Abstract
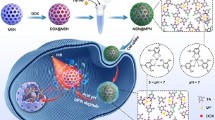
A mesoporous silica/gold (MSN/Au) nanocomposite was designed for photo-controlled drug delivery targeted specifically at tumor cells. The MSN/Au nanocomposite was composed of MSN-based drug carriers and gold nanoparticle (AuNP)-based indicators. While the MSN-based drug carrier was a mesoporous silica nanoparticle immobilized with photo-switchable azobenzene (Azo) moieties, the AuNP-based indicator was a fluorescence-quenched AuNP modified with a matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) substrate and poly(ethylene glycol). The two kinds of nanoparticles were connected by an α,β cyclodextrin (α,β CD) dimer “bridge.” In vitro studies demonstrated that the nanocomposite specifically interacted with tumor sites overexpressing MMP-2, which enabled guidance of the subsequent UV light irradiation for releasing entrapped drugs. Through integration of the AuNP-based indicator and the MSN-based drug carrier, the MSN/Au nanocomposite could precisely localize the released drug to tumor sites, thereby significantly improving therapeutic efficacy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
He, Q.; Shi, J. MSN anti-cancer nanomedicines: Chemotherapy enhancement, overcoming of drug resistance, and metastasis inhibition. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 391–411.
Ambrogio, M. W.; Thomas, C. R.; Zhao, Y. L.; Zink, J. I.; Stoddart, J. F. Mechanized silica nanoparticles: A new frountier in theranostic nanomedicine. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 903–913.
Wu, S. H.; Hung, Y.; Mou, C. Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as nanocarriers. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 9972–9985.
Tang, F.; Li, L.; Chen, D. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles: Synthesis, biocompatibility and drug delivery. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1504–1534.
Popat, A.; Hartono, S. B.; Stahr, F.; Liu, J.; Qiao, S. Z.; Qing Max Lu, G. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bioadsorption, enzyme immobilization, and delivery carriers. Nanoscale 2011, 3, 2801–2818.
Yang, P.; Gai, S.; Lin, J. Functionalized mesoporous silica materials for controlled drug delivery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 3679–3698.
Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. In vivo bio-safety evaluations and diagnostic/therapeutic applications of chemically designed mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2013, 25, 3144–3176.
Chen, A. M.; Zhang, M.; Wei, D.; Stueber, D.; Taratula, O.; Minko, T.; He, H. Co-delivery of doxorubicin and Bcl-2 siRNA by mesoporous silica nanoparticles enhances the efficacy of chemotherapy in multidrug-resistant cancer cells. Small 2009, 5, 2673–2677.
Guardado-Alvarez, T. M.; Sudha Devi, L.; Russell, M. M.; Schwartz, B. J.; Zink, J. I. Activation of snap-top capped mesoporous silica nanocontainers using two near-infrared photons. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 14000–14003.
Mei, X.; Yang, S.; Chen, D.; Li, N.; Li, H.; Xu, Q.; Ge, J.; Lu, J. Light-triggered reversible assemblies of azobenzene-containing amphiphilic copolymer with β-cyclodextrin-modified hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles for controlled drug release. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10010–10012.
Qian, R.; Ding, L.; Ju, H. Switchable fluorescent imaging of intracellular telomerase activity using telomerase-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 13282–13285.
Zhu, C. L.; Lu, C. H.; Song, X. Y.; Yang, H. H.; Wang, X. R. Bioresponsive controlled release using mesoporous silica nanoparticles capped with aptamer-based molecular gate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 1278–1281.
Yan, H.; Teh, C.; Sreejith, S.; Zhu, L.; Kwok, A.; Fang, W.; Ma, X.; Nguyen, K. T.; Korzh, V.; Zhao, Y. Functional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for photothermal-controlled drug delivery in vivo. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 8373–8377.
Díez, P.; Sánchez, A.; Gamella, M.; Martínez-Ruíz, P.; Aznar, E.; de la Torre, C.; Murguía, J. R.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Villalonga, R.; Pingarrón, J. M. Toward the design of smart delivery systems controlled by integrated enzyme-based biocomputing ensembles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 9116–9123.
