decline in soil organic carbon density, total nitrogen density and soil microbial activity. Soil carbon emissions from alpine meadow conversion were released to the atmosphere and could influence climatic change.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bending GD, Turner MK, Jones JE (2002) Interactions between crop residue and soil organic matter quality and the functional diversity of soil microbial communities. Soil Biol Biochem 34:1073–1082. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(02)00040-8
Braimoh AK, Vlek PLG (2004) The impact of land-cover change on soil properties in northern Ghana. Land Degrad Dev 15:65–74. doi:10.1002/Ldr.590
Brookes PC, Landman A, Pruden G, Jenkinson DS (1985) Chloroform fumigation and the release of soil-nitrogen—a rapid direct extraction method to measure microbial biomass nitrogen in soil. Soil Biol Biochem 17:837–842. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(85)90144-0
Chakraborty A, Chakrabarti K, Chakraborty A, Ghosh S (2011) Effect of long-term fertilizers and manure application on microbial biomass and microbial activity of a tropical agricultural soil. Biol Fertil Soils 47:227–233. doi:10.1007/s00374-010-0509-1
Degens BP, Schipper LA, Sparling GP, Duncan LC (2001) Is the microbial community in a soil with reduced catabolic diversity less resistant to stress or disturbance? Soil Biol Biochem 33:1143–1153. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(01)00018-9
Ding GC, Piceno YM, Heuer H, Weinert N, Dohrmann AB, Carrillo A, Andersen GL, Castellanos T, Tebbe CC, Smalla K (2013) Changes of soil bacterial diversity as a consequence of agricultural land use in a semi-arid ecosystem. PLoS One 8:e59497. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059497
Fernandez CW, Kennedy PG (2015) Moving beyond the black-box: fungal traits, community structure, and carbon sequestration in forest soils. New Phytol 205:1378–1380. doi:10.1111/Nph.13289
Garland JL, Mills AL (1991) Classification and characterization of heterotrophic microbial communities on the basis of patterns of community-level sole-carbon-source utilization. Appl Environ Microbiol 57:2351–2359
Genxu W, Yuanshou L, Yibo W, Qingbo W (2008) Effects of permafrost thawing on vegetation and soil carbon pool losses on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Geoderma 143:143–152. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2007.10.023
Grandy AS, Strickland MS, Lauber CL, Bradford MA, Fierer N (2009) The influence of microbial communities, management, and soil texture on soil organic matter chemistry. Geoderma 150:278–286. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2009.02.007
Guo LB, Gifford RM (2002) Soil carbon stocks and land use change: a meta analysis. Glob Change Biol 8:345–360. doi:10.1046/j.1354-1013.2002.00486.x
Harris RB (2010) Rangeland degradation on the Qinghai–Tibetanan plateau: a review of the evidence of its magnitude and causes. J Arid Environ 74:1–12. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2009.06.014
Hietel E, Waldhardt R, Otte A (2004) Analysing land-cover changes in relation to environmental variables in Hesse, Germany. Landscape Ecol 19:473–489. doi:10.1023/B:Land.0000036138.82213.80
Insam H (1997) A new set of substrates proposed for community characterization in environmental samples. Springer, USA
Islam MR, Chauhan PS, Kim Y, Kim M, Sa T (2011) Community level functional diversity and enzyme activities in paddy soils under different long-term fertilizer management practices. Biol Fertil Soils 47:599–604. doi:10.1007/s00374-010-0524-2
Jannike W, Florian W, Georg JR (2006) Impact of salinity on soil microbial communities and the decomposition of maize in acidic soils. Geoderma 137:100–108. doi:10.1016/j.geoderma.2006.08.001
Jiang W, Wang JJ, Tang JS, Hou F, Lu YT (2010) Soil bacterial functional diversity as influenced by cadmium, phenanthrene and degrade bacteria application. Environ Earth Sci 59:1717–1722. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0153-y
Jones SE, Lennon JT (2010) Dormancy contributes to the maintenance of microbial diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci 107:5881–5886. doi:10.1073/pnas.0912765107
