Abstract
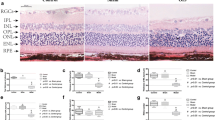
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activation is considered as a major regulator of cell death in various pathophysiological conditions, however, no direct information is available about its role in chronic hypoperfusion-induced neuronal death. Here, we provide evidence for the protective effect of PARP inhibition on degenerative retinal damage induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion (BCCAO), an adequate chronic hypoperfusion murine model. We found that BCCAO in adult male Wistar rats led to severe degeneration of all retinal layers that was attenuated by a carboxaminobenzimidazol-derivative PARP inhibitor (HO3089) administered unilaterally into the vitreous body immediately following carotid occlusion and then 4 times in a 2-week-period. Normal morphological structure of the retina was preserved and the thickness of the retinal layers was increased in HO3089-treated eyes compared to the BCCAO eyes. For Western blot studies, HO3089 was administered immediately after BCCAO and retinas were removed 4 h later. According to Western blot analysis utilizing phosphorylation-specific primary antibodies, besides activating poly-ADP-ribose (PAR) synthesis, BCCAO induced phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). HO3089 inhibited PAR synthesis, and decreased the phosphorylation of these proapoptotic MAPKs. In addition, HO3089 treatment induced phosphorylation, that is activation, of the protective Akt/glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3beta and extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK1/2) signaling pathways. These data indicate that PARP activation has a major role in mediating chronic hypoperfusion-induced neuronal death, and inhibition of the enzyme prevents the pathological changes both in the morphology and the kinase signaling cascades involved. These results identify PARP inhibition as a possible molecular target in the clinical management of chronic hypoperfusion-induced neurodegenerative diseases including ocular ischemic syndrome.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Quesada R, Muñoz-Gamez JA, Martín-Oliva D, Peralta-Leal A, Quiles-Perez R, Rodríguez-Vargas JM, Ruiz de Almodovar M, Conde C, Ruiz-Extremera A, Oliver FJ (2007) Modulation of transcription by PARP-1: consequences in carcinogenesis and inflammation. Curr Med Chem 14:1179–1187
Akiyama H, Nakazawa T, Shimura M, Tomita H, Tamai M (2002) Presence of mitogen-activated protein kinase in retinal Muller cells and its retinoprotective effect ischemia/reperfusion injury. NeuroReport 13:2103–2107
Alexy T, Toth A, Marton Z, Horvath B, Koltai K, Feher G, Kesmarky G, Kalai T, Hideg K, Sumegi B, Toth K (2004) Inhibition of ADP-evoked platelet aggregation by selected poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 43:423–431
Aliev G, Smith MA, Obrenovich ME, de la Torre JC, Perry G (2003) Role of vascular hypoperfusion-induced oxidative stress and mitochondria failure in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer disease. Neurotox Res 5:491–504
Atlasz T, Babai N, Reglodi D, Kiss P, Tamas A, Bari F, Domoki F, Gabriel R (2007a) Diazoxide is protective in the rat retina against ischemic injury induced by bilateral carotid occlusion and glutamate-induced degeneration. Neurotox Res 12:105–111
Atlasz T, Babai N, Kiss P, Reglodi D, Tamas A, Szabadfi K, Toth G, Hegyi O, Lubics A, Gabriel R (2007b) Pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide is protective in bilateral carotid occlusion-induced retinal lesion in rats. Gen Comp Endocrinol 153:108–114
Chavarría T, Valenciano AI, Mayordomo R, Egea J, Comella JX, Hallböök F, de Pablo F, de la Rosa EJ (2007) Differential, age-dependent MEK-ERK and PI3K-Akt activation by insulin acting as a survival factor during embryonic retinal development. Dev Neurobiol 67:1777–1788
Chiang SK, Lam TT (2000) Post-treatment at 12 or 18 hours with 3-aminobenzamide ameliorates retinal ischemia-reperfusion damage. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 41:3210–3214