Yang, K. N.; Zhang, C. Q.; Wang, W.; Wang, P. C.; Zhou, J. P.; Liang, X. J. pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles employed in controlled drug delivery systems for cancer treatment. Cancer Biol. Med. 2014, 11, 34–43.
Muhammad, F.; Guo, M.; Qi, W.; Sun, F.; Wang, A.; Guo, Y.; Zhu, G. pH-triggered controlled drug release from mesoporous silica nanoparticles via intracellular dissolution of ZnO nanolids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 8778–8781.
Fu, J.; Chen, T.; Wang, M.; Yang, N.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Acid and alkaline dual stimuli-responsive mechanized hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles as smart nanocontainers for intelligent anticorrosion coating. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11397–11408.
Xiao, D.; Jia, H. Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C. W.; Zhuo, R. X.; Zhang, X. Z. A dual-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticle for tumor-triggered targeting drug delivery. Small 2014, 10, 591–598.
Zhang, Q.; Liu, F.; Nguyen, K. T.; Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Xing, B.; Zhao, Y. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for cancer-targeted and controlled drug delivery. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 5144–5156.
Wang, A.; Guo, M.; Wang, N.; Zhao, J.; Qi, W.; Muhammad, F.; Chen, L.; Guo, Y.; Nguyen, N. T.; Zhu, G. Redox-mediated dissolution of paramagnetic nanolids to achieve a smart theranostic system. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 5270–5278.
Kim, H.; Kim, S.; Park, C.; Lee, H.; Park, H. J.; Kim, C. Glutathione-induced intracellular release of guests from mesoporous silica nanocontainers with cyclodextrin gatekeepers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4280–4283.
Nadrah, P.; Maver, U.; Jemec, A.; Tišler, T.; Bele, M.; Dražić, G.; Benčina, M.; Pintar, A.; Planinšek, O.; Gaberšček, M. Hindered disulfide bonds to regulate release rate of model drug from mesoporous silica. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 3908–3915.
Frasconi, M.; Liu, Z.; Lei, J.; Wu, Y.; Strekalova, E.; Malin, D.; Ambrogio, M. W.; Chen, X.; Botros, Y. Y.; Cryns, V. L. et al. Photoexpulsion of surface-grafted ruthenium complexes and subsequent release of cytotoxic cargos to cancer cells from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 11603–11613.
Croissant, J.; Maynadier, M.; Gallud, A.; Peindy N’dongo, H.; Nyalosaso, J. L.; Derrien, G.; Charnay, C.; Durand, J. O.; Raehm, L.; Serein-Spirau, F. et al. Two-photon-triggered drug delivery in cancer cells using nanoimpellers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 13813–13817.
Wen, Y.; Xu, L.; Wang, W.; Wang, D.; Du, H.; Zhang, X. Highly efficient remote controlled release system based on light-driven DNA nanomachine functionalized mesoporous silica. Nanoscale 2012, 4, 4473–4476.
Sun, Y. L.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Q. L.; Yang, Y. W. Enzyme-responsive supramolecular nanovalves crafted by mesoporous silica nanoparticles and cholinesulfonatocalix[4]arene [2]pseudorotaxanes for controlled cargo release. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 9033–9035.
Agostini, A.; Mondragón, L.; Bernardos, A.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M. D.; Sancenón, F.; Soto, J.; Costero, A.; Manguan-García, C.; Perona, R.; Moreno-Torres, M.; Aparicio-Sanchis, R.; Murguía, J. R. Targeted cargo delivery in senescent cells using capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 10556–10560.
De la Torre, C.; Agostini, A.; Mondragón, L.; Orzáez, M.; Sancenón, F.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M. D.; Amorós, P.; Pérez-Payá, E. Temperature-controlled release by changes in the secondary structure of peptides anchored onto mesoporous silica supports. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3184–3186.
