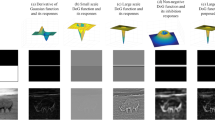
Abstract
Background
The predictive coding/biased competition (PC/BC) model of V1 has previously been applied to locate boundaries defined by local discontinuities in intensity within an image.
Objective
Here PC/BC is extended to perform contour detection for colour images. Methods The proposed extensions are inspired by neurophysiological data from single neurons in macaque primary visual cortex (V1).
Results
The behaviour of this extended model is consistent with the neurophysiological experimental results. Furthermore, when compared to methods used for contour detection in computer vision, the colour PC/BC model of V1 slightly outperforms some recently proposed algorithms which use more cues and/or require a complicated training procedure.
Conclusions
The colour PC/BC model of V1 can successfully simulate the responses properties of orientation-selective double-opponent neuron in macaque V1 and has practical applications for contour detection in natural images.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Walther DB, Chai B, Caddigan E, Beck DM, Fei-Fei L. Simple line drawings suffice for functional MRI decoding of natural scene categories. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2011;108(23):9661–6.
Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2011;33:898–916.
Lowe DG. Object recognition from local scale-invariant features. In: The proceedings of the seventh IEEE international conference on computer vision, 1999, vol 2, pp 1150–1157.
Comport A, Marchand É, Chaumette F. Robust model-based tracking for robot vision. In: The proceedings of IEEE/RSJ international conference on intelleligence robots and systems, 2004, vol 1, pp 692–697.
Chalana V, Linker DT, Haynor DR, Kim Y. A multiple active contour model for cardiac boundary detection on echocardiographic sequences. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 1996;15:290–8.
Canny J. A computational approach to edge detection. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 1986;8:679–98.
Perez F, Koch C. Toward color image segmentation in analog VLSI: algorithm and hardware. Int J Comput Vis. 1994;12:17–42.
Martin DR, Fowlkes CC, Malik J. Learning to detect natural image boundaries using local brightness, color and texture cues. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2004;26(5):530–49.
Mairal J, Leordeanu M, Bach F, Hebert M, Ponce J. Discriminative sparse image models for class-specific edge detection and image interpretation. Computer vision-ECCV2008, vol 5304, pp 43–56. Berlin: Springer; 2008
Mairal J, Elad M, Sapiro G. Sparse representation for color image restoration. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2008;17:53–69.
Spratling MW. Predictive coding as a model of response properties in cortical area V1. J Neurosci. 2010;30:3531–43.
Spratling MW. Image segmentation using a sparse coding model of cortical area V1. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2013;22(4):1631–43.
Johnson EN, Hawken MJ, Shapley R. The spatial transformation of color in the primary visual cortex of the macaque monkey. Nat Neurosci. 2001;4:409–16.
Johnson EN, Hawken MJ, Shapley R. The orientation selectivity of colour-responsive neurons in macaque V1. J Neurosci. 2008;28:8096–106.
Yang KF, Gao S, Guo C, Li C, Li Y. Boundary detection using double-opponency and spatial sparseness constraint. IEEE Trans Image Process. 2015;24:2565–78.
Martin D, Fowlkes C, Tal D, Malik J. A database of human segmented natural images and its application to evaluating segmentation algorithms and measuring ecological statistics. Proc Int Conf Comput Vis. 2001;2:416–23.
Burghouts GJ, Geusebroek JM. Performance evaluation of local colour invariants. Comput Vis Image Underst. 2009;113:48–62.
Van De Sande KEA, Gevers T, Snoek CGM. Evaluating color descriptors for object and scene recognition. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2010;32:1582–96.
Linde O, Lindeberg T. Composed complex-cue histograms: an investigation of the information content in receptive field based image descriptors for object recognition. Comput Vis Image Underst. 2012;116:538–60.
Arbelaez P, Maire M, Fowlkes C, Malik J. Contour detection and hierarchical image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2011;33:898–916.