Lawler JJ, Lewis DJ, Nelson E, Plantinga AJ, Polasky S, Withey JC, Helmers DP, Martinuzzi S, Pennington D, Radeloff VC (2014) Projected land-use change impacts on ecosystem services in the United States. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:7492–7497. doi:10.1073/pnas.1405557111
Li XG, Zhang ML, Li ZT, Shi XM, Ma Q, Long RJ (2009) Dynamics of soil properties and organic carbon pool in topsoil of zokor-made mounds at an alpine site of the Qinghai–Tibetanan Plateau. Biol Fertil Soils 45:865–872. doi:10.1007/s00374-009-0398-3
Liu W, Chen S, Qin X, Baumann F, Scholten T, Zhou Z, Sun W, Zhang T, Ren J, Qin D (2012) Storage, patterns, and control of soil organic carbon and nitrogen in the northeastern margin of the Qinghai–Tibetanan Plateau. Environ Res Lett 7:035401. doi:10.1088/1748-9326/7/3/035401
Lu RK (1999) Analytical methods for soils and agricultural chemistry. China Agricultural Science and Technology Press, Beijing, pp 107–240
Mcdaniel PA, Munn LC (1985) Effect of temperature on organic carbon-texture relationships in mollisols and aridisols. Soil Sci Soc Am J 49:1486–1489. doi:10.2136/sssaj1985.03615995004900060031x
Melo VS, Desjardins T, Silva ML, Santos ER, Sarrazin M, Santos MMLS (2012) Consequences of forest conversion to pasture and fallow on soil microbial biomass and activity in the eastern Amazon. Soil Use Manag 28:530–535. doi:10.1111/Sum.12003
Nannipieri P, Ascher J, Ceccherini MT, Landi L, Pietramellara G, Renella G (2003) Microbial diversity and soil functions. Eur J Soil Sci 54:655–670. doi:10.1046/j.1351-0754.2003.0556.x
Ni J (2002) Carbon storage in grasslands of China. J Arid Environ 50:205–218. doi:10.1006/jare.2201.0902
Ninh HT, Grandy AS, Wickings K, Snapp SS, Kirk W, Hao J (2015) Organic amendment effects on potato productivity and quality are related to soil microbial activity. Plant Soil 386:223–236. doi:10.1007/s11104-014-2223-5
Qin Y, Yi S, Ren S, Li N, Chen J (2014) Responses of typical grasslands in a semi-arid basin on the Qinghai–Tibetanan Plateau to climate change and disturbances. Environ Earth Sci 71:1421–1431. doi:10.1007/s12665-013-2547-0
Ross DJ, Tate KR, Scott NA, Feltham CW (1999) Land-use change: effects on soil carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus pools and fluxes in three adjacent ecosystems. Soil Biol Biochem 31:803–813. doi:10.1016/S0038-0717(98)00180-1
Talbot JM, Bruns TD, Taylor JW, Smith DP, Branco S, Glassman SI, Erlandson S, Vilgalys R, Liao HL, Smith ME, Peay KG (2014) Endemism and functional convergence across the North American soil mycobiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:6341–6346. doi:10.1073/pnas.1402584111
Turner BL, Skole D, Sanderson S, Fischer G, Fresco L, Leemans R (1995) Land-use and land-cover change. Global Change Report, Sweden
Vance ED, Brookes PC, Jenkinson DS (1987) An extraction method for measuring soil microbial biomass-C. Soil Biol Biochem 19:703–707. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(87)90052-6
Wang GX, Qian J, Cheng GD, Lai YM (2002) Soil organic carbon pool of grassland soils on the Qinghai–Tibetanan Plateau and its global implication. Sci Total Environ 291:207–217. doi:10.1016/S0048-9697(01)01100-7
Wang GX, Cheng GD, Shen YP, Qian J (2003) Influence of land cover changes on the physical and chemical properties of alpine meadow soil. Chin Sci Bull 48:118–124. doi:10.1360/03tb9023
Wang G, Wang Y, Kubota J (2006a) Land-cover changes and its impacts on ecological variables in the headwaters area of the Yangtze River, China. Environ Monit Assess 120:361–385. doi:10.1007/s10661-005-9068-6
Wang WY, Wang QJ, Wang HC (2006b) The effect of land management on plant community composition, species diversity, and productivity of alpine Kobersia steppe meadow. Ecol Res 21:181–187. doi:10.1007/s11284-005-0108-z
Wang G, Wang Y, Li Y, Cheng H (2007) Influences of alpine ecosystem responses to climatic change on soil properties on the Qinghai–Tibetan Plateau, China. Catena 70:506–514. doi:10.1016/j.catena.2007.01.001
