Abstract
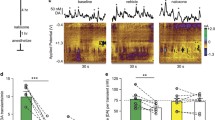
Phasic dopamine (DA) signaling, during which burst firing by DA neurons generates short-lived elevations in extracellular DA in terminal fields called DA transients, is implicated in reinforcement learning. Disrupted phasic DA signaling is proposed to link DA depletions and cognitive-behavioral impairment in methamphetamine (METH)-induced neurotoxicity. Here, we further investigated this disruption by assessing effects of METH pretreatment on DA transients elicited by a drug cocktail of raclopride, a D2 DA receptor antagonist, and nomifensine, an inhibitor of the dopamine transporter (DAT). One advantage of this approach is that pharmacological activation provides a large, high-quality data set of transients elicited by endogenous burst firing of DA neurons for analysis of regional differences and neurotoxicity. These pharmacologically evoked DA transients were measured in the dorsomedial (DM) and dorsolateral (DL) striatum of urethane-anesthetized rats by fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. Electrically evoked DA levels were also recorded to quantify DA release and uptake, and DAT binding was determined by means of autoradiography to index DA denervation. Pharmacologically evoked DA transients in intact animals exhibited a greater amplitude and frequency and shorter duration in the DM compared to the DL striatum, despite similar pre- and post-drug assessments of DA release and uptake in both sub-regions as determined from the electrically evoked DA signals. METH pretreatment reduced transient activity. The most prominent effect of METH pretreatment on transients across striatal sub-region was decreased amplitude, which mirrored decreased DAT binding and was accompanied by decreased DA release. Overall, these results identify marked intrastriatal differences in the activity of DA transients that appear independent of presynaptic mechanisms for DA release and uptake and further support disrupted phasic DA signaling mediated by decreased DA release in rats with METH-induced neurotoxicity.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abercrombie ED, Bonatz AE, Zigmond MJ (1990) Effects of l-dopa on extracellular dopamine in striatum of normal and 6-hydroxydopamine-treated rats. Brain Res 525:36–44
Aragona BJ, Cleaveland NA, Stuber GD, Day JJ, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2008) Preferential enhancement of dopamine transmission within the nucleus accumbens shell by cocaine is attributable to a direct increase in phasic dopamine release events. J Neurosci 28:8821–8831
Avelar AJ, Juliano SA, Garris PA (2013) Amphetamine augments vesicular dopamine release in the dorsal and ventral striatum through different mechanisms. J Neurochem 125:373–385
Bales JW, Wagner AK, Kline AE, Dixon CE (2009) Persistent cognitive dysfunction after traumatic brain injury: a dopamine hypothesis. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33:981–1003
Bales JW, Kline AE, Wagner AK, Dixon CE (2010) Targeting dopamine in acute traumatic brain injury. Open Drug Discov J 2:119–128
Barker-Haliski ML, Oldenburger K, Keefe KA (2012) Disruption of subcellular Arc/Arg 3.1 mRNA expression in striatal efferent neurons following partial monoamine loss induced by methamphetamine. J Neurochem 123:845–855
Bergstrom BP, Garris PA (2003) ‘Passive stabilization’ of striatal extracellular dopamine across the lesion spectrum encompassing the presymptomatic phase of Parkinson’s disease: a voltammetric study in the 6-OHDA-lesioned rat. J Neurochem 87:1224–1236
Bergstrom BP, Sanberg SG, Andersson M, Mithyantha J, Carroll FI, Garris PA (2011) Functional reorganization of the presynaptic dopaminergic terminal in Parkinsonism. Neuroscience 193:310–322
Boja JW, Mitchell WM, Patel A, Kopajtic TA, Carroll FI, Lewin AH, Abraham P, Kuhar MJ (1992) High-affinity binding of [125I]RTI-55 to dopamine and serotonin transporters in rat brain. Synapse 12:27–36
