Abstract
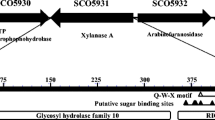
A xylanase (XynA) was purified from the culture medium of Streptomyces sp. FA1, which was previously isolated from a bamboo retting system. XynA had a molecular mass of 43 kDa, displayed maximal activity at pH 5.5, retained 41% of its maximal activity at pH 11.0, and was stable over a wide pH range (3.0 ∼ 11.0). Purified XynA was subjected to peptide mass fingerprinting, which led to the cloning of the xynA gene. The xynA gene, which encodes a mature protein of 436 amino acids, was heterologously expressed in E. coli BL21(DE3). The activity in the culture medium could reach 213.5 U/mL, which was 11.2-fold higher than that produced by Streptomyces sp. FA1. BLAST searching revealed that full-length XynA shares less than 90% identity with most of its homologues, whereas amino acids 48-436 of the enzyme share 97% identity with an open reading frame encoding a putative full-length mature xylanase from Streptomyces tendae. The truncated xynA gene, xynA 48-436, was cloned and expressed in E. coli, however, no xylanase activity could be detected in the culture medium. Based on these results, it is suggested that XynA is a new member of glycoside hydrolases family10 with exceptional catalytic efficiency at alkaline pH.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beg, Q., M. Kapoor, L. Mahajan, and G. Hoondal (2001) Microbial xylanases and their industrial applications: A review. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56: 326–338.
Collins, T., C. Gerday, and G. Feller (2005) Xylanases, xylanase families and extremophilic xylanases. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 29: 3–23.
Biely, P. (1985) Microbial xylanolytic systems. Trends in Biotechnol. 3: 286–290.
Henrissat, B. and A. Bairoch (1993) New families in the classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 293: 781–788.
Amaya-Delgado, L., T. Mejía-Castillo, A. Santiago-Hernández, J. Vega-Estrada, F.-G.-S. Amelia, B. Xoconostle-Cázares, R. Ruiz-Medrano, M. D. C. Montes-Horcasitas, and M. E. Hidalgo-Lara (2010) Cloning and expression of a novel, moderately thermostable xylanase-encoding gene (Cfl xyn11A) from Cellulomonas flavigena. Bioresour.Technol. 101: 5539–5545.
Kim, D. Y., M. K. Han, H. -W. Oh, K. S. Bae, T. -S. Jeong, S. U. Kim, D. -H. Shin, I. -H. Kim, Y. H. Rhee, and K. -H. Son (2010) Novel intracellular GH10 xylanase from Cohnellalaeviribosi HY-21: Biocatalytic properties and alterations of substrate specificities by site-directed mutagenesis of Trp residues. Bioresour. Technol. 101: 8814–8821.
Zhou, C., J. Bai, S. Deng, J. Wang, J. Zhu, M. Wu, and W. Wang (2008) Cloning of a xylanase gene from Aspergillus usamii and its expression in Escherichia coli. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 831–838.
Ninawe, S., M. Kapoor, and R. C. Kuhad (2008) Purification and characterization of extracellular xylanase from Streptomyces cyaneus SN32. Bioresour. Technol. 99: 1252–1258.
Jiang, Z., W. Deng, Q. Yan, Q. Zhai, L. Li, and I. Kusakabe (2006) Subunit composition of a large xylanolytic complex (xylanosome) from Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86. J.Biotechnol. 126: 304–312.
Shareck, F., C. Roy, Y. Makoto, R. Morosoli, and D. Kluepfel (1991) Sequences of three genes specifying xylanases in Streptomyces lividans. Gene. 107: 75–82.
Mondou, F., F. Shareck, R. Morosoli, and D. Kluepfel (1986) Cloning of the xylanase gene of Streptomyces lividans. Gene. 49: 323–329.
Li, N., P. Shi, P. Yang, Y. Wang, H. Luo, Y. Bai, Z. Zhou, and B. Yao (2009) A xylanase with high pH stability from Streptomyces sp.S27 and its carbohydrate-binding module with/without linkerregion-truncated versions. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 83: 99–107.
