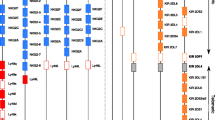
Abstract
Natural killer (NK) lymphocytes kill infected and tumorous cells. A balance of stimulatory and inhibitory receptor signals determine their activity. The most important NK cell receptors are the polymorphic killer cell immunoglobulin-like receptors (KIR), which bind to HLA class I molecules on target cells. The enormous genetic and genomic diversity of the KIR/HLA system influences the susceptibility to various diseases. Here, we will give an overview of this system and its impact on HIV infection.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Ljunggren H-G, Kärre K (1990) In search of the ‘missing self’: MHC molecules and NK cell recognition. Immunol Today 11:237–244
Uhrberg M, Valiante NM, Shum BP et al. (1997) Human diversity in killer cell inhibitory receptor genes. Immunity 7:753–763
Schönberg K, Sribar M, Enczmann J et al. (2011) Analyses of HLA-C-specific KIR repertoires in donors with group A and B haplotypes suggest a ligand-instructed model of NK cell receptor acquisition. Blood 117:98–107
Kim S, Poursine-Laurent J, Truscott SM et al. (2005) Licensing of natural killer cells by host major histocompatibility complex class I molecules. Nature 436:709–713
Parham P (2005) MHC class I molecules and KIRs in human history, health and survival. Nat Rev Immunol 5:201–214
Martin MP, Gao X, Lee J-H et al. (2002) Epistatic interaction between KIR3DS1 and HLA-B delays the progression to AIDS. Nat Genet 31:429–434
Albrecht C, Malzahn D, Brameier M et al. (2014) Progression to AIDS in SIV-infected rhesus macaques is associated with distinct KIR and MHC class I polymorphisms and NK cell dysfunction. Front Immunol 5:600
Alter G, Rihn S, Walter K et al. (2009) HLA class I subtype-dependent expansion of KIR3DS1+ and KIR3DL1+ NK cells during acute human immunodeficiency virus type 1 infection. J Virol 83:6798–6805
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Beatrix Petersen 2001–2007 Biologiestudium an der Universität Göttingen. 2007–2008 wissenschaft - liche Mitarbeiterin am Deutschen Primatenzentrum, Göttingen. 2008–2012 Promotion, 2012–2013 Postdoc am Institut für Immunologie der Universität Münster. Seit 2015 Postdoc in der Abteilung Primatengenetik am Deutschen Primatenzentrum, Göttingen.
Lutz Walter 1985–1992 Biologiestudium, 1992–1994 Promotion, 1994–1999 wissenschaftlicher Mitarbeiter, 1999–2004 wissenschaftlicher Assistent, 2005 Habilitation im Fach Immunologie und Immungenetik, 2009 apl. Professor an der Universität Göttingen. Seit 2004 Leiter der Abteilung Primatengenetik am Deutschen Primatenzentrum, Göttingen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Petersen, B., Walter, L. Genomik des KIR/HLA-Systems und Regulation von NK-Lymphozyten. Biospektrum 22, 600–602 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-016-0736-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12268-016-0736-6