Cohausz O, Althaus FR (2008) Role of PARP-1 and PARP-2 in the expression of apoptosis-regulating genes in HeLa cells. Cell Biol Toxicol (in press)
Cozzi A, Cipriani G, Fossati S, Faraco G, Formentini L, Min W, Cortes U, Wang ZQ, Moroni F, Chiarugi A (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose) accumulation and enhancement of postischemic brain damage in 110-kDa poly(ADP-ribose) glycohydrolase null mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 26:684–695
Davidson CM, Pappas BA, Stevens WD, Fortin T, Bennett SA (2000) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion: loss of pupillary reflex, visual impairment and retina neurodegeneration. Brain Res 859:96–103
de Keyser J, Steen C, Mostert JP, Koch MW (2008) Hypoperfusion of the cerebral white matter in multiple sclerosis: possible mechanisms and pathophysiological significance. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 28:1645–1651
de la Torre JC, Stefano GB (2000) Evidence that Alzheimer’s disease is a microvascular disorder: the role of constitutive nitric oxide. Brain Res Rev 34:119–136
Dugan JD, Green WR Jr (1991) Ophthalmologic manifestations of carotid occlusive disease. Eye 5:226–238
Ettaiche M, Fillacier K, Widmann C, Heurteaux C, Lazdunski M (1999) Riluzole improves functional recovery after ischemia in the rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 40:729–736
Farkas E, Luiten PG, Bari F (2007) Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev 54:162–180
Ferrer I, Planas AM (2003) Signaling of cell death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemia: life and death struggle in the penumbra. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62:329–339
Fontaine V, Mohand-Said S, Hanoteau N, Fuchs C, Pfizenmaier K, Eisel U (2002) Neurodegenerative and neuroprotective effects of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) in retinal ischemia: opposite roles of TNF receptor 1 and TNF receptor 2. J Neurosci 22:RC216
Goebel DJ, Winkler BS (2006) Blockade of PARP activity attenuates poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation but offers only partial neuroprotection against NMDA-induced cell death in the rat retina. J Neurochem 98:1732–1745
Halmosi R, Berente Z, Osz E, Toth K, Literati-Nagy P, Sumegi B (2001) Effect of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors on the ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative cell damage and mitochondrial metabolism in Langendorff heart perfusion system. Mol Pharmacol 59:1497–1505
He X-L, Wang Y-H, Gao M, Li X-X, Zhang T-T, Du G-H (2009) Baicalein protects rat brain mitochondria against chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-induced oxidative damage. Brain Res 1249:212–221
Hong SJ, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2004) Nuclear and mitochondrial conversations in cell death: PARP-1 and AIF signaling. Trends Pharmacol Sci 25:259–264
Ikeda Y, Hokamura K, Kawai T, Ishiyama J, Ishikawa K, Anraku T, Uno T, Umemura K (2005) Neuroprotective effects of KCL-440, a new poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Brain Res 1060:73–80
Kalesnykas G, Tuulos T, Uusitalo H, Jolkkonen J (2008) Neurodegeneration and cellular stress in the retina and optic nerve in rat cerebral ischemia and hypoperfusion models. Neuroscience 155:937–947
Kasparova S, Brezova V, Valko M, Horecký J, Mlynarik V, Liptaj T, Vancova O, Ulicna O, Dobrota D (2005) Study of the oxidative stress in a rat model of chronic brain hypoperfusion. Neurochem Int 46:601–611
Kauppinen TM, Swanson RA (2007) The role of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 in CNS disease. Neuroscience 145:1267–1272
Kilic O, Kilic E, Soliz J, Bassetti CI, Gassmann M, Hermann DM (2005) Erythropoetin protects from axotomy-induced degeneration of retinal ganglion cells by activating ERK-1/2. FASEB J 19:249–251
Kim JS, Yun I, Choi YB, Lee KS, Kim YI (2008) Ramipril protects from free radical induced white matter damage in chronic hypoperfusion in the rat. J Clin Neurosci 15:174–178
Kovacs K, Toth A, Deres P, Kalai T, Hideg K, Gallyas F Jr, Sumegi B (2006) Critical role of PI3-kinase/Akt activation in the PARP inhibitor induced heart function recovery during ischemia-reperfusion. Biochem Pharmacol 71:441–452
