Abstract
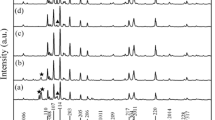
In this paper, single-phase and fine-grain hexagonal barium ferrite powder was prepared based on the optimal calcination condition. The influence of calcination conditions including temperature and holding time on microstructure and magnetic properties of powder were studied in detail. Firstly, θ–2θ scan X-ray diffraction (XRD) results reveal that it is hard to obtain single phase of powder when the calcination temperature is lower than 850 °C. In addition, the calcination time for single phase of barium ferrite powder was reduced with the increase in calcination temperature. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) images and magnetic hysteresis loops show that the condition of low temperature and long holding time is beneficial for obtaining homogeneous size of grain and excellent magnetic properties. Consequently, hexagonal barium ferrite powder with uniform grain size of ~ 180 nm, high purity and excellent magnetic properties is obtained at optimal calcination condition of 850 °C–10.0 h.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghasemi A, Hossienpour A, Morisako A, Saatchi A, Salehi M. Electromagnetic properties and microwave absorbing characteristics of doped barium hexaferrite. J Magn Magn Mater. 2006;302(2):429.
Zheng H, Han MG, Zheng L, Deng JX, Zheng P, Wu Q, Deng LJ, Qin HB. Magnetic properties of hexagonal barium ferrite films on Pt/MgO(111) substrates annealed at different temperatures. J Magn Magn Mater. 2016;413:25.
Nikmanesh H, Moradi M, Bordbar GH, Alam RS. Effect of multi dopant barium hexaferrite nanoparticles on the structural, magnetic, and X-Ku bands microwave absorption properties. J Alloy Compd. 2017;708:99.
Liu GF, Fan RH, Zhang ZD, Li J, Chen M, Li QQ, Lu L, Xie PT. Magnetic properties and special morphology of barium ferrite via electrospinning. Rare Met. 2017;36(2):113.
Che S, Wang J, Chen QW. Soft magnetic nanoparticles of BaFe12O19 fabricated under mild conditions. J Phys Condens Matter. 2003;15(22):L335.
Gubin SP, Koksharov YA, Khomutov GB, Yurkov GY. Magnetic nanoparticles preparation, structure and properties. Russ Chem Rev. 2006;37(1):489.
Zheng H, Han M, Wu Y, Zheng L, Zhao WJ, Deng LJ, Qin HB. Magnetic properties of hexagonal barium ferrite films on Pt(111)/Al2O3(0001) substrate based on optimized thickness of Pt. IEEE Trans Nanotechnol. 2018;17(1):56.
Dimri MC, Kashyap SC, Dube DC. Complex permittivity and permeability of Co2U(Ba4Co2Fe36O60) hexaferrite bulk and composite thick films at radio and microwave frequencies. IEEE Trans Magn. 2006;42(11):3635.
Wang JP, Liu Y, Zhang ML, Qiao YJ, Xia T. Comparison of the sol-gel method with the coprecipitation technique for preparation of hexagonal barium ferrite. Chem Res Chin Univ. 2008;24(5):525.
Tian G, Chen X. Structure and multiferroic properties of barium hexaferrite ceramics. J Magn Magn Mater. 2013;327(3):87.
Lisjak D, Drofenik M. Synthesis and characterization of A-Sn-substituted (A = Zn, Ni, Co) BaM–hexaferrite powders and ceramics. J Eur Ceram Soc. 2004;24(6):1841.
Harris VG. Modern microwave ferrites. IEEE Trans Magn. 2012;48(3):1075.
Radwan M, Rashad MM, Hessien MM. Synthesis and characterization of barium hexaferrite nanoparticles. J Mater Process Technol. 2007;181(1):106.
Hao GD, Hao XL, Zhu ZF. Phase composition, morphology and element contents of micro-arc oxidation ceramic coatings on Ti–6Al–4V alloy under different calcination conditions. Rare Met. 2016;35(11):836.
Ebrahimi F, Yazdi SS. Ferromagnetic resonance investigation of hexaferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. J Supercond Novel Magn. 2016;30(4):973.