Shapley R, Hawken MJ. Colour in the cortex: single-and double-opponent cells. Vis Res. 2011;51:701–17.
Beaudot WH, Mullen KT. Orientation selectivity in luminance and color vision assessed using 2-d band-pass filtered spatial noise. Vis Res. 2005;45:687–96.
Gegenfurtner KR. Cortical mechanisms of color vision. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:563–72.
Leventhal AG, Thompson KG, Liu D, Zhou Y, Ault SJ. Concomitant sensitivity to orientation, direction, and color of cells in layers 2, 3, and 4 of monkey striate cortex. J Neurosci. 1995;15:1808–18.
Friedman HS, Zhou H, Heydt R. The coding of uniform color figures in monkey visual cortex. J Physiol. 2003;548:593–613.
Caywood MS, Willmore B, Tolhurst DJ. Independent components of color natural scenes resemble V1 neurons in their spatial and colour tuning. J Neurophysiol. 2004;91:2859–73.
Girard P, Morrone MC. Spatial structure of chromatically opponent receptive fields in the human visual system. Vis Neurosci. 1995;12:103–16.
Ringach DL. Spatial structure and symmetry of simple-cell receptive fields in macaque primary visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2002;88:455–63.
Lennie P, Movshon JA. Coding of color and form in the geniculostriate visual pathway (invited review). JOSA A. 2005;22(10):2013–33.
Lennie P, Krauskopf J, Sclar G. Chromatic mechanisms in striate cortex of macaque. J Neurosci. 1990;10:649–69.
Johnson EN, Hawken MJ, Shapley R. Cone inputs in macaque primary visual cortex. J Neurophysiol. 2004;91:2501–14.
Mullen KT, Dumoulin SO, McMahon KL, De Zubicaray GI, Hess RF. Selectivity of human retinotopic visual cortex to S-cone-opponent, L/M-cone-opponent and achromatic stimulation. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;25:491–502.
Johnson EN, Van Hooser SD, Fitzpatrick D. The representation of S-cone signals in primary visual cortex. J Neurosci. 2010;30:10337–50.
Lindeberg T. A computational theory of visual receptive fields. Biol Cybern. 2013;107:589–635.
Young AR, Lesperance RM. The gaussian derivative model for spatial-temporal vision: II cortical data. Spat Vis. 2001;14:321–89.
Lindeberg T. Time-causal and time-recursive spatio-temporal receptive fields. J Math Imaging Vis. 2016;55:50–88.
Lindeberg T. Generalized axiomatic scale-space theory. Adv Imaging Electron Phys. 2013;178:1–96.
Hunt J, Bosking W, Goodhill G. Statistical structure of lateral connections in the primary visual cortex. Neural Syst Circuits. 2011;1(1):3.
Ren X. Multi-scale improves boundary detection in natural image. Computer vision-ECCV. 2008; pp 533–545.
Shi J, Malik J. Normalized cuts and image segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2000;22:888–905.
Maire M, Arbelaez P, Fowlkes C, Malik J. Using contours to detect and localize junctions in natural image. Comput Vis Pattern Recog. 2008; pp 1–8
Najman L, Schmitt M. Geodesic saliency of watershed contours and hierarchical segmentation. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 1996;18:1163–73.
Arbelaez P. ‘Boundary extraction in natural images using ultrametric contour maps’. In: IEEE Conference on computer vision and pattern recognition Workshop, 2006, pp 182–182
Dollar P, Tu Z, Belongie S. Supervised learning of edges and object boundaries. In: 2006 IEEE computer society conference on computer vision and pattern recognition, vol 2, pp 1964–1971; 2006
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Qi Wang and Michael Spratling declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Informed Consent
Informed consent was not required as no human or animals were involved.
Human and Animal Rights
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Spratling, M.W. Contour Detection in Colour Images Using a Neurophysiologically Inspired Model. Cogn Comput 8, 1027–1035 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-016-9432-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12559-016-9432-6