Borland LM, Michael AC (2004) Voltammetric study of the control of striatal dopamine release by glutamate. J Neurochem 91:220–229
Brown HD, McCutcheon JE, Cone JJ, Ragozzino ME, Roitman MF (2011) Primary food reward and reward-predictive stimuli evoke different patterns of phasic dopamine signaling throughout the striatum. Eur J Neurosci 34:1997–2006
Budygin EA, Phillips PE, Robinson DL, Kennedy AP, Gainetdinov RR, Wightman RM (2001) Effect of acute ethanol on striatal dopamine neurotransmission in ambulatory rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 297:27–34
Cass WA, Manning MW (1999) Recovery of presynaptic dopaminergic functioning in rats treated with neurotoxic doses of methamphetamine. J Neurosci 19:7653–7660
Chapman DE, Hanson GR, Kesner RP, Keefe KA (2001) Long-term changes in basal ganglia function after a neurotoxic regimen of methamphetamine. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 296:520–527
Cheer JF, Wassum KM, Heien ML, Phillips PE, Wightman RM (2004) Cannabinoids enhance subsecond dopamine release in the nucleus accumbens of awake rats. J Neurosci 24:4393–4400
Cheer JF, Heien ML, Garris PA, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2005) Simultaneous electrochemical and single-unit recordings in the nucleus accumbens reveal GABA-mediated responses: implications for intracranial self-stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:19150–19155
Cheer JF, Wassum KM, Sombers LA, Heien ML, Ariansen JL, Aragona BJ, Phillips PE, Wightman RM (2007) Phasic dopamine release evoked by abused substances requires cannabinoid receptor activation. J Neurosci 27:791–795
Cragg SJ, Hille CJ, Greenfield SA (2000) Dopamine release and uptake dynamics within nonhuman primate striatum in vitro. J Neurosci 20:8209–8217
Daberkow DP, Kesner RP, Keefe KA (2005) Relation between methamphetamine-induced monoamine depletions in the striatum and sequential motor learning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:198–204
Daberkow DP, Riedy MD, Kesner RP, Keefe KA (2007) Arc mRNA induction in striatal efferent neurons associated with response learning. Eur J Neurosci 26:228–241
Daberkow DP, Riedy MD, Kesner RP, Keefe KA (2008) Effect of methamphetamine neurotoxicity on learning-induced Arc mRNA expression in identified striatal efferent neurons. Neurotox Res 14:307–315
Daberkow DP, Brown HD, Bunner KD, Kraniotis SA, Doellman MA, Ragozzino ME, Garris PA, Roitman MF (2013) Amphetamine paradoxically augments exocytotic dopamine release and phasic dopamine signals. J Neurosci 33:452–463
Everitt BJ, Robbins TW (2005) Neural systems of reinforcement for drug addiction: from actions to habits to compulsion. Nat Neurosci 8:1481–1489
Fiorillo CD, Tobler PN, Schultz W (2003) Discrete coding of reward probability and uncertainty by dopamine neurons. Science 299:1898–1902
Frank MJ, Seeberger LC, O’reilly RC (2004) By carrot or by stick: cognitive reinforcement learning in Parkinsonism. Science 306:1940–1943
Garris PA, Wightman RM (1994) Different kinetics govern dopaminergic transmission in the amygdala, prefrontal cortex, and striatum: an in vivo voltammetric study. J Neurosci 14:442–450
Garris PA, Walker QD, Wightman RM (1997) Dopamine release and uptake rates both decrease in the partially denervated striatum in proportion to the loss of dopamine terminals. Brain Res 753:225–234
Grace AA, Floresco SB, Goto Y, Lodge DJ (2007) Regulation of firing of dopaminergic neurons and control of goal-directed behaviors. Trends Neurosci 30:220–227
Harden DG, Grace AA (1995) Activation of dopamine cell firing by repeated l-DOPA administration to dopamine-depleted rats: its potential role in mediating the therapeutic response to l-DOPA treatment. J Neurosci 15:6157–6166
