Abstract
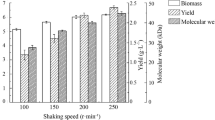
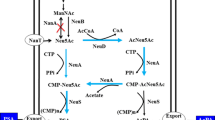
Polysialic acid (PSA) is a capsular polysaccharide obtained from aerobic fermentation with Escherichia coli. To enhance PSA production and eliminate the influence of phosphate on the PSA purification process, a lower level of initial phosphate was adopted with pH control. The resulting PSA yield reached 4.1 g/L in fed-batch fermentation with 2.5 g/L K2HPO4 and E. coli strain CCTCC M208088. In addition, an ammonia water (NH4OH) feeding strategy to control the pH at 6.4 was developed resulting in PSA production that reached as high as 5.2 g/L. NMR spectra confirmed the purified biopolymer as a α-2,8 linked PSA, identical to the published NMR spectra, with a molecular weight in the range of 16 ∼ 50 kDa.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bhattacharjee, A. K., H. J. Jennings, C. P. Kenny, A. Martin, and I. C. Smith (1975) Structural determination of the sialic acid polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C with carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Biol. Chem. 250: 1926–1932.
Troy, F. A. (1996) Sialobiology and the polysialic acid glycotope. pp 95–144. In: Rosenberg, A. (ed). Biology of the Sialic Acids. Plenum Press, NY, USA.
Barry, G. T. and W. F. Goebel (1957) Colominic acid, a substance of bacterial origin related to sialic acid. Nature 179: 206.
Bergfeld, A. K., H. Claus, U. Vogel, and M. Muhlenhoff (2007) Biochemical characterization of the polysialic acid-specific Oacetyltransferase NeuO of Escherichia coli K1. J. Biol. Chem. 282: 22217–22227.
Andreishcheva, E. N. and W. F. Vann (2006) Gene products required for de novo synthesis of polysialic acid. J. Bacteriol. 188: 1786–1797.
Wunder, D. E., W. Aaronson, S. F. Hayes, J. Bliss, and R. P. Silver (1994) Nucleotide sequence and mutational analysis of the gene encoding KpsD, a periplasmic protein involved in transport of polysialic acid in Escherichia coli K1. J. Bacteriol. 176: 4025–4033.
Gregoriadis, G., S. Jain, I. Papaioannous, and P. Liang (2005) Improving the therapeutic efficacy of peptides and proteins: A role for polysialic acids. Int. J. Pharm. 300: 125–130.
Haile, Y., K. Haastert, K. Cesnulevicius, K. Stummeyer, M. Timmer, S. Berski, G. Drager, R. Gerardy-Schahn, and C. Grothe (2007) Culturing of glial and neuronal cells on polysialic acid. Biomaterials 28: 1163–1173.
Rosenburg, G. A. and C. L. Schengrund (1976) Biological roles of sialic acid. pp 59–86. Plenum Press, NY, USA.
Witczak, Z. J. and K. A. Nieforth (1997) Carbohydrate in drugs design. pp 82–134. Marcel Dekker, NY, USA.
McNicholl, I. R. and J. J. McNicholl (2001) Neuraminidase inhibitors: Zanamivir and oseltamivir. Ann. Pharmacother. 35: 57–70.
Nacalai USA Inc. http://www.nacalaiusa.com/product.php?id=33.
Uchida, Y. and Y. Tsukada (1973) Improved microbial production of colominic acid, a homopolymer of N-acetylneuraminic acid. Agric. Biol. Chem. 37: 2105–2110.
Rodriguez-Aparicio, L. B., A. Reglero, A. I. Ortiz, and J. M. Luenge (1988) Effect of physical and chemical conditions on the production of colominic acid by Escherichia coli in a defined medium. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 27: 474–483.
Camino, G. C., J. M. Luengo, and L. B. Rodríguez-Aparicio (1990) High production of polysialic acid [Neu5Ac alpha (2–8)-Neu5Ac alpha(2–9)]n by Escherichia coli K92 grown in a chemically defined medium: Regulation of temperature. Biol. Chem. Hoppe. Seyler. 371: 1101–1106.
Zhan, X. B., L. Zhu, J. R. Wu, Z. Y. Zheng, and W. Jia (2002) Production of polysialic acid from fed-batch fermentation with pH control. Biochem. Eng. J. 11: 201–204.
Rode, B., C. Endres, C. Ran, F. Stahl, S. Beutel, C. Kasper, S. Galuska, R. Geyer, M. Muhlenhoff, R. Gerardy-Schahn, and T. Scheper (2008) Large-scale production and homogenous purification of long chain polysialic acids from E. coli K1. J. Biotechnol. 135: 202–209.
Kapre, S. V. and U. Shaligram (2008) Process for the preparation of highly pure polysialic acid of high molecular weights. PCT Patent 2008/035373.
Honda, H., T. Nakazeko, K. Ogiso, Y. Kawase, N. Aoki, M. Kawase, and T. Kobayashi (1997) Colominic acid production from Escherichia coli in a fed-batch culture under the control of ammonium ions using an FIA System. J. Ferment. Bioeng. 83: 59–63.
Svennerholm, L. (1957) Quantitative estimation of sialic acids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 24: 604–611.
Pesez, M. and J. Bartos (1974) Colorimetric and fluorometric analysis of organic compounds and drugs. pp 291–328. Marcel Dekker, NY, USA.
Harwood, J. E. and D. J. Huysen (1970) Automated analysis of ammonia in water. Water Res. 4: 695–704.
Yu, D. F., X. B. Zhan, J. L. Liu, and J. R. Wu (2008) Application of cetyl pyridinium chloride for purification of polysialic acid. Chin. J. Bioproc. Eng. 24: 46–51.
Bhattacharjee, A. K., H. J. Jennings, C. P. Kenny, A. Martin, and I. C. Smith (1975) Structural determination of the sialic acid polysaccharide antigens of Neisseria meningitidis serogroups B and C with carbon 13 nuclear magnetic resonance. J. Biol. Chem. 250: 1926–1932.
Egan, W., T. Y. Liu, D. Dorow, J. S. Cohen, J. D. Robbins, E. C. Gotschlich, and J. B. Robbins (1977) Structural studies on the sialic acid polysaccharide antigen of E. coli strain Bos-12. Biochemistry 16: 3687–3692.
Egan, W. and T. Y. Liu (1977) Structural studies on the sialic acid polysaccharide antigen of E. coli strain Bos-12. Biochemistry 16: 3687–3692.
Ly, A., J. Henderson, A. Lu, D. E. Culham, and J.M. Wood (2004) Osmoregulatory systems of Escherichia coli: Identification of betaine-carnitine-choline transporter family member BetU and distributions of betU and trkG among pathogenic and nonpathogenic isolates. J. Bacteriol. 186: 296–306.
Jain, S., P. Laing, and G. Gregoriadis (2008) Reduction of endotoxin in polysialic acids. PCT Patent 2008/104811.
Gregoriadis, G., B. McCormack, and R. Lifely (1993) Polysialic acid: Potential in drug delivery. FEBS Lett. 315: 271–276.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, JR., Liu, JL., Zhan, XB. et al. Enhancement of polysialic acid yield by reducing initial phosphate and feeding ammonia water to Escherichia coli CCTCC M208088. Biotechnol Bioproc E 15, 657–663 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3128-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-009-3128-7