Li, N., K. Meng, Y. Wang, P. Shi, H. Luo, Y. Bai, P. Yang, and B. Yao (2008) Cloning, expression, and characterization of a new xylanase with broad temperature adaptability from Streptomyces sp. S9. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 80: 231–240.
Li, N., P. Yang, Y. Wang, H. Luo, K. Meng, N. Wu, Y. Fan, and B. Yao (2008) Cloning, expression, and characterization of protease-resistant xylanase from Streptomyces fradiae var. 11. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 18: 410–416.
Choi, J. -H., O. -S. Lee, J. -H. Shin, Y. -Y. Kwak, Y. M. Kim, and I. -K. Rhee (2006) Thermostable xylanase encoded by xynA of Streptomyces thermocyaneoviolaceus: Cloning, purification, characterization and production of xylooligosaccharides. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 16: 57–63.
Ahmed, S., S. Riaz, and A. Jamil (2009) Molecular cloning of fungal xylanases: An overview. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 84: 19–35.
Zhang, H., B. Yao, Y. Wang, T. Yuan, W. Zhang, N. Wu, and Y. Fan (2003) Expression of xylanase gene xynA from Streptomyces olivaceoviridis A1 in Escherichia coli and Pichia pastoris. Chin. J. Biotechnol. 19: 41–45.
Ruiz-Arribas, A., J. M. Fernández-Ábalos, P. Sánchez, A. L. Garda, and R. I. Santamaría (1995) Overproduction, purification, and biochemical characterization of a xylanase (Xys1) from Streptomyces halstedii JM8. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 2414–2419.
Bertrand, J. L., R. Morosoli, F. Shareck, and D. Kluepfel (1989) Expression of the xylanase gene of Streptomyces lividans and production of the enzyme on natural substrates. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 33: 791–794.
Miller, G. L. (1959) Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428.
Bradford, M. M. (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 72: 248–254.
Sambrook, J. and D. W. Russell (2001) Molecular cloning: A laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbour LaboratoryPress, Cold Spring Harbour, NY, USA.
Juturu, V. and J. C. Wu (2012) Microbial xylanases: Engineering, production and industrial applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 30: 1219–1227.
Fujimoto, Z., A. Kuno, S. Kaneko, H. Kobayashi, I. Kusakabe, and H. Mizuno (2002) Crystal structures of the sugar complexes of Streptomyces olivaceoviridis E-86 xylanase: Sugar binding structure of the family 13 carbohydrate binding module. J. Mol. Biol. 316: 65–78.
Kumagai, Y., H. Usuki, Y. Yamamoto, A. Yamasato, T. Mukaihara, and T. Hatanaka (2012) Preparation of hemicellulolic oligosaccharides from Chamaecyparis obtuse (Hinoki) slurry using commercial enzymes. Frontiers of Chem. Sci. Eng. 6: 224–231.
Deesukon, W., Y. Nishimura, N. Harada, T. Sakamoto, and W. Sukhumsirichart (2011) Purification, characterization and gene cloning of two forms of a thermostable endo-xylanase from Streptomyces sp. SWU10. Proc. Biochem. 46: 2255–2262.
Qiu, Z., P. Shi, H. Luo, Y. Bai, T. Yuan, P. Yang, S. Liu, and B. Yao (2010) A xylanase with broad pH and temperature adaptability from Streptomyces megasporus DSM 41476, and its potential application in brewing industry. Enz. Microbial. Technol. 46: 506–512.
Fu, J., X. Li, W. Gao, H. Wang, A. Cavaco-Paulo, and C. Silva (2012) Bio-processing of bamboo fibres for textile applications: A mini review. Biocatal. Biotransform. 30: 141–153.
Ninawe, S. and R. C. Kuhad (2006) Bleaching of wheat strawrich soda pulp with xylanase from a thermoalkalophilic Streptomyces cyaneus SN32. Bioresour. Technol. 97: 2291–2295.
Ninawe, S., R. Lal, and R. Kuhad (2006) Isolation of three xylanase-producing strains of actinomycetes and their identification using molecular methods. Curr. Microbiol. 53: 178–182.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
He, J., Su, L., Sun, X. et al. A novel xylanase from Streptomyces sp. FA1: Purification, characterization, identification, and heterologous expression. Biotechnol Bioproc E 19, 8–17 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0490-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-013-0490-2