Heien ML, Khan AS, Ariansen JL, Cheer JF, Phillips PE, Wassum KM, Wightman RM (2005) Real-time measurement of dopamine fluctuations after cocaine in the brain of behaving rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:10023–10028
Hollerman JR, Grace AA (1990) The effects of dopamine-depleting brain lesions on the electrophysiological activity of rat substantia nigra dopamine neurons. Brain Res 533:203–212
Howard CD, Keefe KA, Garris PA, Daberkow DP (2011) Methamphetamine neurotoxicity decreases phasic, but not tonic, dopaminergic signaling in the rat striatum. J Neurochem 118:668–676
Howard CD, Daberkow DP, Ramsson ES, Keefe KA, Garris PA (2013a) Methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity disrupts naturally occurring phasic dopamine signaling. Eur J Neurosci 38:2078–2088
Howard CD, Pastuzyn ED, Barker-Haliski ML, Garris PA, Keefe KA (2013b) Phasic-like stimulation of the medial forebrain bundle augments striatal gene expression despite methamphetamine-induced partial dopamine denervation. J Neurochem 125:555–565
Howe MW, Tierney PL, Sandberg SG, Phillips PE, Graybiel AM (2013) Prolonged dopamine signalling in striatum signals proximity and value of distant rewards. Nature 500:575–579
Hyland B, Reynolds J, Hay J, Perk C, Miller R (2002) Firing modes of midbrain dopamine cells in the freely moving rat. Neuroscience 114:475
Izquierdo A, Belcher AM, Scott L, Cazares VA, Chen J, O’Dell SJ, Malvaez M, Wu T, Marshall JF (2010) Reversal-specific learning impairments after a binge regimen of methamphetamine in rats: possible involvement of striatal dopamine. Neuropsychopharmacology 35:505–514
Kelland MD, Chiodo LA, Freeman AS (1990) Anesthetic influences on the basal activity and pharmacological responsiveness of nigrostriatal dopamine neurons. Synapse 6:207–209
Koulchitsky S, De BB, Quertemont E, Charlier C, Seutin V (2012) Differential effects of cocaine on dopamine neuron firing in awake and anesthetized rats. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:1559–1571
Lammel S, Hetzel A, Hackel O, Jones I, Liss B, Roeper J (2008) Unique properties of mesoprefrontal neurons within a dual mesocorticolimbic dopamine system. Neuron 57:760–773
Loewinger GC, Beckert MV, Tejeda HA, Cheer JF (2012) Methamphetamine-induced dopamine terminal deficits in the nucleus accumbens are exacerbated by reward-associated cues and attenuated by CB1 receptor antagonism. Neuropharmacology 62:2192–2201
Marshall JF, O’Dell SJ (2012) Methamphetamine influences on brain and behavior: unsafe at any speed? Trends Neurosci 35:536–545
Michael D, Travis ER, Wightman RM (1998) Color images for fast-scan CV measurements in biological systems. Anal Chem 70:586A–592A
Morita K, Morishima M, Sakai K, Kawaguchi Y (2012) Reinforcement learning: computing the temporal difference of values via distinct corticostriatal pathways. Trends Neurosci 35:457–467
Nordahl TE, Salo R, Leamon M (2003) Neuropsychological effects of chronic methamphetamine use on neurotransmitters and cognition: a review. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 15:317–325
O’Dell SJ, Feinberg LM, Marshall JF (2011) A neurotoxic regimen of methamphetamine impairs novelty recognition as measured by a social odor-based task. Behav Brain Res 216:396–401
Owesson-White CA, Roitman MF, Sombers LA, Belle AM, Keithley RB, Peele JL, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2012) Sources contributing to the average extracellular concentration of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens. J Neurochem 121:252–262
Park J, Aragona BJ, Kile BM, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2010) In vivo voltammetric monitoring of catecholamine release in subterritories of the nucleus accumbens shell. Neuroscience 169:132–142
Park J, Takmakov P, Wightman RM (2011) In vivo comparison of norepinephrine and dopamine release in rat brain by simultaneous measurements with fast-scan cyclic voltammetry. J Neurochem 119:932–944