Climent, E.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Sancenón, F.; Marcos, M. D.; Soto, J.; Maquieira, A.; Amorós, P. Controlled delivery using oligonucleotide-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7281–7283.
Yuan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, T.; Lu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Yan, C. H.; Tan, W. Photo-manipulated drug release from a mesoporous nanocontainer controlled by azobenzene-modified nucleic acid. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6337–6344.
Mal, N. K.; Fujiwara, M.; Tanaka, Y. Photocontrolled reversible release of guest molecules from coumarin-modified mesoporous silica. Nature 2003, 421, 350–353.
Lu, J.; Choi, E.; Tamanoi, F.; Zink, J. I. Light-activated nanoimpeller-controlled drug release in cancer cells. Small 2008, 4, 421–426.
Ferris, D. P.; Zhao, Y. L.; Khashab, N. M.; Khatib, H. A.; Stoddart, J. F.; Zink, J. I. Light-operated mechanized nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 1686–1688.
Park, C.; Lee, K.; Kim, C. Photoresponsive cyclodextrin-covered nanocontainers and their sol-gel transition induced by molecular recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2009, 48, 1275–1278.
Vivero-Escoto, J. L.; Slowing, I. I.; Wu, C. W.; Lin, V. S. Photoinduced intracellular controlled release drug delivery in human cells by gold-capped mesoporous silica nanosphere. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 3462–3463.
Kessenbrock, K.; Plaks, V.; Werb, Z. Matrix metalloproteinases: Regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Cell 2010, 141, 52–67.
Jiang, T.; Olson, E. S.; Nguyen, Q. T.; Roy, M.; Jennings, P. A.; Tsien, R. Y. Tumor imaging by means of proteolytic activation of cell-penetrating peptides. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 17867–17872.
Zhang, X. X.; Eden, H. S.; Chen, X. Peptides in cancer nanomedicine: Drug carriers, targeting ligands and protease substrates. J. Controlled Release 2012, 159, 2–13.
Egeblad, M.; Werb, Z. New functions for the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2002, 2, 161–174.
Andresen, T. L.; Thompson, D. H.; Kaasgaard, T. Enzyme-triggered nanomedicine: Drug release strategies in cancer therapy. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2010, 27, 353–363.
Merdad, A.; Karim, S.; Schulten, H. J.; Dallol, A.; Buhmeida, A.; Al-Thubaity, F.; Gari, M. A.; Chaudhary, A. G.; Abuzenadah, A. M.; Al-Qahtani, M. H. Expression of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) in primary human breast cancer: MMP-9 as a potential biomarker for cancer invasion and metastasis. Anticancer Res. 2014, 34, 1355–1366.
Garripelli, V. K.; Kim, J. K.; Son, S.; Kim, W. J.; Repka, M. A.; Jo, S. Matrix metalloproteinase-sensitive thermogelling polymer for bioresponsive local drug delivery. Acta Biomater. 2011,7,1984–1992.
Sarkar, N. R.; Rosendahl, T.; Krueger, A. B.; Banerjee, A. L.; Benton, K.; Mallik, S.; Srivastava, D. K. “Uncorking” of liposomes by matrix metalloproteinase-9. Chem. Commun. 2005, 8, 999–1001.
Elegbede, A. I.; Banerjee, J.; Hanson, A. J.; Tobwala, S.; Ganguli, B.; Wang, R.; Lu, X.; Srivastava, D. K.; Mallik, S. Mechanistic studies of the triggered release of liposomal contents by matrix metalloproteinase-9. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10633–10642.
Sun, I. C.; Eun, D. K.; Koo, H.; Ko, C. Y.; Kim, H. S.; Yi, D. K.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, K.; Ahn, C. H. Tumor-targeting gold particles for dual computed tomography/optical cancer imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 9348–9351.
Myochin, T.; Hanaoka, K.; Komatsu, T.; Terai, T.; Nagano, T. Design strategy for a near-infrared fluorescence probe for matrix metalloproteinase utilizing highly cell permeable boron dipyrromethene. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 13730–13737.
