Abstract
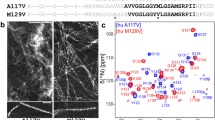
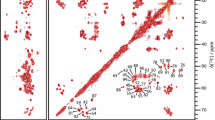
The Y145Stop prion protein (PrP23-144), which has been linked to the development of a heritable prionopathy in humans, is a valuable in vitro model for elucidating the structural and molecular basis of amyloid seeding specificities. Here we report the sequential backbone and side-chain 13C and 15N assignments of mouse and Syrian hamster PrP23-144 amyloid fibrils determined by using 2D and 3D magic-angle spinning solid-state NMR. The assigned chemical shifts were used to predict the secondary structures for the core regions of the mouse and Syrian hamster PrP23-144 amyloids, and the results compared to those for human PrP23-144 amyloid, which has previously been analyzed by solid-state NMR techniques.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguzzi A, Polymenidou M (2004) Mammalian prion biology: one century of evolving concepts. Cell 116:313–327
Aguzzi A, Sigurdson C, Heikenwaelder M (2008) Molecular mechanisms of prion pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol 3:11–40
Caughey B, Chesebro B (2001) Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies and prion protein interconversions. Adv Virus Res 56:277–311
Choi JK, Cali I, Surewicz K, Kong Q, Gambetti P, Surewicz WK (2016) Amyloid fibrils from the N-terminal prion protein fragment are infectious. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 113:13851–13856
Cobb NJ, Surewicz WK (2009) Prion diseases and their biochemical mechanisms. BioChemistry 48:2574–2585
Collinge J (2001) Prion diseases of humans and animals: Their causes and molecular basis. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:519–550
Collinge J, Clarke AR (2007) A general model of prion strains and their pathogenicity. Science 318:930–936
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
Ghetti B, Piccardo P, Spillantini MG, Ichimiya Y, Porro M, Perini F, Kitamoto T, Tateishi J, Seiler C, Frangione B, Bugiani O, Giaccone G, Prelli F, Goedert M, Dlouhy SR, Tagliavini F (1996) Vascular variant of prion protein cerebral amyloidosis with τ-positive neurofibrillary tangles: The phenotype of the stop codon 145 mutation in PRNP. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:744–748
Goddard TD, Kneller DG (2006) SPARKY 3. University of California, San Francisco
Helmus JJ, Jaroniec CP (2013) Nmrglue: an open source Python package for the analysis of multidimensional NMR data. J Biomol NMR 55:355–367
Helmus JJ, Surewicz K, Nadaud PS, Surewicz WK, Jaroniec CP (2008) Molecular conformation and dynamics of the Y145Stop variant of human prion protein in amyloid fibrils. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6284–6289
Helmus JJ, Surewicz K, Surewicz WK, Jaroniec CP (2010) Conformational flexibility of Y145Stop human prion protein amyloid fibrils probed by solid-state nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 132:2393–2403
Helmus JJ, Surewicz K, Apostol MI, Surewicz WK, Jaroniec CP (2011) Intermolecular alignment in Y145Stop human prion protein amyloid fibrils probed by solid-state NMR spectroscopy. J Am Chem Soc 133:13934–13937
Jones EM, Surewicz WK (2005) Fibril conformation as the basis of species- and strain-dependent seeding specificity of mammalian prion amyloids. Cell 121:63–72
Jones EM, Wu B, Surewicz K, Nadaud PS, Helmus JJ, Chen S, Jaroniec CP, Surewicz WK (2011) Structural polymorphism in amyloids: New insights from studies with Y145Stop prion protein fibrils. J Biol Chem 286:42777–42784
Kundu B, Maiti NR, Jones EM, Surewicz KA, Vanik DL, Surewicz WK (2003) Nucleation-dependent conformational conversion of the Y145Stop variant of human prion protein: Structural clues for prion propagation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:12069–12074
Morillas M, Swietnicki W, Gambetti P, Surewicz WK (1999) Membrane environment alters the conformational structure of the recombinant prion protein. J Biol Chem 274:36859–36865
Prusiner SB (1998) Prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:13363–13383
Sejvar JJ, Schonberger LB, Belay ED (2008) Transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. J Am Vet Med Assoc 233:1705–1712
Shen Y, Bax A (2013) Protein backbone and sidechain torsion angles predicted from NMR chemical shifts using artificial neural networks. J Biomol NMR 56:227–241
Surewicz WK, Jones EM, Apetri AC (2006) The emerging principles of mammalian prion propagation and transmissibility barriers: Insight from studies in vitro. Acc Chem Res 39:654–662
Vanik DL, Surewicz KA, Surewicz WK (2004) Molecular basis of barriers for interspecies transmissibility of mammalian prions. Mol Cell 14:139–145
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by NIH (Grants R01GM094357 and S10OD012303 to C.P.J. and P01AI106705 and R01NS083687 to W.K.S.) and the Camille & Henry Dreyfus Foundation (Camille Dreyfus Teacher-Scholar Award to C.P.J.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Theint, T., Nadaud, P.S., Surewicz, K. et al. 13C and 15N chemical shift assignments of mammalian Y145Stop prion protein amyloid fibrils. Biomol NMR Assign 11, 75–80 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-016-9723-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12104-016-9723-6