Krishnakumar R, Gamble MJ, Frizzell KM, Berrocal JG, Kininis M, Kraus WL (2008) Reciprocal binding of PARP-1 and histone H1 at promoters specifies transcriptional outcomes. Science 319:819–821
Lai RK, Chun T, Hasson D, Lee S, Mehrbod F, Wheeler L (2002) Alpha-2 adrenoceptor agonist protects retinal function after acute retinal ischemic injury in the rat. Vis Neurosci 19:175–185
Lam TT (1997) The effect of 3-aminobenzamide, an inhibitor of poly-ADP-ribose polymerase, on ischemia/reperfusion damage in rat retina. Res Commun Mol Pathol Pharmacol 95:241–252
Lavinsky D, Arterni NS, Achaval M, Netto CA (2006) Chronic bilateral common carotid artery occlusion: a model for ocular ischemic syndrome in the rat. Graefe`s Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 244:199–204
Li GY, Osborne NN (2008) Oxidative-induced apoptosis to an immortalized ganglion cell line is caspase independent but involves the activation of poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase and apoptosis-inducing factor. Brain Res 1188:35–43
Luo JM, Cen LP, Zhang XM, Chiang SW, Huang Y, Lin D, Fan YM, van Rooijen N, Lam DS, Pang CP, Cui Q (2007) PI3 K/akt, JAK/STAT and MEK/ERK pathway inhibition protects retinal ganglion cells via different mechanisms after optic nerve injury. Eur J NeuroSci 26:828–842
Meli E, Pangallo M, Baronti R, Chiarugi A, Cozzi A, Pellegrini-Giampietro DE, Moroni F (2003) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as a key player in excitotoxicity and post-ischemic brain damage. Toxicol Lett 139:153–162
Merienne K, Friedman J, Akimoto M, Abou-Sleymane G, Weber C, Swaroop A, Trottier Y (2007) Preventing polyglutamine-induced activation of c-Jun delays neuronal dysfunction in a mouse model of SCA7 retinopathy. Neurobiol Dis 25:571–581
Munemasa Y, Ohtani-kaneko R, Kitaoka Y, Kuribayashi K, Isenoumi K, Kogo J, Yamashita K, Kumai T, Kobayashi S, Hirata K, Ueno S (2005) Contribution of mitogen-activated protein kinases to NMDA-induced neurotoxicity in the rat retina. Brain Res 1044:227–240
Nakazawa T, Shimura M, Tomita H, Akivama H, Yoshioka Y, Kudou H, Tamai M (2003) Intrinsic activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and its neuroprotective effect against retinal injury. Curr Eye Res 26:55–63
Oliff HS, Coyle P, Weber E (1997) Rat strain and vendor differences in collateral anastomoses. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:571–576
Osborne NN, Casson RJ, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Graham M, Melena J (2004) Retinal ischemia: mechanisms of damage and potential therapeutic strategies. Prog Retin Eye Res 23:91–147
Pacher P, Szabo C (2008) Role of the peroxynitrite-poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase pathway in human disease. Am J Pathol 173:2–13
Paquet-Durand F, Silva J, Talukdar T, Johnson LE, Azadi S, van Veen T, Ueffing M, Hauck SM, Ekstrom PA (2007) Excessive activation of poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase contributes to inherited photoreceptor degeneration in the retinal degeneration 1 mouse. Neurobiol Dis 27:10311–10319
Park CH, Kim YS, Kim YH, Choi MY, Yoo JM, Kang SS, Choi WS, Cho GJ (2008) Calcineurin mediates AKT dephosphorylation in the ischemic rat retina. Brain Res 1234:148–157
Patil K, Sharma SC (2004) Broad spectrum caspase inhibitor rescues retinal ganglion cells after ischemia. NeuroReport 15:981–984
Racz B, Gallyas F Jr, Kiss P, Tamas A, Lubics A, Lengvari I, Roth E, Toth G, Hegyi O, Verzar Zs, Fabricsek Cs, Reglodi D (2007) Effects of pituitary adenylate cyclase activating polypeptide (PACAP) on the PKA-Bad-14–3-3 signaling pathway in glutamate-induced retinal injury in neonatal rats. Neurotox Res 12:95–104
Roduit R, Schorderet DF (2008) MAP kinase pathways in UV-induced apoptosis of retinal pigment epithelium ARPE19 cells. Apoptosis 13:343–353
Roth S, Shaikh A, Hennelly MM, Li Q, Bindokas V, Graham CE (2003) Mitogen activated protein kinases and retinal ischemia. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 44:5385–5395