Xu, J. H.; Gao, F. P.; Liu, X. F.; Zeng, Q.; Guo, S. S.; Tang, Z. Y.; Zhao, X. Z.; Wang, H. Supramolecular gelatin nanoparticles as matrix metalloproteinase responsive cancer cell imaging probes. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 4462–4464.
Ryu, J. H.; Shin, J. Y.; Kim, S. A.; Kang, S. W.; Kim, H.; Kang, S.; Choi, K.; Kwon, I. C.; Kim, B. S.; Kim, K. Non-invasive optical imaging of matrix metalloproteinase activity with albumin-based fluorogenic nanoprobes during angiogenesis in a mouse hindlimb ischemia model. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 6871–6881.
Chen, P.; Selegård, R.; Aili, D.; Liedberg, B. Peptide functionalized gold nanoparticles for colorimetric detection of matrilysin (MMP-7) activity. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 8973–8976.
Kim, J. H.; Chung, B. H. Proteolytic fluorescent signal amplification on gold nanoparticles for a highly sensitive and rapid protease assay. Small 2010, 6, 126–131.
Lee, S.; Cha, E. J.; Park, K.; Lee, S. Y.; Hong, J. K.; Sun, I. C.; Kim, K.; Ahn, C. H. A near-infrared-fluorescence-quenched gold-nanoparticle imaging probe for in vivo drug screening and protease activity determination. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 2804–2807.
Zhang, J.; Yuan, Z. F.; Wang, Y.; Chen, W. H.; Luo, G. F.; Cheng, S. X.; Zhuo, R. X.; Zhang, X. Z. Multifunctional envelope-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles for tumor-triggered targeting drug delivery. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5068–5073.
Rekharsky, M. V.; Inoue, Y. Complexation thermodynamics of cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1875–1918.
Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Agarwal, A.; Mueller, L. J.; Feng, P. pH-responsive nanogated ensemble based on gold-capped mesoporous silica through an acid-labile acetal linker. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 1500–1501.
Lee, H.; Lee, K.; Kim, I. K.; Park, T. G. Synthesis, characterization, and in vivo diagnostic applications of hyaluronic acid immobilized gold nanoprobes. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 4709–4718.
Kang, B.; Afifi, M. M.; Austin, L. A.; El-Sayed, M. A. Exploiting the nanoparticle plasmon effect: Observing drug delivery dynamics in single cells via Raman/fluorescence imaging spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 7420–7427.
Chen, W. H.; Xu, X. D.; Jia, H. Z.; Lei, Q.; Luo, G. F.; Cheng, S. X.; Zhuo, R. X.; Zhang, X. Z. Therapeutic nanomedicine based on dual-intelligent functionalized gold nanoparticles for cancer imaging and therapy in vivo. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8798–8807.
Xiao, W.; Chen, W. H.; Xu, X. D.; Li, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhuo, R. X.; Zhang, X. Z. Design of a cellular-uptake-shielding “plug and play” template for photo controllable drug release. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3526–3530.
Dugave, C.; Demange, L. Cis-trans isomerization of organic molecules and biomolecules: Implications and applications. Chem. Rev. 2003, 103, 2475–2532.
Luo, G. F.; Chen, W. H.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, S. X.; Zhuo, R. X.; Zhang, X. Z. Charge-reversal plug gate nanovalves on peptide-functionalized mesoporous silica nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 5723–5732.
Fields, G. B.; Noble, R. L. Solid phase peptide synthesis utilizing 9-fluorenylmethoxycarbonyl amino acids. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1990, 35, 161–214.
Pan, L.; He, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Ma, M.; Zhang, L.; Shi, J. Nuclear-targeted drug delivery of TAT peptide-conjugated monodisperse mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 5722–5725.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, G., Chen, W., Jia, H. et al. An indicator-guided photo-controlled drug delivery system based on mesoporous silica/gold nanocomposites. Nano Res. 8, 1893–1905 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0698-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0698-2