Liu CY, Zhang YJ, Tang Y, Wang ZR, Ma N, Du PY. The tunable magnetic and microwave absorption properties of the Nb5+–Ni2+ co-doped M-type barium ferrite. J Mater Chem C. 2017;5(14):3461.
Pubby K, Narang SB, Chawla SK, Mudsainiyan RK. Effect of temperature on dielectric and electrical properties of Co–Zr doped barium hexaferrites prepared by sol–gel method. J Mater Sci Mater Electron. 2016;27(11):11220.
Roohani E, Arabi H, Sarhaddi R, Sudkhah S. M-type strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel auto-combustion method: the role of Co substitution in structural, morphological, and magnetic properties. J Supercond Novel Magn. 2017;30(6):1599.
George M, John AM, Nair SS, Joy PA, Anantharaman MR. Finite size effects on the structural and magnetic properties of sol–gel synthesized NiFe2O4 powders. J Magn Magn Mater. 2006;302(1):190.
Zheng L, Zheng H, Deng JX, Ying ZH, Wu J, Zhou JJ, Qin HB. Synthesis of single-phase nanocrystalline YIG by co-precipitation: the influence of pH value of precursor solution and calcinating. Adv Mater Res. 2011;311–313:1294.
Zhang JR, Gao L. Synthesis and characterization of nanocrystalline tin oxide by sol–gel method. J Solid State Chem. 2004;177(4):1425.
Zhao WY, Wei P, Wu XY, Wang W, Zhang QJ. Lattice vibration characterization and magnetic properties of M-type barium hexaferrite with excessive iron. J Appl Phys. 2008;103(6):1188.
Wu CS, Chen CH. A visible-light response vanadium-dopedtitania nanocatalyst by sol–gel method. J Photochem Photobiol A. 2004;163(3):509.
Huang JG, Zhuang HR, Li WL. Synthesis and characterization of nano crystalline BaFe12O19 powders by low temperature combustion. Mater Res Bull. 2003;38(1):149.
Kim SG, Wang WN, Iwaki T, Yabuki A, Okuyama K. Low-temperature crystallization of barium ferrite nanoparticles by a sodium citrate-aided synthetic process. J Phys Chem C. 2007;111(28):1.
Mali A, Ataie A. Influence of Fe/Ba molar ratio on the characteristics of Ba-hexaferrite particles prepared by sol–gel combustion method. J Alloy Compd. 2005;399(1–2):245.
Martirosyan KS, Galstyan E, Hossain SM, Wang YJ, Litvinov D. Barium hexaferrite nanoparticles: synthesis and magnetic properties. Mater Sci Eng B. 2011;176(1):8.
Mali A, Ataie A. Structural characterization of nano-crystalline BaFe12O19 powders synthesized by sol–gel combustion route. Scripta Mater. 2005;53(9):1065.
Chen IW, Wang XH. Sintering dense nanocrystalline ceramics without final-stage grain growth. Nature. 2000;404(6774):168.
Li XX, Zhou JJ, Deng JX, Zheng H, Zheng P, Qin HB. Synthesis of dense, fine-grained YIG ceramics by two-step sintering. J Electron Mater. 2016;45(10):1.
Goya GF, Berquo TS, Fonseca FC, Morales MP. Static and dynamic magnetic properties of spherical magnetite nanoparticles. J Appl Phys. 2003;94(5):3520.
Ji DH, Hou X, Tang GD, Li ZZ, Hou DL, Zhu MG. Oxygen content and magnetic properties of composites La0.75Sr0.25MnO3–δ calcined at different temperatures. Rare Met. 2014;33(4):452.
Alam RS, Moradi M, Rostami M, Nikmanesh H, Moayedi R, Bai Y. Structural, magnetic and microwave absorption properties of doped Ba-hexaferrite nanoparticles synthesized by co-precipitation method. J Magn Magn Mater. 2015;381(381):1.
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province of China (Nos. LQ17A040002 and LY17F010021), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51702075), the Key R&D Program of Zhejiang Province of China (No. 2017C01004) and the Nonprofit technology Research Program of Zhejiang Province (No. 2017C31019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, SY., Zheng, H., Zheng, P. et al. Microstructure, magnetic properties of hexagonal barium ferrite powder based on calcination temperature and holding time. Rare Met. 40, 981–986 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1153-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12598-018-1153-4