Russo R, Cavaliere F, Berliocchi L, Nucci C, Gliozzi M, Mazzei C, Tassorelli C, Corasaniti MT, Rotiroti D, Bagetta G, Morrone LA (2008) Modulation of pro-survival and death associated pathways under retinal ischemia/reperfusion: effects of NMDA receptor blockade. J Neurochem (in press)
Shojaee N, Patton WF, Hechtmann HB, Shepro D (1999) Myosin translocation in retinal pericytes during free radical induced apoptosis. J Cell Biochem 75:118–129
Spertus AD, Slakter JS, Weissman SS, Henkind P (1984) Experimental carotid occlusion: fundoscopic and fluorescein angiographic findings. Br J Ophthalmol 68:47–57
Tapodi A, Debreceni B, Hanto K, Bognar Z, Wittmann I, Gallyas F Jr, Varbiro G, Sumegi B (2005) Pivotal role of Akt activation in mitochondrial protection and cell survival by poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase-1 inhibition in oxidative stress. J Biol Chem 280:35767–35775
Uehara N, Miki K, Tsukamoto R, Matsuoka Y, Tsubura A (2006) Nicotinamide blocks N-methyl-N-nitrosourea-induced photoreceptor cell apoptosis in rats through poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase activity and Jun N-terminal kinase/activator protein-1 pathway inhibition. Exp Eye Res 82:488–495
Veres B, Gallyas F Jr, Varbiro G, Berente Z, Osz E, Szekeres G, Szabo C, Sumegi B (2003) Decrease of the inflammatory response and induction of the Akt/protein kinase B pathway by poly-(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 inhibitor in endotoxin-induced septic shock. Biochem Pharmacol 65:1373–1382
Vidal-Sanz M, Lafuente M, Sobrado-Calvo P, Selles-Navarro I, Rodriguez E, Mayor-Torroglosa S, Villegas-Perez MP (2000) Death and neuroprotection of retinal ganglion cells after different types of injury. Neurotox Res 2:215–227
Virag L, Szabo C (2002) The therapeutic potential of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors. Pharmacol Rev 54:375–429
Weise J, Isenmann S, Bahr M (2001) Increased expression and activation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) contribute to retinal ganglion cell death following rat optic nerve transection. Cell Death Differ 8:801–807
Weishaupt JH, Rohde G, Polking E, Siren AL, Ehrenreich H, Bahr M (2004) Effects of erythropoietin axotomy-induced apoptosis in rat retinal ganglion cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 45:1514–1522
Xiao CY, Chen M, Zsengeller Z, Szabo C (2004) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase contributes to the development of myocardial infarction in diabetic rats and regulates the nuclear translocation of apoptosis-inducing factor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 310:498–504
Xu Y, Huang S, Liu ZG, Han J (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 signaling to mitochondria in necrotic cell death requires RIP1/TRAF2-mediated JNK1 activation. J Biol Chem 281:8788–8795
Yamamoto H, Schmidt-Kastner R, Hamasaki DI, Yamamoto H, Parel JM (2006) Complex neurodegeneration in retina following moderate ischemia induced by bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in Wistar rats. Exp Eye Res 82:767–779
Yu SW, Wang H, Poitras MF, Coombs C, Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Poirier GG, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2002) Mediation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor. Science 297:259–263
Zhang C, Rosenbaum DM, Shaikh AR, Li Q, Rosenbaum PS, Pelham DJ, Roth S (2002) Ischemic preconditioning attenuates apoptotic cell death in the rat retina. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 43:3059–3066
Zlokovic BV (2005) Neurovascular mechanisms of Alzheimer’s neurodegeneration. Trends Neurosci 28:202–208
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by OTKA K72592, T061766, 78480; F67830, ETT 439/2006, Bolyai Scholarship, and Gedeon Richter Foundation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mester, L., Szabo, A., Atlasz, T. et al. Protection Against Chronic Hypoperfusion-Induced Retinal Neurodegeneration by PARP Inhibition via Activation of PI-3-kinase Akt Pathway and Suppression of JNK and p38 MAP Kinases. Neurotox Res 16, 68–76 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9049-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-009-9049-6