Pastuzyn ED, Chapman DE, Wilcox KS, Keefe KA (2012) Altered learning and Arc-regulated consolidation of learning in striatum by methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:885–895
Paxinos G, Watson C (1986) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, New York
Phillips PE, Stuber GD, Heien ML, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2003) Subsecond dopamine release promotes cocaine seeking. Nature 422:614–618
Robinson DL, Wightman RM (2004) Nomifensine amplifies subsecond dopamine signals in the ventral striatum of freely-moving rats. J Neurochem 90:894–903
Robinson TE, Mocsary Z, Camp DM, Whishaw IQ (1994) Time course of recovery of extracellular dopamine following partial damage to the nigrostriatal dopamine system. J Neurosci 14:2687–2696
Robinson DL, Phillips PE, Budygin EA, Trafton BJ, Garris PA, Wightman RM (2001) Sub-second changes in accumbal dopamine during sexual behavior in male rats. NeuroReport 12:2549–2552
Robinson DL, Heien ML, Wightman RM (2002) Frequency of dopamine concentration transients increases in dorsal and ventral striatum of male rats during introduction of conspecifics. J Neurosci 22:10477–10486
Robinson DL, Howard EC, McConnell S, Gonzales RA, Wightman RM (2009) Disparity between tonic and phasic ethanol-induced dopamine increases in the nucleus accumbens of rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33:1187–1196
Sandberg SG, Phillips PEM (2009) Phasic dopaminergic signaling: implications for Parkinson’s disease. In: Tseng KY (ed) Cortico-subcortical dynamics in Parkinson’s disease. Humana Press, New York, pp 37–53
Schonberg T, O’Doherty JP, Joel D, Inzelberg R, Segev Y, Daw ND (2010) Selective impairment of prediction error signaling in human dorsolateral but not ventral striatum in Parkinson’s disease patients: evidence from a model-based fMRI study. Neuroimage 49:772–781
Schultz W (1998) Predictive reward signal of dopamine neurons. J Neurophysiol 80:1–27
Schultz W (2007) Behavioral dopamine signals. Trends Neurosci 30:203–210
Scott JC, Woods SP, Matt GE, Meyer RA, Heaton RK, Atkinson JH, Grant I (2007) Neurocognitive effects of methamphetamine: a critical review and meta-analysis. Neuropsychol Rev 17:275–297
Shi WX, Pun CL, Zhang XX, Jones MD, Bunney BS (2000) Dual effects of d-amphetamine on dopamine neurons mediated by dopamine and nondopamine receptors. J Neurosci 20:3504–3511
Shi WX, Pun CL, Zhou Y (2004) Psychostimulants induce low-frequency oscillations in the firing activity of dopamine neurons. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:2160–2167
Simon SL, Domier C, Carnell J, Brethen P, Rawson R, Ling W (2000) Cognitive impairment in individuals currently using methamphetamine. Am J Addict 9:222–231
Sombers LA, Beyene M, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2009) Synaptic overflow of dopamine in the nucleus accumbens arises from neuronal activity in the ventral tegmental area. J Neurosci 29:1735–1742
Son JH, Latimer C, Keefe KA (2011) Impaired formation of stimulus-response, but not action-outcome, associations in rats with methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:2441–2451
Son JH, Kuhn J, Keefe KA (2013) Perseverative behavior in rats with methamphetamine-induced neurotoxicity. Neuropharmacology 67:95–103
Stuber GD, Roitman MF, Phillips PE, Carelli RM, Wightman RM (2005a) Rapid dopamine signaling in the nucleus accumbens during contingent and noncontingent cocaine administration. Neuropsychopharmacology 30:853–863
Stuber GD, Wightman RM, Carelli RM (2005b) Extinction of cocaine self-administration reveals functionally and temporally distinct dopaminergic signals in the nucleus accumbens. Neuron 46:661–669
Venton BJ, Wightman RM (2007) Pharmacologically induced, subsecond dopamine transients in the caudate-putamen of the anesthetized rat. Synapse 61:37–39
