Abstract
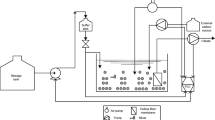
Nitric oxide (NO) removal from a gas stream containing ~500 ppm NO was studied in a hollow fiber membrane (HFM) bioreactor. Compared to other biological NO removal methods the HFM bioreactor achieved NO removal rates that were as good if not better, of up to 92% NO removal, under comparable loadings and reactor size. Results showed that a wastewater stream containing organic carbon can be used as the electron donor to reduce the NO. Hence, combining biological NO treatment with treatment of a wastewater containing organic carbon has may be an effective overall cost-reducing strategy. The effect of different nitrate (NO −3 ) concentrations on the NO reduction rate was also evaluated, and results showed that NO −3 does enhance the NO removal rate. The reactor’s performance was studied under six different NO:NO −3 loading regimes and the NO removal rate as well as the microbial denitrifier community in the reactor was tracked. Specifically, the relevant genes responsible for each denitrification step were tracked during each different NO:NO −3 loading regime to the reactor. Results showed that the denitrifying microbial community adjust rapidly to changes in the different N loadings, but overall the performance of the reactor is robust and can withstand such variability in terms of NO, NO −3 and organic carbon removal.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dentener, F., et al.: Nitrogen and sulfur deposition on regional and global scales: a multimodel evaluation. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 20(4), GB4003 (2006)
US-EPA: Nitrogen oxides (NOx) control regulations. https://www3.epa.gov/region1/airquality/nox.html (2015). Accessed 16 Oct 2017
Clais, P., Sabine, C.: IPCC report. Chapter 6: carbon and other biogeochemical cycles (2013)
Wei, Z.S., et al.: Coupling membrane catalysis and biodegradation for nitric oxide removal in a novel hybird catalytic membrane biofilm reactor. Chem. Eng. J. 296, 154–161 (2016)
Molina, M.J., Molina, L.T.: Megacities and atmospheric pollution. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 54(6), 644–680 (2004)
Weinberger, B., et al.: The toxicology of inhaled nitric oxide. Toxicol. Sci. 59, 5–16 (2001)
Pandey, R., Chandrashekhar, B.: Physicochemical and biochemical approaches for treatment of gaseous emissions containing NOx. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 44(1), 34–96 (2014)
Li, Z., et al.: Effect of selective catalytic reduction (SCR) on fine particle emission from two coal-fired power plants in China. Atmos. Environ. 120, 227–233 (2015)
Chen, J., et al.: Dynamic model for nitric oxide removal by a rotating drum biofilter. J. Hazard. Mater. 168(2–3), 1047–1052 (2009)
Wei, L., et al.: Removal of nitric oxide in a biotrickling filter under thermophilic condition using Chelatococcus daeguensis. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 62(5), 509–516 (2012)
Hiroyasu, N., et al.: Uptake pathway and continuous removal of nitric oxide from flue gas using microalgae. Biochem. Eng. J. 7(3), 241–246 (2001)
Jun, C., et al.: Effect of key parameters on nitric oxide removal by anaerobic rotating drum biofilters. Environ. Technol. 29(11), 1241–1247 (2008)
Buisman, C.J.N., et al.: Process for purifying flue gas containing nitrogen oxides (1999)
van der Maas, P., et al.: NOx removal from flue gas by an integrated physicochemical absorption and biological denitrification process. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 90(4), 433–441 (2005)
van der Maas, P., et al.: Enzymatic versus nonenzymatic conversions during the reduction of EDTA-chelated Fe(III) in BioDeNOx reactors. Environ. Sci. Technol. 39(8), 2616–2623 (2005)
Zhang, X., et al.: Removal of nitric oxide from simulated flue gas via denitrification in a hollow-fiber membrane bioreactor. J. Environ. Sci. 25(11), 2239–2246 (2013)
Min, K.-N., Ergas, S.J., Harrison, J.M.: Hollow-fiber membrane bioreactor for nitric oxide removal. Environ. Eng. Sci. 19(6), 575–583 (2002)
Kumar, A., et al.: Modeling of a hollow fiber membrane biofilm reactor for nitric oxide removal: Model development and experimental validation. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 85(3), 423–428 (2010)
Li, W., Wu, C.-Z., Shi, Y.: Metal chelate absorption coupled with microbial reduction for removal of NOx from flu gas. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 81(3), 306–311 (2006)
Durmazpinar, S., et al.: Biological NOx removal by denitrification process in a jet-loop bioreactor: system performance and model development. Environ. Technol. 35(9–12), 1358–1366 (2014)
Wei, L., et al.: Biological reduction integrated system: complexed NO conversion pathways and nitrogen equilibrium analysis. Energy Fuels 28(7), 4725–4730 (2014)
Niu, H., et al.: Nitric oxide removal by wastewater bacteria in a biotrickling filter. J. Environ. Sci. 26(3), 555–565 (2014)
Hanaki, K., Hong, Z., Matsuo, T.: Production of nitrous oxide gas during denitrification of wastewater. Water Sci. Technol. 26(5–6), 1027–1036 (1992)
Glassa, C., Silversteinb, J.: Denitrification kinetics of high nitrate concentration water: pH effect on inhibition and nitrite accumulation. Water Res. 32(3), 831–839 (1998)
Petersen, D.G., et al.: Abundance of microbial genes associated with nitrogen cycling as indices of biogeochemical process rates across a vegetation gradient in Alaska. Environ. Microbiol. 14(4), 993–1008 (2012)
Reyna, L., Wunderlin, D.A., Genti-Raimondi, S.: Identification and quantification of a novel nitrate-reducing community in sediments of Suquia River basin along a nitrate gradient. Environ. Pollut. 158(5), 1608–1614 (2010)
Braker, G., Fesefeldt, A., Witzel, K.P.: Development of PCR primer systems for amplification of nitrite reductase genes (nirK and nirS) to detect denitrifying bacteria in environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64(10), 3769–3775 (1998)
Braker, G., Tiedje, J.M.: Nitric oxide reductase (norB) genes from pure cultures and environmental samples. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 69(6), 3476–3483 (2003)
Scala, D.J., Kerkhof, L.J.: Nitrous oxide reductase (nosZ) gene-specific PCR primers for detection of denitri¢ers and three nosZ genes from marine sediments. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 162, 61–68 (1998)
Harms, G., et al.: Real-time PCR quantification of nitrifying bacteria in a municipal wastewater treatment plant. Environ. Sci. Technol. 37, 343–351 (2003)
Chung, Y.-C., Chung, M.-S.: BNP test to evaluate the influence of C/N ratio on N2O production in biological denitrification. Water Sci. Technol. 42(3–4), 23–27 (2000)
Pan, Y., et al.: Effect of pH on N2O reduction and accumulation during denitrification by methanol utilizing denitrifiers. Water Res. 46(15), 4832–4840 (2012)
Acknowledgements
Funding for this work was provided by the Hebei Huafeng Coking & Power Co. The seed was provided by Dr. Eugenio Giraldo from NuOrganics LLC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Razaviarani, V., Ruiz-Urigüen, M. & Jaffé, P.R. Denitrification of Nitric Oxide Using Hollow Fiber Membrane Bioreactor; Effect of Nitrate and Nitric Oxide Loadings on the Reactor Performance and Microbiology. Waste Biomass Valor 10, 1989–2000 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0223-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-018-0223-z