Wang W, Wang QJ, Lu ZY (2009) Soil organic carbon and nitrogen content of density fractions and effect of meadow degradation to soil carbon and nitrogen of fractions in alpine Kobresia meadow. Sci China Ser D 52:660–668. doi:10.1007/s11430-009-0056-5
Wang J, Wang G, Hu H, Wu Q (2010) The influence of degradation of the swamp and alpine meadows on CH4 and CO2 fluxes on the Qinghai–Tibetanan Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 60:537–548. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0193-3
Wardle DA (1992) A comparative-assessment of factors which influence microbial biomass carbon and nitrogen levels in soil. Biol Rev 67:321–358. doi:10.1111/j.1469-185X.1992.tb00728.x
Whitmore AP, Kirk GJD, Rawlins BG (2014) Technologies for increasing carbon storage in soil to mitigate climate change. Soil Use Manag. doi:10.1111/sum.12115
Wu RG, Tiessen H (2002) Effect of land use on soil degradation in alpine grassland soil, China. Soil Sci Soc Am J 66:1648–1655. doi:10.2136/sssaj2002.1648
Wu GL, Liu ZH, Zhang L, Hu TM, Chen JM (2010) Effects of artificial grassland establishment on soil nutrients and carbon properties in a black-soil-type degraded grassland. Plant Soil 333:469–479. doi:10.1007/s11104-010-0363-9
Yang H, Lu Q, Wu B, Yang H, Zhang J, Lin Y (2006) Vegetation diversity and its application in sandy desert revegetation on Tibetan Plateau. J Arid Environ 65:619–631. doi:10.1016/j.jaridenv.2005.08.010
Yang YH, Fang JY, Tang YH, Ji CJ, Zheng CY, He JS, Zhu BA (2008) Storage, patterns and controls of soil organic carbon in the Tibetan grasslands. Glob Change Biol 14:1592–1599. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2486.2008.01591.x
Yang Y, Chen R, Han C, Qing W (2013) Measurement and estimation of the summertime daily evapotranspiration on alpine meadow in the Qilian Mountains, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 68:2253–2261. doi:10.1007/s12665-012-1907-5
Zak JC, Willig MR, Moorhead DL, Wildman HG (1994) Functional diversity of microbial communities - a quantitative approach. Soil Biol Biochem 26:1101–1108. doi:10.1016/0038-0717(94)90131-7
Zeng DH, Hu YL, Chang SX, Fan ZP (2009) Land cover change effects on soil chemical and biological properties after planting Mongolian pine (Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica) in sandy lands in Keerqin, northeastern China. Plant Soil 317:121–133. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9793-z
Zhang XF, Zhao L, Xu SJ Jr, Liu YZ, Liu HY, Cheng GD (2013) Soil moisture effect on bacterial and fungal community in Beilu River (Tibetan Plateau) permafrost soils with different vegetation types. J Appl Microbiol 114:1054–1065. doi:10.1111/jam.12106
Zhao D, Li F, Yang Q, Wang R, Song Y, Tao Y (2013) The influence of different types of urban land use on soil microbial biomass and functional diversity in Beijing, China. Soil Use Manag 29:230–239. doi:10.1111/Sum.12034
Zheng H, Ouyang ZY, Wang XK, Fang ZG, Zhao TQ, Miao H (2005) Effects of regenerating forest cover on soil microbial communities: a case study in hilly red soil region, Southern China. For Ecol Manage 217:244–254. doi:10.1016/j.foreco.2005.06.005
Zhou H, Zhao X, Tang Y, Gu S, Zhou L (2005) Alpine grassland degradation and its control in the source region of the Yangtze and Yellow Rivers, China. Grassl Sci 51:191–203. doi:10.1111/j.1744-697X.2005.00028.x
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by projects of the National Basic Research Program of China (2013CBA01086) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 41222001 and 91025011). We thank our colleagues at the Qilian Alpine Ecology and Hydrology Research Station for their valuable assistance with the fieldwork. We also greatly appreciate the responsible editor and the two anonymous reviewers whose comments dramatically improved this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhu, P., Chen, R., Song, Y. et al. Effects of land cover conversion on soil properties and soil microbial activity in an alpine meadow on the Tibetan Plateau. Environ Earth Sci 74, 4523–4533 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4509-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-4509-1