Abstract
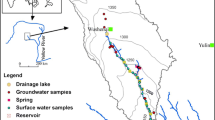
The impacts of environmental flow controls on the water table and chemistry of groundwater in the Ejina Delta, an arid inland river basin in northwest China, were investigated with field observations in 2001 and 2009. The results indicate that the shallow groundwater level rose by 0–2 m in the upper reaches of the east tributary of the Heihe River and in the areas of Saihantaolai—Dalaikubu during the period of environmental flow controls. The chemical constituents of the groundwater show a distinct spatial heterogeneity with the total dissolved solids (TDS) in the groundwater increasing from the periphery towards the depocenter of the Ejina Basin. In addition, the rate of groundwater cycling in the south of the Ejina Delta increased, and the mineralization of groundwater declined, while the overall mineralization and salinity increased in the northern regions, especially in the depocenter of the Ejina Basin. Since shallow groundwater is important to the ecology of arid regions, and because understanding the changes in the shallow groundwater environment (groundwater level and hydrochemistry) in response to environmental flow controls is essential for the sustainable improvement of the ecological environment, the results of this paper can be used as a reference for watershed water resources planning and management to help maintain the health and proper function of rivers in arid regions.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiyama T, Sakai A, Yamazaki Y, Wang G, Fujita K et al (2007) Surface water-groundwater interaction in the Heihe River basin, Northwestern China. Bull Glaciol Res 24:87–94
Chen Y, Zhang D, Sun Y, Liu X, Wang N, Savenije HHG (2005) Water demand management: a case study of the Heihe River basin in China. Phys Chem Earth 30:408–419. doi:10.1016/j.pce.2005.06.019
Chen ZY, Nie ZL, Zhang GH, Wan L, Shen JM (2006) Environmental isotopic study on the recharge and residence time of groundwater in the Heihe River Basin, northwestern China. Hydrogeol J 14:1635–1651. doi:10.1007/s10040-006-0075-7
Deutsch WJ (1997) Groundwater geochemistry: fundamentals and application to contamination. CRC, Boca Raton
Du Q, Xu X, Li H, Peng H (2005) Analysis on ecological security changes of the oases in the middle and lower Heihe River. Acta Sci Nat Univ Pekinensis 41(2):273–281
Feng Q, Wei L, Su YH, Zhang YW, Si JH (2004) Distribution and evolution of water chemistry in Heihe river basin. Environ Geol 45:947–956
Gong J, Dong G (1998) Environmental degradation of the Ejina Oasis and comprehensive rehabilitation in the lower reaches of the Heihe River. J Desert Res 18:44–49
Greiner R (1997) Optimal farm management responses to emerging soil salinisation in a dry land catchment in eastern Australia. Land Degrad Dev 8(4):281–303
Guo Q, Feng Q, Li J (2009) Environmental changes after ecological water transport in the lower reaches of Heihe River, northwest China. Environ Geol 58:1387–1396. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1641-1
Ingerbritsen SE, Sanford WE, Neuzil CE (2006) Groundwater in geologic processes, 2nd edn. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Ma JZ, Edmunds WM (2006) Groundwater and lake evolution in the Badain Jaran desert ecosystem, inner mongolia. Hydrogeol J 14:1231–1243
Piper AM (1944) A graphic procedure in the geochemical interpretation of water analyses. Trans Am Geophys Union 25:914–923
Si J, Feng Q, Wen X, Su Y, Xi H, Chang Z (2009) Major ion chemistry of groundwater in the extreme arid region northwest China. Environ Geol 57:1079–1087. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1394-x
Su Y, Feng Q, Zhu G, Si J, Zhang Y (2007) Identification and evolution of groundwater chemistry in the Ejina sub-basin of the Heihe River, northwest China. Pedosphere 17(3):331–342
Su Y, Zhu G, Feng Q, Li Z, Zhang F (2009) Environmental isotopic and hydrochemical study of groundwater in the Ejina Basin, northwest China. Environ Geol 58:601–614. doi:10.1007/s00254-008-1534-3
Subrahmanyam K, Yadaiah P (2001) Assessment of the industrial effluents on water quality in Patancheru and environs, Medak district, Andhra Pradesh, India. Hydrogeol J 9(3):297–312
Toth J (1999) Ground-water as a geologic agent: an overview of the cause, processes and manifestations. Hydrogeol J 7:1–14
Wang G, Chen G (1999) Water resource development and its influence on the environment in arid areas of China—the case of the Hei River Basin. J Arid Environ 43:121–131
Wang G, Yang L, Chen L, Kubota J (2005) Impacts of land use changes on groundwater resources in the Heihe River Basin. J Geograph Sci 15:405–414
Wen X, Wu Y, Zhang Y, Liu F (2005) Hydrochemical characteristics and salinity of groundwater in the Ejina Basin, Northwestern China. Environ Geol 48:665–675. doi:10.1007/s00254-005-0001-7
Xi H, Feng Q, Liu W, Si J, Chang Z, Su Y (2010) The research of groundwater flow model in Ejina Basin, Northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 60:953–963. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0231-1
Xie Q (1980) Regional hydrogeological survey report of the People’s Republic of China (1:200 000): Ejina K-47-[24] [R] Jiuquan (in Chinese)
Zhang Y, Wu Y, Su J, Wen X, Liu F (2005) Groundwater replenishment analysis by using natural isotopes in Ejina Basin, Northwestern China. Environ Geol 48:6–14. doi:10.1007/s00254-004-1214-x
Zhao W, Chang X, He Z, Zhang Z (2007) Study on vegetation ecological water requirement in Ejina Oasis. Sci China D Earth Sci 50(1):121–129
Zhu G, Su Y, Huang C, Feng Q, Liu Z (2010) Hydrogeochemical processes in the groundwater environment of Heihe River Basin, northwest China. Environ Earth Sci 60:139–153. doi:10.1007/s12665-009-0175-5
Zhu Y, Ren L, Skaggs TH, Lu H, Yu Z, Wu Y, Fang X (2009) Simulation of Populus euphratica root uptake of groundwater in an arid woodland of the Ejina basin, China. Hydrol Process 23:2460–2469. doi:10.1002/hyp.7353
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (973 Program) (No. 2009CB421305), the 47th China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (No. 20100470534), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 40901024), and the Hundred Talents Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences. Special thanks are due to Prof. Lixin Wang and Yushu Zhang (Institute of Geographic Sciences and Natural Resources Research, Chinese Academy of Sciences), who measured the depth of the groundwater table and performed the hydrochemical analysis of the water samples in 2001.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, P., Yu, J., Zhang, Y. et al. Impacts of environmental flow controls on the water table and groundwater chemistry in the Ejina Delta, northwestern China. Environ Earth Sci 64, 15–24 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0811-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-010-0811-0