Venton BJ, Zhang H, Garris PA, Phillips PE, Sulzer D, Wightman RM (2003) Real-time decoding of dopamine concentration changes in the caudate-putamen during tonic and phasic firing. J Neurochem 87:1284–1295
Volkow ND, Chang L, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Leonido-Yee M, Franceschi D, Sedler MJ, Gatley SJ, Hitzemann R, Ding YS, Logan J, Wong C, Miller EN (2001) Association of dopamine transporter reduction with psychomotor impairment in methamphetamine abusers. Am J Psychiatry 158:377–382
Wagner AK, Sokoloski JE, Ren D, Chen X, Khan AS, Zafonte RD, Michael AC, Dixon CE (2005) Controlled cortical impact injury affects dopaminergic transmission in the rat striatum. J Neurochem 95:457–465
Wagner AK, Drewencki LL, Chen X, Santos FR, Khan AS, Harun R, Torres GE, Michael AC, Dixon CE (2009a) Chronic methylphenidate treatment enhances striatal dopamine neurotransmission after experimental traumatic brain injury. J Neurochem 108:986–997
Wagner AK, Sokoloski JE, Chen X, Harun R, Clossin DP, Khan AS, Andes-Koback M, Michael AC, Dixon CE (2009b) Controlled cortical impact injury influences methylphenidate-induced changes in striatal dopamine neurotransmission. J Neurochem 110:801–810
Wassum KM, Ostlund SB, Loewinger GC, Maidment NT (2013) Phasic mesolimbic dopamine release tracks reward seeking during expression of pavlovian-to-instrumental transfer. Biol Psychiatry 73:747–755
Wiecki TV, Frank MJ (2010) Neurocomputational models of motor and cognitive deficits in Parkinson’s disease. Prog Brain Res 183:275–297
Wightman RM, Amatore C, Engstrom RC, Hale PD, Kristensen EW, Kuhr WG, May LJ (1988) Real-time characterization of dopamine overflow and uptake in the rat striatum. Neuroscience 25:513–523
Wightman RM, Heien ML, Wassum KM, Sombers LA, Aragona BJ, Khan AS, Ariansen JL, Cheer JF, Phillips PE, Carelli RM (2007) Dopamine release is heterogeneous within microenvironments of the rat nucleus accumbens. Eur J Neurosci 26:2046–2054
Willuhn I, Burgeno LM, Everitt BJ, Phillips PE (2012) Hierarchical recruitment of phasic dopamine signaling in the striatum during the progression of cocaine use. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 109(50):20703–20708
Wu Q, Reith ME, Kuhar MJ, Carroll FI, Garris PA (2001a) Preferential increases in nucleus accumbens dopamine after systemic cocaine administration are caused by unique characteristics of dopamine neurotransmission. J Neurosci 21:6338–6347
Wu Q, Reith ME, Wightman RM, Kawagoe KT, Garris PA (2001b) Determination of release and uptake parameters from electrically evoked dopamine dynamics measured by real-time voltammetry. J Neurosci Methods 112:119–133
Wu Q, Reith ME, Walker QD, Kuhn CM, Carroll FI, Garris PA (2002) Concurrent autoreceptor-mediated control of dopamine release and uptake during neurotransmission: an in vivo voltammetric study. J Neurosci 22:6272–6281
Yin HH, Knowlton BJ (2006) The role of the basal ganglia in habit formation. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:464–476
Zhang L, Doyon WM, Clark JJ, Phillips PE, Dani JA (2009a) Controls of tonic and phasic dopamine transmission in the dorsal and ventral striatum. Mol Pharmacol 76:396–404
Zhang T, Zhang L, Liang Y, Siapas AG, Zhou FM, Dani JA (2009b) Dopamine signaling differences in the nucleus accumbens and dorsal striatum exploited by nicotine. J Neurosci 29:4035–4043
Acknowledgments
This research was funded by National Institutes of Health grant DA 024036 (KAK and PAG).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Robinson, J.D., Howard, C.D., Pastuzyn, E.D. et al. Methamphetamine-Induced Neurotoxicity Disrupts Pharmacologically Evoked Dopamine Transients in the Dorsomedial and Dorsolateral Striatum. Neurotox Res 26, 152–167 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9459-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-014-9459-y